Membranous Nectin-4 expression is a risk factor for distant relapse of T1-T2, N0 luminal-A early breast cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Membranous Nectin-4 expression is a risk factor for distant relapse of T1-T2, N0 luminal-A early breast cancer
R Lattanzio et al. Oncogenesis. 2014.
Abstract
Nectins are Ca(2+)-independent immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecules that compose a family of four members that regulate several cellular activities such as movement, proliferation, survival, differentiation, polarization, and the entry of viruses. Nectin-4 has recently emerged as a metastatis-associated protein in several cancers. Here, we have evaluated the association between the expression of Nectin-4 and the clinical outcome of patients with node-negative, T1/T2 breast cancers.The study group consisted of 197 patients presenting with primary unilateral breast carcinoma (T1/T2), with no evidence of nodal involvement and distant metastases. Nectin-4 protein expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry on tissue microarrays, and the results correlated with the clinical data using Kaplan-Meier curves and multivariate Cox regression analysis. Thirty-four out of 197 tumors (17.3%) exhibited Nectin-4 expression on cell membrane (m-Nectin-4) and 122 out of the 163m-Nectin-4 negative tumors (74.8%) showed high cytoplasmic expression of Nectin-4 (c-Nectin-4(High)). At Kaplan-Meier analysis, m-Nectin-4 positivity was significantly associated with a lower disease-free survival (DFS) and distant relapse-free survival (DRFS) rate in patients with a luminal-A phenotype (P=0.030 and P=0.002, respectively). Multivariate analysis showed that in luminal-A tumors m-Nectin-4 positivity is an independent prognostic factor for DFS (P=0.018) and DRFS (P=0.004), but not for local relapse-free survival (LRFS). On the other hand, c-Nectin-4(High) was significantly associated with higher rates of DFS and LRFS, but not DRFS, in the whole population (P=0.008 and P=0.004, respectively) and in patients with luminal-A tumors (P=0.022 and P=0.018, respectively). In patients with luminal-A tumors, multivariate analysis showed that the prognostic value of c-Nectin-4(Low/Negative) is limited to DFS (P=0.012) and LRFS (P=0.022). We suggest that Nectin-4 represents a prognostic factor and a therapeutic target in luminal-A early stage breast cancer.
Figures
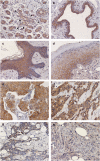
Figure 1
Nectin-4 in non-neoplastic tissues. Specific immunoreactivity is confined to the cytoplasm of almost all luminal cells of terminal duct lobular units (a) and of galactophorous ducts (b). Myoepithelia are negative (A, arrow). In nipple (c) and in non-neoplastic skin (d), Nectin-4 is expressed both in the cytoplasm and on the cell membrane, at cell–cell junctions of keratinocytes. In particular. Nectin-4 can be observed in all the suprabasal layers from the spinous to granular layer. With increasing keratinization, the expression became lower. Nectin-4 in breast tumors. Membranous expression in (e). c-Nectin-4High tumor in (f) with cytoplasmic staining in almost all cancer cells. c-Nectin-4Low: tumor with <36% positively stained cells in (g), and tumor with barely detectable, if any, cytoplasmic Nectin-4 expression in (h). (Original magnification × 40).
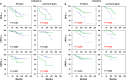
Figure 2
Kaplan–Meier estimates (DFS, LRFS and DRFS) in all patients and in patients with luminal-A tumors. (a) m-Nectin-4 plots: green solid lines and blue dashed lines indicate positive and negative m-Nectin-4 cases, respectively; (b) c-Nectin-4 plots: green solid lines and blue dashed lines indicate high and low/negative expression of c-Nectin-4 cases, respectively.
Similar articles
- Prognostic role of Nectin-4 expression in luminal B (HER2 negative) breast cancer.
Rajc J, Gugić D, Fröhlich I, Marjanović K, Dumenčić B. Rajc J, et al. Pathol Res Pract. 2017 Sep;213(9):1102-1108. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.07.019. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2017. PMID: 28778498 - Overexpression of activated phospholipase Cγ1 is a risk factor for distant metastases in T1-T2, N0 breast cancer patients undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy.
Lattanzio R, Marchisio M, La Sorda R, Tinari N, Falasca M, Alberti S, Miscia S, Ercolani C, Di Benedetto A, Perracchio L, Melucci E, Iacobelli S, Mottolese M, Natali PG, Piantelli M; CINBO (Consorzio Interuniversitario Nazionale per Bio-Oncologia). Lattanzio R, et al. Int J Cancer. 2013 Mar 1;132(5):1022-31. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27751. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 22847294 - Expression and clinical significance of Nectin-4 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Ma J, Sheng Z, Lv Y, Liu W, Yao Q, Pan T, Xu Z, Zhang C, Xu G. Ma J, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Jan 6;9:183-90. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S96999. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 26793002 Free PMC article. - Nectin spot: a novel type of nectin-mediated cell adhesion apparatus.
Mizutani K, Takai Y. Mizutani K, et al. Biochem J. 2016 Sep 15;473(18):2691-715. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160235. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27621480 Review. - Nectin-4 has emerged as a compelling target for breast cancer.
Wang H, Sun D, Chen J, Li H, Chen L. Wang H, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;960:176129. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176129. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38059449 Review.
Cited by
- Antibody-drug conjugates in urothelial carcinoma: scientometric analysis and clinical trials analysis.
Zhang M, Zuo Y, Chen S, Li Y, Xing Y, Yang L, Wang H, Guo R. Zhang M, et al. Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 14;14:1323366. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1323366. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38665947 Free PMC article. Review. - Therapeutic prospects of nectin-4 in cancer: applications and value.
Li K, Zhou Y, Zang M, Jin X, Li X. Li K, et al. Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 28;14:1354543. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1354543. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38606099 Free PMC article. Review. - Production and characterization of single-chain variable fragment antibodies targeting the breast cancer tumor marker nectin-4.
Liu CH, Leu SJ, Lee CH, Lin CY, Wang WC, Tsai BY, Lee YC, Chen CL, Yang YY, Lin LT. Liu CH, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 15;14:1292019. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1292019. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38288120 Free PMC article. - Expression of nectin-4 in prostate cancer.
Ordu M, Karaaslan M, Sirin ME, Yilmaz M. Ordu M, et al. North Clin Istanb. 2023 Sep 25;10(5):583-588. doi: 10.14744/nci.2023.36034. eCollection 2023. North Clin Istanb. 2023. PMID: 37829757 Free PMC article. - Clinical Significance of Nectins in HCC and Other Solid Malignant Tumors: Implications for Prognosis and New Treatment Opportunities-A Systematic Review.
Klekowski J, Zielińska D, Hofman A, Zajdel N, Gajdzis P, Chabowski M. Klekowski J, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 5;15(15):3983. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153983. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Botha JL, Bray F, Sankila R, Parkin DM. Breast cancer incidence and mortality trends in 16 European countries. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39:1718–1729. - PubMed
- Cianfrocca M, Goldstein LJ. Prognostic and predictive factors in early-stage breast cancer. Oncologist. 2004;9:606–616. - PubMed
- Peto R, Boreham J, Clarke M, Davies C, Beral V. UK and USA breast cancer deaths down 25% in year 2000 at ages 20-69 years. Lancet. 2000;355:1822. - PubMed
- Tyczynski JE, Bray F, Parkin DM. Breast cancer in Europe. ENCR Cancer Fact Sheets. 2002;2:1–4.
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365:1687–1717. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous