Three-step hand-assisted laparoscopic surgery for radical distal gastrectomy: an effective surgical approach - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2014 Aug 15;7(8):2156-64.
eCollection 2014.
Affiliations
- PMID: 25232401
- PMCID: PMC4161561
Three-step hand-assisted laparoscopic surgery for radical distal gastrectomy: an effective surgical approach
Jia-Qing Gong et al. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014.
Abstract
Objective: Three-step hand-assisted laparoscopic D2 radical gastrectomy (HALG) is a modified surgical technique based on hand-assisted laparoscopic surgery (HALS) for the treatment of gastric cancer. This surgical approach is particularly easy and convenient for radical distal gastrectomy. In order to thoroughly understand the advantages of applying "three-step HALG" in distal gastrectomy, our center conducted a retrospective study to analyze data from patients who underwent HALG and laparoscopic-assisted D2 radical gastrectomy (LAG) during the corresponding time period.
Methods: The HALG procedure is performed in three steps, namely the operation performed through an auxiliary incision under direct vision, hand-assisted laparoscopic operation, and gastrointestinal tract reconstruction through the auxiliary incision under direct vision. This study performed comprehensive, in-depth comparative analyses on the clinical data of two groups of patients who underwent HALG and LAG.
Results: The auxiliary incision under the xiphoid was maximally utilized in the HALG procedure. The rate of conversion to open surgery in HALG group patients was significantly lower than in the LAG group (P = 0.03), and the operating time was significantly shorter in the HALG group than in the LAG group (P = 0.00). There was no significant difference in the pain rate score on postoperative day 2 and on the day of discharge between the HALG and LAG groups (P > 0.05). No statistically significant difference was found in the time to recovery of bowel function, postoperative hospital stay, or postoperative complications (P > 0.05), although the values were all lower in the HALG group than in the LAG group.
Conclusion: "Three-step HALG" is a highly feasible surgical approach for radical distal gastrectomy.
Keywords: Hand-assisted laparoscopic surgery; distal gastrectomy; laparoscopic-assisted D2 radical gastrectomy; three-step hand-assisted laparoscopic D2 radical gastrectomy.
Figures
Figure 1
Sites of the trocars and the skin incision for the LapDisc or for extracting the tumor-bearing specimen.
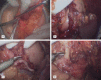
Figure 2
Hand-assisted laparoscopic surgery for radical distal gastrectomy. A. The NO. 6 lymph nodes were dissected, and right gastroepiploic artery was transected; B. NO. 4 lymph nodes were dissected, and left gastroepiploic artery was revealed; C. NO. 11 lymph nodes were dissected, and splenic artery was revealed; D. NO. 7, 8 and 9 lymph nodes were dissected, and left gastric artery was revealed.
Similar articles
- Three-step hand-assisted laparoscopic d2 radical gastrectomy for chinese obese patients: a highly efficient and feasible surgical approach.
Gong J, Cao Y, Wang Y, Zhang G, Wang P, Luo G. Gong J, et al. J Cancer. 2015 Jan 1;6(2):120-7. doi: 10.7150/jca.10639. eCollection 2015. J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25561976 Free PMC article. - Hand-assisted laparoscopic versus laparoscopy-assisted D2 radical gastrectomy: a prospective study.
Gong J, Cao Y, Li Y, Zhang G, Wang P, Luo G. Gong J, et al. Surg Endosc. 2014 Oct;28(10):2998-3006. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3566-y. Epub 2014 May 31. Surg Endosc. 2014. PMID: 24879135 - Learning curve for hand-assisted laparoscopic D2 radical gastrectomy.
Gong JQ, Cao YK, Wang YH, Zhang GH, Wang PH, Luo GD. Gong JQ, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb 7;21(5):1606-13. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1606. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25663780 Free PMC article. - Totally Laparoscopic Gastrectomy Versus Laparoscopic-Assisted Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Meng X, Wang L, Zhu B, Sun T, Guo S, Wang Y, Zhang J, Yang D, Zheng G, Zhang T, Zheng Z, Zhao Y. Meng X, et al. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2021 Jun;31(6):676-691. doi: 10.1089/lap.2020.0566. Epub 2020 Sep 21. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2021. PMID: 32955988 - Comparison of short-term surgical outcomes between totally laparoscopic and laparoscopic-assisted distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a 10-y single-center experience with meta-analysis.
Chen K, Mou YP, Xu XW, Pan Y, Zhou YC, Cai JQ, Huang CJ. Chen K, et al. J Surg Res. 2015 Apr;194(2):367-374. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.10.020. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25488721 Review.
Cited by
- Long-term follow-up after laparoscopic versus open distal gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer.
Zhang Y, Qi F, Jiang Y, Zhai H, Ji Y. Zhang Y, et al. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Aug 15;8(8):13564-70. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26550295 Free PMC article. - Reverse rolling-mat type lymph node dissection is the key step to solve the operative difficulties in hand-assisted laparoscopic D2 radical gastrectomy.
Shu P, Cheng L, Xie C, Zhou J, Yu Q, Dai X, Chen S, Wang Q, Cao Y, Wang T. Shu P, et al. BMC Surg. 2022 Jan 8;22(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12893-021-01460-4. BMC Surg. 2022. PMID: 34996415 Free PMC article. - A comparison of surgical procedures and postoperative cares for minimally invasive laparoscopic gastrectomy and open gastrectomy in gastric cancer.
Tang HN, Hu JH. Tang HN, et al. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jul 15;8(7):10321-9. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26379823 Free PMC article. Review. - Hand-assisted laparoscopic versus open radical resection of gastric remnant cancer: a clinical comparison.
Luo GD, Chen BH, Cao YK, Gong JQ, Tang SH, Li YM. Luo GD, et al. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Nov 15;8(11):21152-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26885048 Free PMC article. - Gastric-jejunum pouch side-to-end anastomosis: a novel and safe operation of gastrojejunostomy for preventing reflux gastritis.
Cao Y, Gong J, Gan W, Zhou J, Huang L, Wang Y, Luo G, Song Y. Cao Y, et al. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):5541-6. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131135 Free PMC article.
References
- Jeong O, Jung MR, Kim GY, Kim HS, Ryu SY, Park YK. Comparison of short-term surgical outcomes between laparoscopic and open total gastrectomy for gastric carcinoma: case-control study using propensity score matching method. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216:184–191. - PubMed
- Zhao XF, Jeong O, Jung MR, Ryu SY, Park YK. A propensity score-matched case-control comparative study of laparoscopic and open extended (D2) lymph node dissection for distal gastric carcinoma. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:2792–2800. - PubMed
- Ozturk E, da Luz Moreira A, Vogel JD. Hand-assisted laparoscopic colectomy: the learning curve is for operative speed, not for quality. Colorectal Dis. 2010;12:e304–309. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources