Cost-utility and cost-effectiveness studies of telemedicine, electronic, and mobile health systems in the literature: a systematic review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Cost-utility and cost-effectiveness studies of telemedicine, electronic, and mobile health systems in the literature: a systematic review
Isabel de la Torre-Díez et al. Telemed J E Health. 2015 Feb.
Abstract
Objective: A systematic review of cost-utility and cost-effectiveness research works of telemedicine, electronic health (e-health), and mobile health (m-health) systems in the literature is presented.
Materials and methods: Academic databases and systems such as PubMed, Scopus, ISI Web of Science, and IEEE Xplore were searched, using different combinations of terms such as "cost-utility" OR "cost utility" AND "telemedicine," "cost-effectiveness" OR "cost effectiveness" AND "mobile health," etc. In the articles searched, there were no limitations in the publication date.
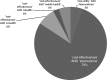
Results: The search identified 35 relevant works. Many of the articles were reviews of different studies. Seventy-nine percent concerned the cost-effectiveness of telemedicine systems in different specialties such as teleophthalmology, telecardiology, teledermatology, etc. More articles were found between 2000 and 2013. Cost-utility studies were done only for telemedicine systems.
Conclusions: There are few cost-utility and cost-effectiveness studies for e-health and m-health systems in the literature. Some cost-effectiveness studies demonstrate that telemedicine can reduce the costs, but not all. Among the main limitations of the economic evaluations of telemedicine systems are the lack of randomized control trials, small sample sizes, and the absence of quality data and appropriate measures.
Keywords: business administration/economics; e-health; mobile health; telemedicine.
Figures
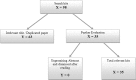
**Fig. 1.
Flowchart of the steps followed in this review.
**Fig. 2.
Percentage of studies found.
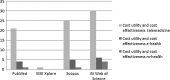
**Fig. 3.
Number of articles about cost-utility and cost-effectiveness in the literature using different scientific databases.
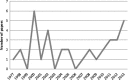
**Fig. 4.
Number of articles in the review versus publication date.
Similar articles
- The Cost-Effectiveness of Digital Health Interventions on the Management of Cardiovascular Diseases: Systematic Review.
Jiang X, Ming WK, You JH. Jiang X, et al. J Med Internet Res. 2019 Jun 17;21(6):e13166. doi: 10.2196/13166. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31210136 Free PMC article. - Critical appraisal of published systematic reviews assessing the cost-effectiveness of telemedicine studies.
Mistry H, Garnvwa H, Oppong R. Mistry H, et al. Telemed J E Health. 2014 Jul;20(7):609-18. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2013.0259. Epub 2014 May 12. Telemed J E Health. 2014. PMID: 24820406 Review. - Telemedicine Cost-Effectiveness for Diabetes Management: A Systematic Review.
Lee JY, Lee SWH. Lee JY, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018 Jul;20(7):492-500. doi: 10.1089/dia.2018.0098. Epub 2018 May 29. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29812965 Review. - Systematic review of studies of the cost-effectiveness of telemedicine and telecare. Changes in the economic evidence over twenty years.
Mistry H. Mistry H. J Telemed Telecare. 2012 Jan;18(1):1-6. doi: 10.1258/jtt.2011.110505. Epub 2011 Nov 18. J Telemed Telecare. 2012. PMID: 22101609 Review. - Cost-effectiveness of Store-and-Forward Teledermatology: A Systematic Review.
Snoswell C, Finnane A, Janda M, Soyer HP, Whitty JA. Snoswell C, et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2016 Jun 1;152(6):702-8. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.0525. JAMA Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27074289 Review.
Cited by
- Telemedicine to deliver diabetes care in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Correia JC, Meraj H, Teoh SH, Waqas A, Ahmad M, Lapão LV, Pataky Z, Golay A. Correia JC, et al. Bull World Health Organ. 2021 Mar 1;99(3):209-219B. doi: 10.2471/BLT.19.250068. Epub 2020 Nov 29. Bull World Health Organ. 2021. PMID: 33716343 Free PMC article. Review. - The Elbow Physical Examination for Telemedicine Encounters.
Lawton CD, Swensen-Buza S, Awender JF, Pinnamaneni S, Lamplot JD, Young WK, Rodeo SA, Nawabi DH, Taylor SA, Dines JS. Lawton CD, et al. HSS J. 2021 Feb;17(1):65-69. doi: 10.1177/1556331620975040. Epub 2021 Feb 21. HSS J. 2021. PMID: 33967644 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Cost analysis of in-home telerehabilitation for post-knee arthroplasty.
Tousignant M, Moffet H, Nadeau S, Mérette C, Boissy P, Corriveau H, Marquis F, Cabana F, Ranger P, Belzile ÉL, Dimentberg R. Tousignant M, et al. J Med Internet Res. 2015 Mar 31;17(3):e83. doi: 10.2196/jmir.3844. J Med Internet Res. 2015. PMID: 25840501 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Improve the cervical cancer prevention behaviors through mobile-based educational intervention based on I-CHANGE model: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.
Kazemi S, Zarei F, Heidarnia A, Alhani F. Kazemi S, et al. Trials. 2022 Sep 24;23(1):805. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06744-5. Trials. 2022. PMID: 36153560 Free PMC article. - An Interactive Text Messaging Intervention to Improve Adherence to Option B+ Prevention of Mother-to-Child HIV Transmission in Kenya: Cost Analysis.
Chen Y, Ronen K, Matemo D, Unger JA, Kinuthia J, John-Stewart G, Levin C. Chen Y, et al. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Oct 2;8(10):e18351. doi: 10.2196/18351. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 33006562 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- American Telemedicine Association. Available at www.americantelemed.org (last accessed February20, 2014)
- World Health Organization. Available at www.who.int (last accessed February20, 2014)
- Dávalos ME, French MT, Burdick AE, Simmons SC. Economic evaluation of telemedicine: Review of the literature and research guidelines for benefit–cost analysis. Telemed J E Health 2009;15:933–948 - PubMed
- Devlin N, Parkin D. Does NICE have a cost-effectiveness threshold and what other factors influence its decisions? A binary choice analysis. Health Econ 2004;13:437–452 - PubMed
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Guide to the methods of technology appraisal. Available at www.nice.org.uk/media/B52/A7/TAMethodsGuideUpdatedJune2008.pdf (last accessed April26, 2014) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical