Archaeal Elp3 catalyzes tRNA wobble uridine modification at C5 via a radical mechanism - PubMed (original) (raw)
Archaeal Elp3 catalyzes tRNA wobble uridine modification at C5 via a radical mechanism
Kiruthika Selvadurai et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2014 Oct.
Abstract
Approximately 25% of cytoplasmic tRNAs in eukaryotic organisms have the wobble uridine (U34) modified at C5 through a process that, according to genetic studies, is carried out by the eukaryotic Elongator complex. Here we show that a single archaeal protein, the homolog of the third subunit of the eukaryotic Elongator complex (Elp3), is able to catalyze the same reaction. The mechanism of action by Elp3 described here represents unprecedented chemistry performed on acetyl-CoA.
Figures
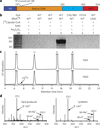
Figure 1. In vitro reconstitution of _Min_Elp3 activity
(a) Schematic view of the domain structure of _Min_Elp3, similar to the structure for human Elp3 shown in Supplementary Figure 1a. The CxxxxCxxC motif that coordinates a [4Fe-4S] cluster is highlighted. (b) Denaturing PAGE analysis of tRNA products from the Elp3-catalyzed reactions. SM, size markers. (c) RP-HPLC chromatograms of the digests of tRNA products from the reactions without (top) and with (bottom) Elp3. The Elp3-produced product cm5U is indicated by an arrow. (d) ESI-LC/MS analyses of cm5U from the Elp3-catalyzed reaction (left) and the synthetic compound (right).
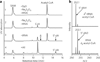
Figure 2. Chromatographic and spectrometric analyses of the consumption of cofactors and the production of 5′-dA
(a) RP-HPLC chromatograms of the reactions differing in components, starting with the one containing only the cofactors (SAM and acetyl-CoA) in the reaction buffer (panel 1). Missing components were added one at a time (panels 2 and 3) until all the components required for the reaction were included (panel 4). (b) ESI-LC/MS analyses of the resulting 5′-dA from the reactions in the presence of the deuterated tRNA (top) and the deuterated acetyl-CoA (bottom).
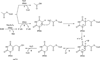
Figure 3. Proposed mechanism of the Elp3-catalyzed reaction
B−, unidentified general base.
Similar articles
- Elongator function in tRNA wobble uridine modification is conserved between yeast and plants.
Mehlgarten C, Jablonowski D, Wrackmeyer U, Tschitschmann S, Sondermann D, Jäger G, Gong Z, Byström AS, Schaffrath R, Breunig KD. Mehlgarten C, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jun 1;76(5):1082-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07163.x. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20398216 Free PMC article. - The Elongator subunit Elp3 is a non-canonical tRNA acetyltransferase.
Lin TY, Abbassi NEH, Zakrzewski K, Chramiec-Głąbik A, Jemioła-Rzemińska M, Różycki J, Glatt S. Lin TY, et al. Nat Commun. 2019 Feb 7;10(1):625. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08579-2. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30733442 Free PMC article. - How Elongator Acetylates tRNA Bases.
Abbassi NE, Biela A, Glatt S, Lin TY. Abbassi NE, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 3;21(21):8209. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218209. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33152999 Free PMC article. Review. - Cryo-EM structures of the human Elongator complex at work.
Abbassi NE, Jaciuk M, Scherf D, Böhnert P, Rau A, Hammermeister A, Rawski M, Indyka P, Wazny G, Chramiec-Głąbik A, Dobosz D, Skupien-Rabian B, Jankowska U, Rappsilber J, Schaffrath R, Lin TY, Glatt S. Abbassi NE, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 May 15;15(1):4094. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48251-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38750017 Free PMC article. - Elongator, a conserved complex required for wobble uridine modifications in eukaryotes.
Karlsborn T, Tükenmez H, Mahmud AK, Xu F, Xu H, Byström AS. Karlsborn T, et al. RNA Biol. 2014;11(12):1519-28. doi: 10.4161/15476286.2014.992276. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 25607684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Iron-sulfur clusters as inhibitors and catalysts of viral replication.
Honarmand Ebrahimi K, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Hagedoorn PL, Nicolet Y, Le Brun NE, Hagen WR, Armstrong FA. Honarmand Ebrahimi K, et al. Nat Chem. 2022 Mar;14(3):253-266. doi: 10.1038/s41557-021-00882-0. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Nat Chem. 2022. PMID: 35165425 Review. - Trm112, a Protein Activator of Methyltransferases Modifying Actors of the Eukaryotic Translational Apparatus.
Bourgeois G, Létoquart J, van Tran N, Graille M. Bourgeois G, et al. Biomolecules. 2017 Jan 27;7(1):7. doi: 10.3390/biom7010007. Biomolecules. 2017. PMID: 28134793 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification of a radical SAM enzyme involved in the synthesis of archaeosine.
Yokogawa T, Nomura Y, Yasuda A, Ogino H, Hiura K, Nakada S, Oka N, Ando K, Kawamura T, Hirata A, Hori H, Ohno S. Yokogawa T, et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2019 Dec;15(12):1148-1155. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0390-7. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Nat Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31740832 - Dph3 Enables Aerobic Diphthamide Biosynthesis by Donating One Iron Atom to Transform a [3Fe-4S] to a [4Fe-4S] Cluster in Dph1-Dph2.
Zhang Y, Su D, Dzikovski B, Majer SH, Coleman R, Chandrasekaran S, Fenwick MK, Crane BR, Lancaster KM, Freed JH, Lin H. Zhang Y, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Jun 30;143(25):9314-9319. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c03956. Epub 2021 Jun 21. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 34154323 Free PMC article. - Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) and Microscale Thermophoresis (MST) Methods to Measure Interactions Between tRNAs and Their Modifying Enzymes.
Chramiec-Głąbik A, Rawski M, Glatt S, Lin TY. Chramiec-Głąbik A, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2666:29-53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3191-1_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37166655
References
- Otero G, et al. Mol. Cell. 1999;3:109–118. - PubMed
- Winkler GS, et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:32743–32749. - PubMed
- Chinenov Y. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002;27:115–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous