Interferons: Success in anti-viral immunotherapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Interferons: Success in anti-viral immunotherapy
Fan-ching Lin et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Aug.
Abstract
The interferons (IFNs) are glycoproteins with strong antiviral activities that represent one of the first lines of host defense against invading pathogens. These proteins are classified into three groups, Type I, II and III IFNs, based on the structure of their receptors on the cell surface. Due to their ability to modulate immune responses, they have become attractive therapeutic options to control chronic virus infections. In combination with other drugs, Type I IFNs are considered as "standard of care" in suppressing Hepatitis C (HCV) and Hepatitis B (HBV) infections, while Type III IFN has generated encouraging results as a treatment for HCV infection in phase III clinical trials. However, though effective, using IFNs as a treatment is not without the need for caution. IFNs are such powerful cytokines that affect a wide array of cell types; as a result, patients usually experience unpleasant symptoms, with a percentage of patients suffering system wide effects. Thus, constant monitoring is required for patients treated with IFN in order to reach the treatment goals of suppressing virus infection and maintaining quality of life.
Keywords: Antiviral therapy; IFN-α/β; IFN-γ; IFN-λ.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests
Figures
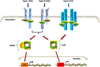
Fig 1. Interferon canonical signaling pathways
Type I, II and III IFNs bind to their specific receptors on the cell membrane and trigger JAK-STAT signaling pathway. While Type I and III can phosphorylate both STAT1 and STAT2 to form ISGF3 and GAF that binds to ISRE and GAS respectively in the promoter region of responding genes, Type II IFN can only phosphorylate STAT1 and induce expression of genes with GAS in the promoter region.
Similar articles
- Antiviral Activity of Type I, II, and III Interferons Counterbalances ACE2 Inducibility and Restricts SARS-CoV-2.
Busnadiego I, Fernbach S, Pohl MO, Karakus U, Huber M, Trkola A, Stertz S, Hale BG. Busnadiego I, et al. mBio. 2020 Sep 10;11(5):e01928-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01928-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32913009 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of antiviral effect of type I, II, and III interferons on direct-acting antiviral-resistant hepatitis C virus.
Hamana A, Takahashi Y, Uchida T, Nishikawa M, Imamura M, Chayama K, Takakura Y. Hamana A, et al. Antiviral Res. 2017 Oct;146:130-138. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.08.017. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Antiviral Res. 2017. PMID: 28864074 - Comparative Analysis of the Antiviral Effects Mediated by Type I and III Interferons in Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Hepatocytes.
Bockmann JH, Stadler D, Xia Y, Ko C, Wettengel JM, Schulze Zur Wiesch J, Dandri M, Protzer U. Bockmann JH, et al. J Infect Dis. 2019 Jul 19;220(4):567-577. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz143. J Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30923817 - The Role of Type III Interferons in Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Therapy.
Bruening J, Weigel B, Gerold G. Bruening J, et al. J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:7232361. doi: 10.1155/2017/7232361. Epub 2017 Feb 1. J Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 28255563 Free PMC article. Review. - Interferons and their use in persistent viral infections.
Chevaliez S, Pawlotsky JM. Chevaliez S, et al. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;189(189):203-41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79086-0_8. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19048202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- IFN-γ derived from activated human CD4+ T cells inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 depending on cell-type and viral strain.
Shimizu J, Sasaki T, Ong GH, Koketsu R, Samune Y, Nakayama EE, Nagamoto T, Yamamoto Y, Miyazaki K, Shioda T. Shimizu J, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 4;14(1):26660. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77969-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39496837 Free PMC article. - Lactobacillus salivarius HHuMin-U Activates Innate Immune Defense against Norovirus Infection through TBK1-IRF3 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.
Kim DH, Jeong M, Kim JH, Son JE, Lee JJY, Park SJ, Lee J, Kim M, Oh JW, Park MS, Byun S. Kim DH, et al. Research (Wash D C). 2022 Dec 19;2022:0007. doi: 10.34133/research.0007. eCollection 2022. Research (Wash D C). 2022. PMID: 39290965 Free PMC article. - Advancing non-small cell lung cancer treatment: the power of combination immunotherapies.
Wu Y, Yu G, Jin K, Qian J. Wu Y, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 2;15:1349502. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1349502. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39015563 Free PMC article. Review. - Respiratory syncytial virus NS1 inhibits anti-viral Interferon-α-induced JAK/STAT signaling, by limiting the nuclear translocation of STAT1.
Efstathiou C, Zhang Y, Kandwal S, Fayne D, Molloy EJ, Stevenson NJ. Efstathiou C, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 13;15:1395809. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395809. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38938568 Free PMC article. - Controlling the Quality of Nanodrugs According to Their New Property-Radiothermal Emission.
Petrov GV, Galkina DA, Koldina AM, Grebennikova TV, Eliseeva OV, Chernoryzh YY, Lebedeva VV, Syroeshkin AV. Petrov GV, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 26;16(2):180. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020180. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399241 Free PMC article.
References
- Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH. Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annual review of immunology. 2005;23:307–336. - PubMed
- van Boxel-Dezaire AH, Rani MR, Stark GR. Complex modulation of cell type-specific signaling in response to type I interferons. Immunity. 2006;25:361–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical