FASTING PLASMA LIPID, GLUCOSE, AND INSULIN LEVELS IN PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME AND OBESE INDIVIDUALS - PubMed (original) (raw)
FASTING PLASMA LIPID, GLUCOSE, AND INSULIN LEVELS IN PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME AND OBESE INDIVIDUALS
Merlin G Butler et al. Dysmorphol Clin Genet. 1990.
Abstract
Plasma lipid, glucose, and insulin levels were measured from 26 patients with Prader-Willi syndrome (16 with the chromosome 15q deletion and 10 with normal chromosomes) and 32 obese, normal individuals. The average percentage of ideal body weight (IBW) for the former group was 175.6 ± 68.0, compared to 150.3 ± 43.8 for the latter. Fasting plasma lipid, glucose, and insulin levels were not significantly different between the two groups. No significant correlations were found among the three measurements in patients with PWS (deletion or nondeletion) or obese individuals and either age or percentage of IBW. Both insulin and glucose levels were higher in the PWS group, while only insulin levels were higher in the obese group compared with normative laboratory standards. Our study supports previously reported lipid, glucose, and insulin data in PWS and obesity.
Keywords: glucose; insulin; lipids; obesity.
Figures
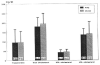
Fig. 1
Fasting plasma triglyceride, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol levels for each group. Values are means ± standard deviation.
Fig. 2
Fasting plasma glucose and immunoreactive insulin levels for each group. Values are means ± standard deviation.
Fig. 3
Fasting plasma glucose and immunoreactive insulin levels plotted for 10 patients with PWS and 15 obese individuals. The regression lines are as follows: solid line, PWS; dashed line, non-PWS obese. A correlation of −0.35 for the patients and 0.22 for the obese persons were calculated but not significant.
Similar articles
- Insulin resistance and obesity-related factors in Prader-Willi syndrome: comparison with obese subjects.
Talebizadeh Z, Butler MG. Talebizadeh Z, et al. Clin Genet. 2005 Mar;67(3):230-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2004.00392.x. Clin Genet. 2005. PMID: 15691361 Free PMC article. - AMINO ACID LEVELS IN PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME AND OBESE INDIVIDUALS.
Butler MG, Murrell JE, Greene HL. Butler MG, et al. Dysmorphol Clin Genet. 1990;4(1):18-22. Dysmorphol Clin Genet. 1990. PMID: 25505361 Free PMC article. - Characterization of alterations in glucose and insulin metabolism in Prader-Willi subjects.
Schuster DP, Osei K, Zipf WB. Schuster DP, et al. Metabolism. 1996 Dec;45(12):1514-20. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(96)90181-x. Metabolism. 1996. PMID: 8969285 - The Prader-Willi syndrome: a study of 40 patients and a review of the literature.
Bray GA, Dahms WT, Swerdloff RS, Fiser RH, Atkinson RL, Carrel RE. Bray GA, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 1983 Mar;62(2):59-80. Medicine (Baltimore). 1983. PMID: 6338343 Review. - Update on Diabetes Mellitus and Glucose Metabolism Alterations in Prader-Willi Syndrome.
Crinò A, Grugni G. Crinò A, et al. Curr Diab Rep. 2020 Feb 6;20(2):7. doi: 10.1007/s11892-020-1284-5. Curr Diab Rep. 2020. PMID: 32030506 Review.
Cited by
- Insulin resistance and obesity-related factors in Prader-Willi syndrome: comparison with obese subjects.
Talebizadeh Z, Butler MG. Talebizadeh Z, et al. Clin Genet. 2005 Mar;67(3):230-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2004.00392.x. Clin Genet. 2005. PMID: 15691361 Free PMC article. - Serum Lipoprotein(a) and High-Sensitivity C-reactive Protein Correlate With Somatic Parameters Including MLPA Subgroups in Children With Prader-Willi Syndrome.
Biswas P, Banerjee S, Bhattacharya P, Mukhoti K, Sarkar M, Chowdhury S, Sahana PK. Biswas P, et al. J Endocr Soc. 2025 May 8;9(7):bvaf082. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaf082. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Endocr Soc. 2025. PMID: 40401233 Free PMC article. - Using sno- lncRNAs as potential markers for Prader-Willi syndrome diagnosis.
Sun JR, Yang LZ, Dai YL, Wu H, Li S, Xu YF, Huang Y, Wu H, Shen Z, Zou C, Chen LL. Sun JR, et al. RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):419-430. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2230406. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37405372 Free PMC article. - Obesity in Prader-Willi syndrome: physiopathological mechanisms, nutritional and pharmacological approaches.
Muscogiuri G, Barrea L, Faggiano F, Maiorino MI, Parrillo M, Pugliese G, Ruggeri RM, Scarano E, Savastano S, Colao A; RESTARE. Muscogiuri G, et al. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021 Oct;44(10):2057-2070. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01574-9. Epub 2021 Apr 23. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021. PMID: 33891302 Free PMC article. Review. - Hypothalamic neuropeptides and neurocircuitries in Prader Willi syndrome.
Correa-da-Silva F, Fliers E, Swaab DF, Yi CX. Correa-da-Silva F, et al. J Neuroendocrinol. 2021 Jul;33(7):e12994. doi: 10.1111/jne.12994. Epub 2021 Jun 22. J Neuroendocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34156126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Prader A, Labhart A, Willi H. Ein Syndrom von Adipositas, Kleinwuchs, Kryptorchisumus und Oligophrenie nach myatonieartigem Zustand im Neugeborenenalter. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1956;86:1260–1261.
- Schoeller DA, Levitsky LL, Bandini LG, Dietz WW, Walczak A. Energy expenditure and body composition in Prader-Willi syndrome. Metabolism. 1988;37:115–120. - PubMed
- Theodoridis CG, Albutt EC, Chance GW. Blood lipids in children with the Prader-Willi syndrome: A comparison with simple obesity. Aust Paediatr J. 1971;7:20–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources