DEAR1, a novel tumor suppressor that regulates cell polarity and epithelial plasticity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
DEAR1, a novel tumor suppressor that regulates cell polarity and epithelial plasticity
Nanyue Chen et al. Cancer Res. 2014.
Abstract
Elucidation of the regulatory controls on epithelial plasticity is pivotal not only to better understand the nature of metastasis but also for the design of targeted therapies to prevent the earliest steps in migration and invasion from the primary tumor. This review will highlight the role of the novel TRIM protein DEAR1 (annotated as TRIM62) in the regulation of apical-basal polarity and acinar morphogenesis as well as its function as a chromosome 1p35 tumor suppressor and negative regulator of TGFβ-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). DEAR1 binds to and promotes the ubiquitination of SMAD3, the major effector of TGFβ-mediated EMT, as well as downregulates SMAD3 targets SNAIL1/2, master transcriptional regulators of EMT. Cumulative results suggest a novel paradigm for DEAR1 in the regulation of the breast tumor microenvironment, polarity, and EMT. Because DEAR1 undergoes loss-of-function mutations, homozygous deletion, as well as copy-number losses in multiple epithelial cancers, including breast cancer, DEAR1 has clinical use as a predictive and prognostic biomarker as well as for stratifying breast cancers and potentially other epithelial tumor types for targeted therapies aimed at the pathways regulated by DEAR1.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
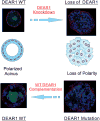
Figure 1. DEAR1 Regulates Cell polarity and Acinar Morphogenesis
Wild type DEAR1 Human mammary epithelial cells (HMECs) undergo acinar morphogenesis in 3D culture in which individual acini are formed containing a polarized layer of luminal epithelial cells surrounded by myoepithelial cells and an intact basement membrane as well as a hollow lumen formed by anoikis; with DEAR1 stable knockdown, HMECs lose apical basal polarity and proper lumen formation (figure adapted from Lott, et.al. Plos Medicine, (24)). In lower panel, introduction of wild type DEAR1 into the 21MT breast cancer cell line containing a missense mutation in DEAR1 rescued acinar morphogenesis.
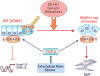
Figure 2. DEAR1 Regulates Epithelial Plasticity by Inhibiting the TGFβ/SMAD3 pathway
Normal DEAR1 expression promotes the fine regulation of SMAD3 and inhibits TGFβ-induced EMT-associated gene expression in HMECs, while loss of function of DEAR1 by genetic alterations, such as mutation, copy number alteration or loss of expression, results in loss of polarity, a dramatic increase of SMAD3 levels, and in the presence of TGFβ, the initiation of EMT.
Similar articles
- Tumor suppressor DEAR1 regulates mammary epithelial cell fate and predicts early onset and metastasis in triple negative breast cancer.
Le UQ, Chen N, Balasenthil S, Lurie E, Yang F, Liu S, Rubin L, Solis Soto LM, Raso MG, Batra H, Sahin AA, Wistuba II, Killary AM. Le UQ, et al. Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 14;12(1):19504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22417-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36376460 Free PMC article. - DEAR1 is a chromosome 1p35 tumor suppressor and master regulator of TGF-β-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Chen N, Balasenthil S, Reuther J, Frayna A, Wang Y, Chandler DS, Abruzzo LV, Rashid A, Rodriguez J, Lozano G, Cao Y, Lokken E, Chen J, Frazier ML, Sahin AA, Wistuba II, Sen S, Lott ST, Killary AM. Chen N, et al. Cancer Discov. 2013 Oct;3(10):1172-89. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0499. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Cancer Discov. 2013. PMID: 23838884 Free PMC article. - DEAR1 is a dominant regulator of acinar morphogenesis and an independent predictor of local recurrence-free survival in early-onset breast cancer.
Lott ST, Chen N, Chandler DS, Yang Q, Wang L, Rodriguez M, Xie H, Balasenthil S, Buchholz TA, Sahin AA, Chaung K, Zhang B, Olufemi SE, Chen J, Adams H, Band V, El-Naggar AK, Frazier ML, Keyomarsi K, Hunt KK, Sen S, Haffty B, Hewitt SM, Krahe R, Killary AM. Lott ST, et al. PLoS Med. 2009 May 26;6(5):e1000068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000068. Epub 2009 May 5. PLoS Med. 2009. PMID: 19536326 Free PMC article. - [The TGF-β signaling pathway induced EMT in breast cancer].
Ma Y, Liu H, Zhang H, Shao RG. Ma Y, et al. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015 Apr;50(4):385-92. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26223118 Review. Chinese. - Reprogramming during epithelial to mesenchymal transition under the control of TGFβ.
Tan EJ, Olsson AK, Moustakas A. Tan EJ, et al. Cell Adh Migr. 2015;9(3):233-46. doi: 10.4161/19336918.2014.983794. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2015. PMID: 25482613 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Emerging roles of tripartite motif family proteins (TRIMs) in breast cancer.
Cao J, Yang M, Guo D, Tao Z, Hu X. Cao J, et al. Cancer Med. 2024 Jul;13(14):e7472. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7472. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39016065 Free PMC article. Review. - Tripartite motif protein 6 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via multiple pathways.
Zhang Y, Yuan L, Cui S, Wu S. Zhang Y, et al. Turk J Med Sci. 2023 Feb 28;53(5):1032-1044. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5668. eCollection 2023. Turk J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 38813007 Free PMC article. - Molecular signature to predict quality of life and survival with glioblastoma using Multiview omics model.
Nassani R, Bokhari Y, Alrfaei BM. Nassani R, et al. PLoS One. 2023 Nov 16;18(11):e0287448. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287448. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37972206 Free PMC article. - Tumor suppressor DEAR1 regulates mammary epithelial cell fate and predicts early onset and metastasis in triple negative breast cancer.
Le UQ, Chen N, Balasenthil S, Lurie E, Yang F, Liu S, Rubin L, Solis Soto LM, Raso MG, Batra H, Sahin AA, Wistuba II, Killary AM. Le UQ, et al. Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 14;12(1):19504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22417-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36376460 Free PMC article. - TRIM family contribute to tumorigenesis, cancer development, and drug resistance.
Huang N, Sun X, Li P, Liu X, Zhang X, Chen Q, Xin H. Huang N, et al. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022 Oct 19;11(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s40164-022-00322-w. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36261847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Debnath J, Brugge JS. Modelling glandular epithelial cancers in three-dimensional cultures. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:675–88. - PubMed
- Reichmann E. Oncogenes and epithelial cell transformation. Semin Cancer Biol. 1994;5:157–65. - PubMed
- Reichert M, Müller T, Hunziker W. The PDZ Domains of Zonula Occludens-1 Induce an Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition of Madin-Darby Canine Kidney I Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2000;275:9492–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials