Secretion of immunoregulatory cytokines by mesenchymal stem cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Secretion of immunoregulatory cytokines by mesenchymal stem cells
Dobroslav Kyurkchiev et al. World J Stem Cells. 2014.
Abstract
According to the minimal criteria of the International Society of Cellular Therapy, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a population of undifferentiated cells defined by their ability to adhere to plastic surfaces when cultured under standard conditions, express a certain panel of phenotypic markers and can differentiate into osteogenic, chondrogenic and adipogenic lineages when cultured in specific inducing media. In parallel with their major role as undifferentiated cell reserves, MSCs have immunomodulatory functions which are exerted by direct cell-to-cell contacts, secretion of cytokines and/or by a combination of both mechanisms. There are no convincing data about a principal difference in the profile of cytokines secreted by MSCs isolated from different tissue sources, although some papers report some quantitative but not qualitative differences in cytokine secretion. The present review focuses on the basic cytokines secreted by MSCs as described in the literature by which the MSCs exert immunodulatory effects. It should be pointed out that MSCs themselves are objects of cytokine regulation. Hypothetical mechanisms by which the MSCs exert their immunoregulatory effects are also discussed in this review. These mechanisms may either influence the target immune cells directly or indirectly by affecting the activities of predominantly dendritic cells. Chemokines are also discussed as participants in this process by recruiting cells of the immune systems and thus making them targets of immunosuppression. This review aims to present and discuss the published data and the personal experience of the authors regarding cytokines secreted by MSCs and their effects on the cells of the immune system.
Keywords: Chemokines; Cytokines; Dendritic cells; Immunomodulation; Mesenchymal stem cells.
Figures
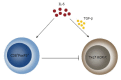
Figure 1
Effect of Interleukin 6 on Th17 formation. IL-6 exerts a dual effect on the generation of Th17 cells. On one side, IL-6 in concert with TGFβ facilitates the generation of this cell population and on the other side, IL-6 inhibits the Th17 cells by inducing the generation of CD8+FoxP3+ T lymphocytes. TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β.
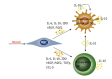
Figure 2
Mesenchymal stem cells provide an immunoregulatory effect by interactions with dendritic cells and T regulatory cells. Under the influence of cytokines secreted by MSCs and autocrine secreted interleukin-10 (IL-10), the dendritic cells acquire an immature tolerogenic phenotype characterized by a low expression of MHC II and B7 molecules, as well as a higher secretion of IL-10. The secretion of IL-10 induces generation of different subtypes of regulatory T cells which further secrete IL-10 and induce tolerogenic phenotype in dendritic cells. Cytokines secreted from MSCs also lead directly to formation of regulatory T cells. VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; IDO: Indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase; TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β; DCs: Dendritic cells; IL: Interleukin; CCL: CC chemokine ligand.
Similar articles
- Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue under xeno-free conditions for cell therapy.
Li CY, Wu XY, Tong JB, Yang XX, Zhao JL, Zheng QF, Zhao GB, Ma ZJ. Li CY, et al. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Apr 13;6(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0066-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25884704 Free PMC article. - Immunomodulatory Properties of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Healthy Donors.
Javorkova E, Matejckova N, Zajicova A, Hermankova B, Hajkova M, Bohacova P, Kossl J, Krulova M, Holan V. Javorkova E, et al. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;14(2):215-225. doi: 10.1007/s11481-018-9812-7. Epub 2018 Sep 21. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30242613 - The effect of pro-inflammatory cytokines on immunophenotype, differentiation capacity and immunomodulatory functions of human mesenchymal stem cells.
Pourgholaminejad A, Aghdami N, Baharvand H, Moazzeni SM. Pourgholaminejad A, et al. Cytokine. 2016 Sep;85:51-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.06.003. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Cytokine. 2016. PMID: 27288632 - Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells: advances and applications.
De Miguel MP, Fuentes-Julián S, Blázquez-Martínez A, Pascual CY, Aller MA, Arias J, Arnalich-Montiel F. De Miguel MP, et al. Curr Mol Med. 2012 Jun;12(5):574-91. doi: 10.2174/156652412800619950. Curr Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22515979 Review. - Human mesenchymal stem cells - current trends and future prospective.
Ullah I, Subbarao RB, Rho GJ. Ullah I, et al. Biosci Rep. 2015 Apr 28;35(2):e00191. doi: 10.1042/BSR20150025. Biosci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25797907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells in critical-care patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Martí-Chillón GJ, Muntión S, Preciado S, Osugui L, Navarro-Bailón A, González-Robledo J, Sagredo V, Blanco JF, Sánchez-Guijo F. Martí-Chillón GJ, et al. Clin Transl Med. 2023 Jan;13(1):e1163. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1163. Clin Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36588089 Free PMC article. Review. - Evaluation of platelet lysate as a substitute for FBS in explant and enzymatic isolation methods of human umbilical cord MSCs.
Kandoi S, L PK, Patra B, Vidyasekar P, Sivanesan D, S V, K R, Verma RS. Kandoi S, et al. Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 20;8(1):12439. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30772-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30127445 Free PMC article. - Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in the pathogenesis and regenerative therapy of inflammatory bowel diseases.
Che Z, Ye Z, Zhang X, Lin B, Yang W, Liang Y, Zeng J. Che Z, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 4;13:952071. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.952071. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35990688 Free PMC article. Review. - Mesenchymal Stem Cells Influence Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells, and Constitute a Promising Therapy for Liver Fibrosis.
Lee C, Kim M, Han J, Yoon M, Jung Y. Lee C, et al. Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 2;9(11):1598. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111598. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829827 Free PMC article. Review. - A Molecular Analysis of Cytokine Content across Extracellular Vesicles, Secretions, and Intracellular Space from Different Site-Specific Adipose-Derived Stem Cells.
Santos J, Dalla PV, Milthorpe BK. Santos J, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 30;23(1):397. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010397. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008824 Free PMC article.
References
- Reinders ME, Leuning DG, de Fijter JW, Hoogduijn MJ, Rabelink TJ. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for cardio renal disorders. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20:2412–2429. - PubMed
- Le Blanc K, Ringdén O. Immunobiology of human mesenchymal stem cells and future use in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11:321–334. - PubMed
- Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143–147. - PubMed
- Siegel G, Schäfer R, Dazzi F. The immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells. Transplantation. 2009;87:S45–S49. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources