Atrial fibrillation incidence and risk factors in relation to race-ethnicity and the population attributable fraction of atrial fibrillation risk factors: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
Atrial fibrillation incidence and risk factors in relation to race-ethnicity and the population attributable fraction of atrial fibrillation risk factors: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Carlos J Rodriguez et al. Ann Epidemiol. 2015 Feb.
Abstract
Purpose: We studied incident atrial fibrillation (AF) in the prospective community-based Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Reportedly, non-Hispanic blacks (NHBs) have a lower AF burden compared with their non-Hispanic white (NHW) counterparts. Information on the epidemiology of AF in Hispanic and Asian populations is much more limited.
Methods: We excluded participants with a history of AF at enrollment. A total of 6721 MESA participants were monitored for the first AF event ascertained according to hospital discharge International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, codes. Age- and sex-adjusted incidence rates (IRs) of AF were calculated per 1000 person-years of observation. IR ratios were calculated using NHWs as the reference group. Age- and sex-adjusted population attributable fractions (PAFs) of established modifiable AF risk factors were ascertained.
Results: In the MESA cohort, 47.2% was male; at baseline, 25.7% had hypertension; 12.5% had diabetes. Three hundred five incident hospitalized AF events occurred over a mean follow-up of 7.3 years. Age- and sex-adjusted IRs and IR ratios showed that overall AF incidence was significantly lower among Hispanics, NHBs and Chinese compared with NHWs (all P < .001). Among participants 65 years of age or greater, Hispanics, Chinese, and blacks had significantly lower AF incidence than NHWs (all P ≤ .01), but IRs were similar among participants under age 65 years. The PAF for smoking was 27% among NHBs but lower among other race-ethnic groups. Among NHWs, the PAF for hypertension was 22.2%, but this was higher among NHBs (33.1%), Chinese (46.3%), and Hispanics (43.9%).
Conclusions: Overall, the incidence of hospitalized AF was significantly lower in Hispanics, NHBs, and Chinese than in NHWs. A larger proportion of AF events appear to be attributable to hypertension among nonwhite populations compared with NHWs.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Chinese; Hispanics; epidemiology.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Fig. 1
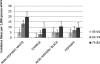
Age-specific unadjusted AF IRs per 1,000 person-years. IRs of AF for each race–ethnic group according to increasing age categories.
Fig. 2
Age- and sex-adjusted AF incidence rate ratios. The incidence rate ratio provides a relative measure of AF IRs using NHWs as the reference groupdshowing that AF incidence is roughly halved among NHBs and Hispanics compared with NHWs; Chinese have about one-third the rate of incident AF events as NHWs.
Similar articles
- Racial and ethnic differences in atrial fibrillation risk factors and predictors in women: Findings from the Women's Health Initiative.
Rodriguez F, Stefanick ML, Greenland P, Soliman EZ, Manson JE, Parikh N, Martin LW, Larson JC, Hlatky M, Nassir R, Cené CW, Rodriguez BL, Albert C, Perez MV. Rodriguez F, et al. Am Heart J. 2016 Jun;176:70-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Am Heart J. 2016. PMID: 27264222 - Differences by Race/Ethnicity in the Prevalence of Clinically Detected and Monitor-Detected Atrial Fibrillation: MESA.
Heckbert SR, Austin TR, Jensen PN, Chen LY, Post WS, Floyd JS, Soliman EZ, Kronmal RA, Psaty BM. Heckbert SR, et al. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2020 Jan;13(1):e007698. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.119.007698. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2020. PMID: 31934795 Free PMC article. - Relative contribution of modifiable risk factors for incident atrial fibrillation in Hispanics, African Americans and non-Hispanic Whites.
Shulman E, Chudow JJ, Essien UR, Shanbhag A, Kargoli F, Romero J, Di Biase L, Fisher J, Krumerman A, Ferrick KJ. Shulman E, et al. Int J Cardiol. 2019 Jan 15;275:89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.10.028. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Int J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30340851 - Racial, ethnic, and sex disparities in atrial fibrillation management: rate and rhythm control.
Gomez SE, Fazal M, Nunes JC, Shah S, Perino AC, Narayan SM, Tamirisa KP, Han JK, Rodriguez F, Baykaner T. Gomez SE, et al. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2023 Aug;66(5):1279-1290. doi: 10.1007/s10840-022-01383-x. Epub 2022 Oct 13. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2023. PMID: 36224481 Free PMC article. Review. - Self-Care Disparities Among Adults with Type 2 Diabetes in the USA.
Mayberry LS, Bergner EM, Chakkalakal RJ, Elasy TA, Osborn CY. Mayberry LS, et al. Curr Diab Rep. 2016 Nov;16(11):113. doi: 10.1007/s11892-016-0796-5. Curr Diab Rep. 2016. PMID: 27671320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA)/Heart Rhythm Society (HRS)/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS)/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS) expert consensus on risk assessment in cardiac arrhythmias: use the right tool for the right outcome, in the right population.
Nielsen JC, Lin YJ, de Oliveira Figueiredo MJ, Sepehri Shamloo A, Alfie A, Boveda S, Dagres N, Di Toro D, Eckhardt LL, Ellenbogen K, Hardy C, Ikeda T, Jaswal A, Kaufman E, Krahn A, Kusano K, Kutyifa V, Lim HS, Lip GYH, Nava-Townsend S, Pak HN, Rodríguez Diez G, Sauer W, Saxena A, Svendsen JH, Vanegas D, Vaseghi M, Wilde A, Bunch TJ; ESC Scientific Document Group; Buxton AE, Calvimontes G, Chao TF, Eckardt L, Estner H, Gillis AM, Isa R, Kautzner J, Maury P, Moss JD, Nam GB, Olshansky B, Pava Molano LF, Pimentel M, Prabhu M, Tzou WS, Sommer P, Swampillai J, Vidal A, Deneke T, Hindricks G, Leclercq C. Nielsen JC, et al. Europace. 2020 Aug 1;22(8):1147-1148. doi: 10.1093/europace/euaa065. Europace. 2020. PMID: 32538434 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - A nomogram for individualized prediction of new-onset postoperative atrial fibrillation in acute type A aortic dissection patients: a retrospective study.
Yang Z, Liu C, Fu C, Zhao X. Yang Z, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Aug 21;11:1429680. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1429680. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39234610 Free PMC article. - Unveiling the Role of Endothelial Dysfunction: A Possible Key to Enhancing Catheter Ablation Success in Atrial Fibrillation.
Zakynthinos GE, Tsolaki V, Oikonomou E, Pantelidis P, Gialamas I, Kalogeras K, Zakynthinos E, Vavuranakis M, Siasos G. Zakynthinos GE, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 15;25(4):2317. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042317. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396990 Free PMC article. Review. - Incidence and Risk Factors for Atrial Fibrillation in Korea: the National Health Insurance Service Database (2002-2010).
Son MK, Lim NK, Cho MC, Park HY. Son MK, et al. Korean Circ J. 2016 Jul;46(4):515-21. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2016.46.4.515. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Korean Circ J. 2016. PMID: 27482260 Free PMC article. - Sex and racial differences in cardiovascular disease risk in patients with atrial fibrillation.
O'Neal WT, Alam AB, Sandesara PB, Claxton JS, MacLehose RF, Chen LY, Bengtson LGS, Chamberlain AM, Norby FL, Lutsey PL, Alonso A. O'Neal WT, et al. PLoS One. 2019 Sep 4;14(9):e0222147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222147. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31483839 Free PMC article.
References
- Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, et al. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 2001;285:2370–5. - PubMed
- Psaty BM, Manolio TA, Kuller LH, Kronmal RA, Cushman M, Fried LP, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for atrial fibrillation in older adults. Circulation. 1997;96:2455–61. - PubMed
- Ruo B, Capra AM, Jensvold NG, Go AS. Racial variation in the prevalence of atrial fibrillation among patients with heart failure: the Epidemiology, Practice, Outcomes, and Costs of Heart Failure (EPOCH) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:429–35. - PubMed
- Sacco RL, Kargman DE, Zamanillo MC. Race-ethnic differences in stroke risk factors among hospitalized patients with cerebral infarction: the Northern Manhattan Stroke Study. Neurology. 1995;45:659–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL104199/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical