Manipulating gene expression in projection-specific neuronal populations using combinatorial viral approaches - PubMed (original) (raw)
Manipulating gene expression in projection-specific neuronal populations using combinatorial viral approaches
Bryan B Gore et al. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2013.
Abstract
The mammalian brain contains tremendous structural and genetic complexity that is vital for its function. The elucidation of gene expression profiles in the brain, coupled with the development of large-scale connectivity maps and emerging viral vector-based approaches for target-selective gene manipulation, now allow for detailed dissection of gene-circuit interfaces. This protocol details how to perform combinatorial viral injections to manipulate gene expression in subsets of neurons interconnecting two brain regions. This method utilizes stereotaxic injection of a retrograde transducing CAV2-Cre virus into one brain region, combined with injection of a locally transducing Cre-dependent AAV virus into another brain region. This technique is widely applicable to the genetic dissection of neural circuitry, as it enables selective expression of candidate genes, dominant-negatives, fluorescent reporters, or genetic tools within heterogeneous populations of neurons based upon their projection targets.
Keywords: AAV; CAV; neural circuit; stereotaxic surgery; viral vector.
Figures
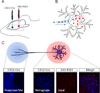
Figure 1
Combinatorial viral delivery to study pathway specific gene function. (A) Illustration of combined viral injections of a conditional AAV-FLEX construct (red) into a region containing a neuronal population of interest and a CAV2-Cre viral vector (blue) into a projection target of the neurons of interest. (B) Illustration of local (red) AAV-FLEX viral vector transduction and retrograde (blue) CAV2-Cre transduction. (C) Demonstration of combinatorial viral-mediated gene expression. Injection of CAV2-Cre into a target region of interest (blue) of a Cre-dependent reporter line (Ai14) illustrates coverage area of viral vector injection and the number of neurons retrogradely transduced. Injection of AAV-FLEX containing conditional expression cassette of interest locally transduces neurons at the sight of injection; however, only neurons with combined CAV2-Cre and AAV-FLEX will express the transgene (red).
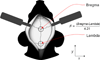
Figure 2
Illustration demonstrating the identification of Bregma and Lambda on a mouse skull. Following incision, the scalp is held open using skin clamps, allowing access to the top of the skull. Bregma can be seen as the intersection of the midline rostral-caudal fissure and the second major medial-lateral fissure. Lambda can be identified as the most rostral medial-lateral fissure. Stereotaxic×and y coordinates are set to zero at Bregma. Moving from midline to the left is in the negative×direction and positive from midline to the right. Similarly, y coordinates are negative caudal to Bregma and positive rostral to Bregma. Stereotaxic targeting of the y coordinate can be improved using a Bregma-Lambda correction factor (F), taken as the distance between Bregma and Lambda and dividing by 4.21 (the distance from Bregma to Lambda in a commonly used mouse brain atlas).
Similar articles
- tTARGIT AAVs mediate the sensitive and flexible manipulation of intersectional neuronal populations in mice.
Sabatini PV, Wang J, Rupp AC, Affinati AH, Flak JN, Li C, Olson DP, Myers MG. Sabatini PV, et al. Elife. 2021 Mar 11;10:e66835. doi: 10.7554/eLife.66835. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33704065 Free PMC article. - A Viral Receptor Complementation Strategy to Overcome CAV-2 Tropism for Efficient Retrograde Targeting of Neurons.
Li SJ, Vaughan A, Sturgill JF, Kepecs A. Li SJ, et al. Neuron. 2018 Jun 6;98(5):905-917.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.028. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 29879392 - Transgene expression in target-defined neuron populations mediated by retrograde infection with adeno-associated viral vectors.
Rothermel M, Brunert D, Zabawa C, Díaz-Quesada M, Wachowiak M. Rothermel M, et al. J Neurosci. 2013 Sep 18;33(38):15195-206. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1618-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24048849 Free PMC article. - Adeno-associated viral vectors for mapping, monitoring, and manipulating neural circuits.
Betley JN, Sternson SM. Betley JN, et al. Hum Gene Ther. 2011 Jun;22(6):669-77. doi: 10.1089/hum.2010.204. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Hum Gene Ther. 2011. PMID: 21319997 Free PMC article. Review. - CAV-2--why a canine virus is a neurobiologist's best friend.
Junyent F, Kremer EJ. Junyent F, et al. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;24:86-93. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2015.08.004. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26298516 Review.
Cited by
- Hippocampal deletion of NaV1.1 channels in mice causes thermal seizures and cognitive deficit characteristic of Dravet Syndrome.
Stein RE, Kaplan JS, Li J, Catterall WA. Stein RE, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Aug 13;116(33):16571-16576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1906833116. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31346088 Free PMC article. - Synergy of Distinct Dopamine Projection Populations in Behavioral Reinforcement.
Heymann G, Jo YS, Reichard KL, McFarland N, Chavkin C, Palmiter RD, Soden ME, Zweifel LS. Heymann G, et al. Neuron. 2020 Mar 4;105(5):909-920.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.11.024. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 31879163 Free PMC article. - Estrogenic-dependent glutamatergic neurotransmission from kisspeptin neurons governs feeding circuits in females.
Qiu J, Rivera HM, Bosch MA, Padilla SL, Stincic TL, Palmiter RD, Kelly MJ, Rønnekleiv OK. Qiu J, et al. Elife. 2018 Aug 6;7:e35656. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35656. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30079889 Free PMC article. - Noncanonical projections to the hippocampal CA3 regulate spatial learning and memory by modulating the feedforward hippocampal trisynaptic pathway.
Lin X, Amalraj M, Blanton C, Avila B, Holmes TC, Nitz DA, Xu X. Lin X, et al. PLoS Biol. 2021 Dec 20;19(12):e3001127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001127. eCollection 2021 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2021. PMID: 34928938 Free PMC article. - Mesoscale connectomics.
Zeng H. Zeng H. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018 Jun;50:154-162. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29579713 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ahmed BY, Chakravarthy S, Eggers R, Hermens WT, Zhang JY, Niclou SP, Levelt C, Sablitzky F, Anderson PN, Lieberman AR, Verhaagen J. Efficient delivery of Cre-recombinase to neurons in vivo and stable transduction of neurons using adeno-associated and lentiviral vectors. BMC neuroscience. 2004;5:4. - PMC - PubMed
- Bernard A, Lubbers LS, Tanis KQ, Luo R, Podtelezhnikov AA, Finney EM, McWhorter MM, Serikawa K, Lemon T, Morgan R, Copeland C, Smith K, Cullen V, Davis-Turak J, Lee CK, Sunkin SM, Loboda AP, Levine DM, Stone DJ, Hawrylycz MJ, Roberts CJ, Jones AR, Geschwind DH, Lein ES. Transcriptional architecture of the primate neocortex. Neuron. 2012;73:1083–1099. - PMC - PubMed
- Consortium IHGS. Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature. 2004;431:931–945. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources