Lipid mediators in the resolution of inflammation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Lipid mediators in the resolution of inflammation
Charles N Serhan et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014.
Abstract
Mounting of the acute inflammatory response is crucial for host defense and pivotal to the development of chronic inflammation, fibrosis, or abscess formation versus the protective response and the need of the host tissues to return to homeostasis. Within self-limited acute inflammatory exudates, novel families of lipid mediators are identified, named resolvins (Rv), protectins, and maresins, which actively stimulate cardinal signs of resolution, namely, cessation of leukocytic infiltration, counterregulation of proinflammatory mediators, and the uptake of apoptotic neutrophils and cellular debris. The biosynthesis of these resolution-phase mediators in sensu stricto is initiated during lipid-mediator class switching, in which the classic initiators of acute inflammation, prostaglandins and leukotrienes (LTs), switch to produce specialized proresolving mediators (SPMs). In this work, we review recent evidence on the structure and functional roles of these novel lipid mediators of resolution. Together, these show that leukocyte trafficking and temporal spatial signals govern the resolution of self-limited inflammation and stimulate homeostasis.
Copyright © 2015 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
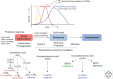
Figure 1.
Lipid-mediator biosynthesis in exudate cell traffic in resolution of acute inflammation. Specialized proresolving mediators (SPMs) are generated during inflammation resolution and control the early events in acute inflammation such as edema formation, leukocyte trafficking, and functions (see text).
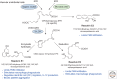
Figure 2.
E-series resolvin biosynthesis and major function (see text for details).
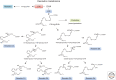
Figure 3.
D-series resolvin biosynthesis. The complete stereochemistry of RvD1, RvD2, and RvD3 is established (see Dalli et al. 2013a and text for further details).
Similar articles
- Natural resolution of inflammation.
Freire MO, Van Dyke TE. Freire MO, et al. Periodontol 2000. 2013 Oct;63(1):149-64. doi: 10.1111/prd.12034. Periodontol 2000. 2013. PMID: 23931059 Free PMC article. Review. - Anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators.
Serhan CN, Yacoubian S, Yang R. Serhan CN, et al. Annu Rev Pathol. 2008;3:279-312. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.151409. Annu Rev Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18233953 Free PMC article. Review. - Novel mediators and mechanisms in the resolution of infectious inflammation: evidence for vagus regulation.
Serhan CN, de la Rosa X, Jouvene C. Serhan CN, et al. J Intern Med. 2019 Sep;286(3):240-258. doi: 10.1111/joim.12871. Epub 2019 Jan 18. J Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30565762 Review. - Resolution phase of inflammation: novel endogenous anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators and pathways.
Serhan CN. Serhan CN. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:101-37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141647. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17090225 Review. - New endogenous anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators: implications for rheumatic diseases.
Yacoubian S, Serhan CN. Yacoubian S, et al. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007 Oct;3(10):570-9; quiz 1 p following 589. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum0616. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17906612 Review.
Cited by
- Neutrophil migration in infection and wound repair: going forward in reverse.
de Oliveira S, Rosowski EE, Huttenlocher A. de Oliveira S, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016 May 27;16(6):378-91. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.49. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27231052 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of inflammation by lipid mediators in oral diseases.
Sommakia S, Baker OJ. Sommakia S, et al. Oral Dis. 2017 Jul;23(5):576-597. doi: 10.1111/odi.12544. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Oral Dis. 2017. PMID: 27426637 Free PMC article. Review. - Diverse Roles of TRPV4 in Macrophages: A Need for Unbiased Profiling.
Nguyen TN, Siddiqui G, Veldhuis NA, Poole DP. Nguyen TN, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 20;12:828115. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.828115. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35126384 Free PMC article. Review. - Cerebrospinal Fluid Profile of Lipid Mediators in Alzheimer's Disease.
Do KV, Hjorth E, Wang Y, Jun B, Kautzmann MI, Ohshima M, Eriksdotter M, Schultzberg M, Bazan NG. Do KV, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Mar;43(2):797-811. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01216-5. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 35362880 Free PMC article. - Possibility of averting cytokine storm in SARS-COV 2 patients using specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators.
Yasmeen N, Selvaraj H, Lakhawat SS, Datta M, Sharma PK, Jain A, Khanna R, Srinivasan J, Kumar V. Yasmeen N, et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Mar;209:115437. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115437. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36731803 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Arita M, Yoshida M, Hong S, Tjonahen E, Glickman JN, Petasis NA, Blumberg RS, Serhan CN 2005b. Resolvin E1, an endogenous lipid mediator derived from omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid, protects against 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102: 7671–7676. - PMC - PubMed
- Arita M, Oh S, Chonan T, Hong S, Elangovan S, Sun Y-P, Uddin J, Petasis NA, Serhan CN 2006. Metabolic inactivation of resolvin E1 and stabilization of its anti-inflammatory actions. J Biol Chem 281: 22847–22854. - PubMed
- Arita M, Ohira T, Sun YP, Elangovan S, Chiang N, Serhan CN 2007. Resolvin E1 selectively interacts with leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 and ChemR23 to regulate inflammation. J Immunol 178: 3912–3917. - PubMed
- Avicenna (Abu Ali Sina adapted by Lalech Bakhtiar). 1999. The canon of medicine [al-Qanun fi'l-tibb]. Great Books of the Islamic World, Chicago.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM038765/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM095467/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL68669/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068669/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM38765/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01GM095467/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122531/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources