Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (PHPT1) also dephosphorylates phospholysine of chemically phosphorylated histone H1 and polylysine - PubMed (original) (raw)
Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (PHPT1) also dephosphorylates phospholysine of chemically phosphorylated histone H1 and polylysine
Pia Ek et al. Ups J Med Sci. 2015 Mar.
Abstract
Background: Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (PHPT1), also named protein histidine phosphatase (PHP), is a eukaryotic enzyme dephosphorylating proteins and peptides that are phosphorylated on a histidine residue. A preliminary finding that histone H1, which lacks histidine, was phosphorylated by phosphoramidate and dephosphorylated by PHPT1 prompted the present investigation.
Methods: Histone H1 and polylysine were phosphorylated at a low concentration (3.9 mM) of phosphoramidate. Their dephosphorylation by recombinant human PHPT1 was investigated by using a DEAE-Sepharose spin column technique earlier developed by us for studies on basic phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides. Determination of protein-bound, acid-labile phosphate was performed by a malachite green method. Mass spectrometry (MS) was used to investigate the occurrence of N-ε-phospholysine residues in a phosphorylated histone H1.2 preparation, and to measure the activity of PHPT1 against free N-ω-phosphoarginine.
Results: Histone H1.2, which lacks histidine, was phosphorylated by phosphoramidate on several lysine residues, as shown by MS. PHPT1 was shown to dephosphorylate phosphohistone H1 at a rate similar to that previously described for the dephosphorylation of phosphohistidine-containing peptides. In addition, phosphopolylysine was an equally good substrate for PHPT1. However, no dephosphorylation of free phosphoarginine by PHPT1 could be detected.
Conclusion: The finding that PHPT1 can dephosphorylate phospholysine in chemically phosphorylated histone H1 and polylysine demonstrates a broader specificity for this enzyme than known so far.
Keywords: Histone H1; PHP; PHPT1; phosphohistidine phosphatase; phospholysine; phospholysine phosphatase; protein histidine phosphatase.
Figures
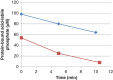
Figure 1.
Decrease in phosphate in phosphoramidate phosphorylated histone H1 (▪) and 30 kDa polylysine (⧫) during incubation with PHPT1. The concentration was 1 mg/mL of phosphohistone and 2 mg/mL of phosphopolylysine. An amount of 5 pmol PHPT1 was added per 51 µL incubation volume. The reaction was performed at pH 7.5 and 30°C during indicated times and was interrupted by centrifugation of 50 µL of the reaction mixture through a spin column containing 200 µL of DEAE-Sepharose equilibrated in 25 mM Tris/HCl pH 8.5. The protein-bound, acid-labile phosphate in the final eluate was analyzed as described under Methods. Each time point was analyzed in duplicate.
Figure 2.
Amino acid sequence and phosphorylated sites of bovine histone H1.2 as determined by mass spectrometry. Lysine residues are marked red, and those identified as targets for the phosphorylation by phosphoramidate (i.e. seven residues) are highlighted. Out of the 305 peptides that were used to identify the protein, 14 peptides were reported to contain phospholysine.
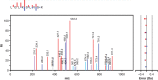
Figure 3.
MS/MS spectrum showing the fragmentation pattern of one of the peptides obtained after trypsin treatment of histone H1 from SignalChem. The y-ion series is shown in red, and the b-ions series is in blue. Also shown is y- and b-ions fitting with the loss of 18 Da in violet and turquoise, respectively. Other observed but unspecified mached ions are grey. The small inset at the top shows only the y- and b-ions, with the length of the staples representing the intensity of the ions.
Similar articles
- Chemical phosphorylation of histidine-containing peptides based on the sequence of histone H4 and their dephosphorylation by protein histidine phosphatase.
Attwood PV, Ludwig K, Bergander K, Besant PG, Adina-Zada A, Krieglstein J, Klumpp S. Attwood PV, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Jan;1804(1):199-205. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.10.007. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19836471 - Two phosphatases for 6-phospholysine and 3-phosphohistidine from rat brain.
Ohmori H, Kuba M, Kumon A. Ohmori H, et al. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7625-7. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8385112 - A screening method for phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 activity.
Beckman-Sundh U, Ek B, Zetterqvist O, Ek P. Beckman-Sundh U, et al. Ups J Med Sci. 2011 Aug;116(3):161-8. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2011.585253. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Ups J Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21679093 Free PMC article. - Focus on phosphoarginine and phospholysine.
Besant PG, Attwood PV, Piggott MJ. Besant PG, et al. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009 Dec;10(6):536-50. doi: 10.2174/138920309789630598. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009. PMID: 19751195 Review. - P-N bond protein phosphatases.
Attwood PV. Attwood PV. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1834(1):470-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22450136 Review.
Cited by
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC): Chromogenic Detection of 3-Phosphohistidine Proteins in Formaldehyde-Fixed, Frozen Mouse Liver Tissue Sections.
Luhtala N, Hunter T. Luhtala N, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2077:193-208. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9884-5_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31707660 Free PMC article. - The actions of NME1/NDPK-A and NME2/NDPK-B as protein kinases.
Attwood PV, Muimo R. Attwood PV, et al. Lab Invest. 2018 Mar;98(3):283-290. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2017.125. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Lab Invest. 2018. PMID: 29200201 Review. - Microcystin Levels in Selected Cyanobacteria Exposed to Varying Salinity.
Walker D, Fathabad SG, Tabatabai B, Jafar S, Sitther V. Walker D, et al. J Water Resour Prot. 2019 Apr;11(4):395-403. doi: 10.4236/jwarp.2019.114023. J Water Resour Prot. 2019. PMID: 32042367 Free PMC article. - Strong anion exchange-mediated phosphoproteomics reveals extensive human non-canonical phosphorylation.
Hardman G, Perkins S, Brownridge PJ, Clarke CJ, Byrne DP, Campbell AE, Kalyuzhnyy A, Myall A, Eyers PA, Jones AR, Eyers CE. Hardman G, et al. EMBO J. 2019 Oct 4;38(21):e100847. doi: 10.15252/embj.2018100847. Epub 2019 Aug 21. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 31433507 Free PMC article. - Derivatives of the Fungal Natural Product Illudalic Acid Inhibit the Activity of Protein Histidine Phosphatase PHPT1.
Wang H, Gaston R Jr, Ahmed KT, Dudley GB, Barrios AM. Wang H, et al. ChemMedChem. 2023 Aug 1;18(15):e202300187. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202300187. Epub 2023 Jun 16. ChemMedChem. 2023. PMID: 37267298 Free PMC article.
References
- Boyer PD, DeLuca M, Ebner KE, Hultquist DE, Peter JB. Identification of phosphohistidine in digests from a probable intermediate of oxidative phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:PC3306–8. - PubMed
- Kee JM, Muir TW. Chasing phosphohistidine, an elusive sibling in the phosphoamino acid fa... . ACS Chem Biol. 2012;7:44–51. - PMC - PubMed
- Västermark Å, Saier MH., Jr The involvement of transport proteins in transcriptional and metabolic r... . Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014;18:8–15. - PMC - PubMed
- Podgornaia AI, Laub MT. Determinants of specificity in two-component signal transduction . Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013;16:156–62. - PubMed
- Matthews HR. Protein kinases and phosphatases that act on histidine, lysine, or argin... . Pharmac Ther. 1995;67:323–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous