Precise and efficient genome editing in zebrafish using the CRISPR/Cas9 system - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2014 Dec;141(24):4827-30.
doi: 10.1242/dev.115584. Epub 2014 Nov 19.
Affiliations
- PMID: 25411213
- PMCID: PMC4299274
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.115584
Precise and efficient genome editing in zebrafish using the CRISPR/Cas9 system
Uwe Irion et al. Development. 2014 Dec.
Abstract
The introduction of engineered site-specific DNA endonucleases has brought precise genome editing in many model organisms and human cells into the realm of possibility. In zebrafish, loss-of-function alleles have been successfully produced; however, germ line transmission of functional targeted knock-ins of protein tags or of SNP exchanges have not been reported. Here we show by phenotypic rescue that the CRISPR/Cas system can be used to target and repair a premature stop codon at the albino (alb) locus in zebrafish with high efficiency and precision. Using circular donor DNA containing CRISPR target sites we obtain close to 50% of larvae with precise homology-directed repair of the alb(b4) mutation, a small fraction of which transmitted the repaired allele in the germ line to the next generation (3/28 adult fish). The in vivo demonstration of germ line transmission of a precise SNP exchange in zebrafish underscores its suitability as a model for genetic research.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas; Genome editing; Zebrafish; albino; slc45a2.
© 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures
Fig. 1.
CRISPR-mediated alb knockout. (A) Schematic representation of the alb locus. The gene consists of seven exons (introns are not drawn to scale). The mutation albb4 introduces a premature stop codon into exon 6. (B) The sequence of exon 6 (in capitals). The CRISPR target site, PAM motif and the albb4 mutation are indicated; the SNPs introduced into the donor DNA fragments are shown beneath the CRISPR target site. (C-F) Dorsal views of larvae at 5 dpf: uninjected control wild type (C) and albb4 (D) larvae, and injected wild-type larvae with moderate (E) and good (F) alb knockout efficiency.
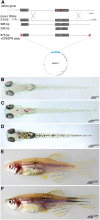
Fig. 2.
Homology-directed repair at the alb locus. (A) Donor DNAs used. The PCR fragments were also cloned into pGEM-T and injected as circular DNA molecules; the construct with the two CRISPR target sites is depicted. (B-D) Dorsal views of larvae 5 dpf: uninjected albb4 control (B), low efficiency repair using linear donor DNA (C) and high efficiency repair using circular donor DNA (D). (E,F) Two examples of adult F0 fish showing pigmented melanophores as a consequence of HDR in melanophore stem cells.
References
- Cade L., Reyon D., Hwang W. Y., Tsai S. Q., Patel S., Khayter C., Joung J. K., Sander J. D., Peterson R. T. and Yeh J.-R. J. (2012). Highly efficient generation of heritable zebrafish gene mutations using homo- and heterodimeric TALENs. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 8001-8010 10.1093/nar/gks518 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Cermak T., Doyle E. L., Christian M., Wang L., Zhang Y., Schmidt C., Baller J. A., Somia N. V., Bogdanove A. J. and Voytas D. F. (2011). Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector-based constructs for DNA targeting. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, e82 10.1093/nar/gkr218 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous