Evolution of Staphylococcus aureus under vancomycin selective pressure: the role of the small-colony variant phenotype - PubMed (original) (raw)
Evolution of Staphylococcus aureus under vancomycin selective pressure: the role of the small-colony variant phenotype
Justin R Lenhard et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Feb.
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants (SCVs) often persist despite antibiotic therapy. Against a 10(8)-CFU/ml methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) (strain COL) population of which 0%, 1%, 10%, 50%, or 100% was an isogenic hemB knockout (Ia48) subpopulation displaying the SCV phenotype, vancomycin achieved maximal reductions of 4.99, 5.39, 4.50, 3.28, and 1.66 log10 CFU/ml over 48 h. Vancomycin at ≥16 mg/liter shifted a population from 50% SCV cells at 0 h to 100% SCV cells at 48 h, which was well characterized by a Hill-type model (R2>0.90).
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
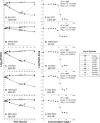
FIG 1
Vancomycin time-kill experiments involving exclusively strains of the NP at an inoculum of 0% SCV/100% NP cells (A) and exclusively strains of the SCV phenotype at an inoculum of 100% SCV/0% NP cells (B), as well as three mixed-population experiments consisting of 1% SCV/99% NP (C), 10% SCV/90% NP (D), and 50% SCV/50% NP (E) cell inoculums. The pharmacodynamic relationship between log ratio area and vancomycin concentration are also displayed for 0% SCV/100% NP (F), 100% SCV/0% NP (G), 1% SCV/99% NP (H), 10% SCV/90% NP (I), and 50% SCV/50% NP (J) cells. _R_2, _E_max, and EC50s are listed next to the corresponding Hill plots (percent standard errors are listed parenthetically).
FIG 2
Colony counts used to track SCV subpopulations. In mixed-culture experiments, samples were plated on plain BHI agar as well as BHI containing 2.0 mg/liter gentamicin. Gentamicin plates permitted only the growth of SCVs, and the corresponding CFU plots derived from the drug plates are displayed for 1% SCV/99% NP (A), 10% SCV/90% NP (B), and 50% SCV/50% NP (C) cell inoculums. Additionally, the maximum percentages of the SCV detected over 48 h for each vancomycin concentration are plotted and fit to a Hill-type function for 1% SCV/99% NP (D), 10% SCV/90% NP (E), and 50% SCV/50% NP (F) cell inoculums.
Similar articles
- Daptomycin pharmacodynamics against Staphylococcus aureus hemB mutants displaying the small colony variant phenotype.
Begic D, von Eiff C, Tsuji BT. Begic D, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009 May;63(5):977-81. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp069. Epub 2009 Mar 19. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19304733 - Extracellular and intracellular bactericidal activities of XF-70 against small-colony variant hemB mutants of meticillin-susceptible and meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Vaudaux P, Huggler E, Rhys-Williams W, Love WG, Lew DP. Vaudaux P, et al. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011 Jun;37(6):576-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.01.015. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011. PMID: 21414759 - In Vitro Pharmacodynamics of Vancomycin against Methicillin-Susceptible and -Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Considering the Variability in Observed Tissue Exposure.
Hamada Y, Kuti JL, Nicolau DP. Hamada Y, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Nov 30;60(2):955-61. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01553-15. Print 2016 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26621619 Free PMC article. - Structure-activity relationships of vancomycin-type glycopeptide antibiotics.
Nagarajan R. Nagarajan R. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1993 Aug;46(8):1181-95. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.46.1181. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1993. PMID: 8407579 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Detection, Identification and Diagnostic Characterization of the Staphylococcal Small Colony-Variant (SCV) Phenotype.
Becker K. Becker K. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Sep 14;12(9):1446. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12091446. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760742 Free PMC article. Review. - Phenotypic and Genotypic Characteristics of Small Colony Variants and Their Role in Chronic Infection.
Johns BE, Purdy KJ, Tucker NP, Maddocks SE. Johns BE, et al. Microbiol Insights. 2015 Sep 22;8:15-23. doi: 10.4137/MBI.S25800. eCollection 2015. Microbiol Insights. 2015. PMID: 26448688 Free PMC article. Review. - Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants isolated from wound specimen of a tertiary care hospital in China.
Min C, Wang H, Xia F, Tang M, Li J, Hu Y, Dou Q, Zou M. Min C, et al. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jan;36(1):e24121. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24121. Epub 2021 Nov 27. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 34837244 Free PMC article. - High-intensity meropenem combinations with polymyxin B: new strategies to overcome carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii.
Lenhard JR, Bulitta JB, Connell TD, King-Lyons N, Landersdorfer CB, Cheah SE, Thamlikitkul V, Shin BS, Rao G, Holden PN, Walsh TJ, Forrest A, Nation RL, Li J, Tsuji BT. Lenhard JR, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017 Jan;72(1):153-165. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw355. Epub 2016 Sep 15. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017. PMID: 27634916 Free PMC article. - Adjuvant intra-articular vancomycin for recalcitrant Staphylococcal prosthetic joint infections of the knee.
Doub JB, Heil EL, Manson T. Doub JB, et al. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024 Feb;34(2):1031-1036. doi: 10.1007/s00590-023-03764-y. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 37864658
References
- Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, Daum RS, Fridkin SK, Gorwitz RJ, Kaplan SL, Karchmer AW, Levine DP, Murray BE, J Rybak M, Talan DA, Chambers HF. 2011. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children. Clin Infect Dis 52:e18–55. doi:10.1093/cid/ciq146. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical