Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and inflammation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and inflammation
Xing-Chun Wang et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014.
Abstract
Glucagon-like peptide1 (GLP-1) is secreted from Langerhans cells in response to oral nutrient intake. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are a new class of incretin-based anti-diabetic drugs. They function to stimulate insulin secretion while suppressing glucagon secretion. GLP-1-based therapies are now well established in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and recent literature has suggested potential applications of these drugs in the treatment of obesity and for protection against cardiovascular and neurological diseases. As we know, along with change in lifestyles, the prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in China is rising more than that of viral hepatitis and alcoholic fatty liver disease, and NAFLD has become the most common chronic liver disease in recent years. Recent studies further suggest that GLP-1RAs can reduce transaminase levels to improve NAFLD by improving blood lipid levels, cutting down the fat content to promote fat redistribution, directly decreasing fatty degeneration of the liver, reducing the degree of liver fibrosis and improving inflammation. This review shows the NAFLD-associated effects of GLP-1RAs in animal models and in patients with T2DM or obesity who are participants in clinical trials.
Keywords: Fat content; Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; Inflammation; Liver function; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Figures
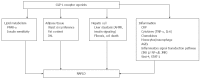
Figure 1
Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and inflammation. PPAR-α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; IHL: intrahepatic lipids; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; CRP: C reactive protein; AGEs: Advanced glycation and end products; JNK: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; GLP-1RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Similar articles
- Potential roles of glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Liu Y, Wei R, Hong TP. Liu Y, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 21;20(27):9090-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9090. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25083081 Free PMC article. Review. - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; New Kids on the Block.
Athyros VG, Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Katsiki N, Anagnostis P, Doumas M, Mantzoros CS. Athyros VG, et al. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(2):172-181. doi: 10.2174/1570161117666190405164313. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 30961499 Review. - The effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on glycemic control and anthropometric profiles among diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Nowrouzi-Sohrabi P, Rezaei S, Jalali M, Ashourpour M, Ahmadipour A, Keshavarz P, Akbari H. Nowrouzi-Sohrabi P, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 15;893:173823. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173823. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33352183 - Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on the degree of liver fibrosis and CRP in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Fang L, Li J, Zeng H, Liu J. Fang L, et al. Prim Care Diabetes. 2024 Jun;18(3):268-276. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2024.03.005. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Prim Care Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38555202 Review. - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease risk with GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide nested case-control study.
Chang KC, Kuo FC, Yang CY, Yang CT, Ou HT, Kuo S. Chang KC, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Oct 17;23(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02461-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39420429 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Efficacy and Safety of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.
Njei B, Al-Ajlouni Y, Lemos SY, Ugwendum D, Ameyaw P, Njei LP, Boateng S. Njei B, et al. Cureus. 2024 Oct 13;16(10):e71366. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71366. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39534801 Free PMC article. Review. - Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: mechanisms and advances in therapy.
Zheng Z, Zong Y, Ma Y, Tian Y, Pang Y, Zhang C, Gao J. Zheng Z, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Sep 18;9(1):234. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01931-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39289339 Free PMC article. Review. - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes: Emerging evidence of benefit of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors agonists and incretin-based therapies.
Pramanik S, Pal P, Ray S. Pramanik S, et al. World J Methodol. 2024 Jun 20;14(2):91319. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i2.91319. eCollection 2024 Jun 20. World J Methodol. 2024. PMID: 38983664 Free PMC article. Review. - Management of Cardiovascular Risk in the Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Setting.
Linero PL, Castilla-Guerra L. Linero PL, et al. Eur Cardiol. 2024 May 9;19:e02. doi: 10.15420/ecr.2023.19. eCollection 2024. Eur Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38807854 Free PMC article. Review. - The effect of GLP-1R agonists on the medical triad of obesity, diabetes, and cancer.
Ibrahim SS, Ibrahim RS, Arabi B, Brockmueller A, Shakibaei M, Büsselberg D. Ibrahim SS, et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Dec;43(4):1297-1314. doi: 10.1007/s10555-024-10192-9. Epub 2024 May 27. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 38801466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Drucker DJ, Nauck MA. The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2006;368:1696–1705. - PubMed
- Agersø H, Jensen LB, Elbrønd B, Rolan P, Zdravkovic M. The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability of NN2211, a new long-acting GLP-1 derivative, in healthy men. Diabetologia. 2002;45:195–202. - PubMed
- Lund A, Knop FK, Vilsbøll T. Emerging GLP-1 receptor agonists. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2011;16:607–618. - PubMed
- Vanni E, Bugianesi E, Kotronen A, De Minicis S, Yki-Järvinen H, Svegliati-Baroni G. From the metabolic syndrome to NAFLD or vice versa? Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42:320–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials