Stroke after Initiating IV Penicillin for Neurosyphilis: A Possible Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction - PubMed (original) (raw)
Stroke after Initiating IV Penicillin for Neurosyphilis: A Possible Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction
Vineet Punia et al. Case Rep Neurol Med. 2014.
Abstract
Introduction. Syphilis incidence has increased in the US in the last decade. Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction (JHR) is a well-documented adverse effect of penicillin treatment in syphilis. Stroke has not been reported as part of its phenomenology. Case Report. A 57-year-old man presented with worsening memory. His minimental status examination score was 14/30. Serum RPR test was positive and VDRL test in the CSF was reactive. Within six hours of first dose of IV crystalline penicillin G, he was found to have hemineglect and difficulty moving the left leg. MRI of the brain showed multiple acute ischemic strokes. Immediate MRA ruled out vascular occlusion. Penicillin treatment was stopped. Four hours later, he was found to be febrile and had two episodes of generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Conclusions. We report a case of confirmed neurosyphilis with no known modifiable stroke risk factors, who developed acute ischemic stroke and other constitutional symptoms consistent with JHR after IV penicillin. This is the first reported case in literature where an acute ischemic stroke can be attributed to Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. Given an increase in incidence of syphilis in recent years, our case underlies the importance of keeping in mind potential catastrophic drug adverse reactions in neurosyphilis patients.
Figures
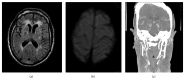
Figure 1
Pre-penicillin therapy imaging. (a) FLAIR, (b) DWI sequence, and (c) CT angiogram.
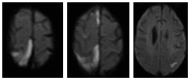
Figure 2
Diffusion sequence immediately after symptom onset.
Similar articles
- Generalized Convulsive Status Epilepticus Secondary to Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction in Neurosyphilis: A Case Report and Literature Review.
Rissardo JP, Caprara ALF, Silveira JOF. Rissardo JP, et al. Neurologist. 2019 Jan;24(1):29-32. doi: 10.1097/NRL.0000000000000219. Neurologist. 2019. PMID: 30586032 Review. - Penicillin-induced Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction.
See S, Scott EK, Levin MW. See S, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 2005 Dec;39(12):2128-30. doi: 10.1345/aph.1G308. Epub 2005 Nov 15. Ann Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 16288069 - A Case of Early Neurosyphilis.
Walker M, Wisler R, Simmons J, Johnson A. Walker M, et al. J La State Med Soc. 2017 Mar-Apr;169(2):47-48. Epub 2017 Apr 15. J La State Med Soc. 2017. PMID: 28414665 - An observational prospective study based on a large cohort of HIV-negative neurosyphilis patients with particular reference to the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction.
Peng RR, Wu J, Zhao W, Zhu L, Guan Z, Gu X, Shi M, Yu J, Cheng Y, Zhou P. Peng RR, et al. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Jun;43(6):1073-1080. doi: 10.1007/s10096-024-04810-1. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38557924 Free PMC article. - The Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction associated with doxycycline in a patient with Lyme arthritis.
Nykytyuk S, Boyarchuk O, Klymnyuk S, Levenets S. Nykytyuk S, et al. Reumatologia. 2020;58(5):335-338. doi: 10.5114/reum.2020.99143. Epub 2020 Oct 3. Reumatologia. 2020. PMID: 33227092 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A Narrative Review of the Many Psychiatric Manifestations of Neurosyphilis: The Great Imitator.
Kaur B, Khanna D. Kaur B, et al. Cureus. 2023 Sep 7;15(9):e44866. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44866. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37814742 Free PMC article. Review. - Epilepsy and syphilis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Zhang C, Yue W, Hou S, Cui W, Xiang L. Zhang C, et al. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021 [SEASON];87(4):483-490. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_681_19. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021. PMID: 34219436 - Acute Ischaemic Stroke in the Context of Neurosyphilis: How Does Antibiotic Therapy Help, and When Should It Be Given?
Gomes Santos P, Martins Dos Santos P, Abegão T, Rosa Domingos R, Varela AV, Florêncio A, Fidalgo AP. Gomes Santos P, et al. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2024 Jan 8;11(2):004231. doi: 10.12890/2024_004231. eCollection 2024. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 38352810 Free PMC article. - Takayasu Arteritis Coexisting with Cutaneous Leishmaniasis.
Zhao M, Liu Y, Hu Z, Sun J, Yang Z, Wei L, Xu Z, Ma L. Zhao M, et al. J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 24;12(5):1819. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051819. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902606 Free PMC article. - The Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction After Antibiotic Treatment of Spirochetal Infections: A Review of Recent Cases and Our Understanding of Pathogenesis.
Butler T. Butler T. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017 Jan 11;96(1):46-52. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0434. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017. PMID: 28077740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources