A comparison of the predictive accuracy of three screening models for pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0517-5.
Vivek Thakkar 3 4 5, Wendy Stevens 6, Kathleen Morrisroe 7, David Prior 8, Candice Rabusa 9, Peter Youssef 10, Eli Gabbay 11, Janet Roddy 12, Jennifer Walker 13, Jane Zochling 14, Joanne Sahhar 15, Peter Nash 16, Susan Lester 17, Maureen Rischmueller 18 19, Susanna M Proudman 20 21, Mandana Nikpour 22 23
Affiliations
- PMID: 25596924
- PMCID: PMC4332896
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0517-5
Comparative Study
A comparison of the predictive accuracy of three screening models for pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis
Yanjie Hao et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015.
Abstract
Introduction: There is evidence that early screening for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in systemic sclerosis (SSc) improves outcomes. We compared the predictive accuracy of two recently published screening algorithms (DETECT 2013 and Australian Scleroderma Interest Group (ASIG) 2012) for SSc-associated PAH (SSc-PAH) with the commonly used European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society (ESC/ERS 2009) guidelines.
Methods: We included 73 consecutive SSc patients with suspected PAH undergoing right heart catheterization (RHC). The three screening models were applied to each patient. For each model, contingency table analysis was used to determine sensitivity, specificity, and positive (PPV) and negative (NPV) predictive values for PAH. These properties were also evaluated in an 'alternate scenario analysis' in which the prevalence of PAH was set at 10%.
Results: RHC revealed PAH in 27 (36.9%) patients. DETECT and ASIG algorithms performed equally in predicting PAH with sensitivity and NPV of 100%. The ESC/ERS guidelines had sensitivity of 96.3% and NPV of only 91%, missing one case of PAH; these guidelines could not be applied to three patients who had absent tricuspid regurgitant (TR) jet. The ASIG algorithm had the highest specificity (54.5%). With PAH prevalence set at 10%, the NPV of the models was unchanged, but the PPV dropped to less than 20%.
Conclusions: In this cohort, the DETECT and ASIG algorithms out-perform the ESC/ERS guidelines, detecting all patients with PAH. The ESC/ERS guidelines have limitations in the absence of a TR jet. Ultimately, the choice of SSc-PAH screening algorithm will also depend on cost and ease of application.
Figures
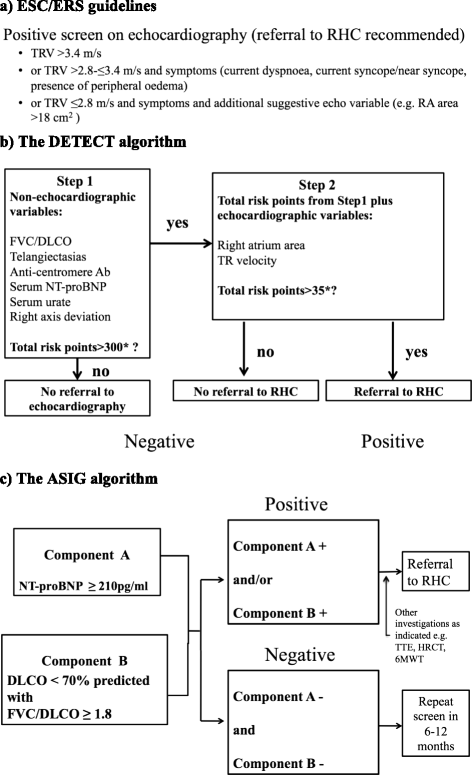
Figure 1
Summary of screening algorithms. Ab, antibody; ASIG, Australian Scleroderma Interest Group; DLCO, diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide; ESC/ERS, European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society; FVC, forced vital capacity (percentage predicted); HRCT, high-resolution computed tomography (chest); PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension; PH, pulmonary hypertension; RA, right atrium; RHC, right heart catheterization; SSc, systemic sclerosis; TR, tricuspid regurgitation; TRV, tricuspid regurgitant velocity; TTE, transthoracic echocardiography; WHO, World Health Organization.
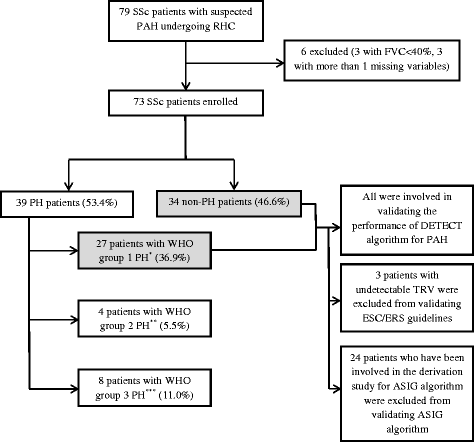
Figure 2
Study cohort. *World Health Organization (WHO) group 1 pulmonary hypertension (PH) means pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). **WHO group 2 PH means left heart disease-associated PH. This group was excluded for validating the performance of all models for PAH but included in validating the performance for PH. ***WHO group 3 PH means lung disease/hypoxia-associated PH. This group was excluded for validating the performance of all models for PAH but included in validating the performance for precapillary PH and PH. ASIG, Australian Scleroderma Interest Group; ESC/ERS, European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society; FVC, forced vital capacity (percentage predicted); RHC, right heart catheterization; SSc, systemic sclerosis; TRV, tricuspid regurgitant velocity.
Similar articles
- Screening for pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with systemic sclerosis in the era of new pulmonary arterial hypertension definitions.
Erdogan M, Kilickiran Avci B, Ebren C, Ersoy Y, Ongen Z, Ongen G, Hamuryudan V, Hatemi G. Erdogan M, et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2024 Aug;42(8):1590-1597. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/gzo4r2. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38489342 - Application of the DETECT algorithm for detection of risk of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: data from a Czech tertiary centre.
Soukup T, Pudil R, Kubinova K, Hromadkova L, Dusek J, Tosovsky M, Bradna P, Hrncir Z, Bures J. Soukup T, et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016 Jan;55(1):109-14. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev327. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016. PMID: 26320140 - The inclusion of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in a sensitive screening strategy for systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary arterial hypertension: a cohort study.
Thakkar V, Stevens W, Prior D, Youssef P, Liew D, Gabbay E, Roddy J, Walker JG, Zochling J, Sahhar J, Nash P, Lester S, Rischmueller M, Proudman SM, Nikpour M. Thakkar V, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R193. doi: 10.1186/ar4383. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24246100 Free PMC article. - Performance of screening algorithms in systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary arterial hypertension: a systematic review.
Thakkar V, Stevens WM, Moore OA, Nikpour M. Thakkar V, et al. Intern Med J. 2013 Jul;43(7):751-60. doi: 10.1111/imj.12167. Intern Med J. 2013. PMID: 23611651 Review. - Screening for pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: A systematic literature review.
Bruni C, De Luca G, Lazzaroni MG, Zanatta E, Lepri G, Airò P, Dagna L, Doria A, Matucci-Cerinic M. Bruni C, et al. Eur J Intern Med. 2020 Aug;78:17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.042. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Eur J Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32540411 Review.
Cited by
- Towards a Better Prognosis in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis-Related Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Recent Developments and Perspectives.
Boutel M, Dara A, Arvanitaki A, Deuteraiou C, Mytilinaiou M, Dimitroulas T. Boutel M, et al. J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 30;13(19):5834. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195834. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39407897 Free PMC article. Review. - Attitudes and barriers to pulmonary arterial hypertension screening in systemic sclerosis patients: A survey of UK-based rheumatologists.
Álvarez-Hernández MP, Allanore Y, Andrade I, Buch MH, Coghlan G, Del Galdo F, Denton CP, Khanna D, Kiely DG, Pauling JD, Ramjug S, Hughes M. Álvarez-Hernández MP, et al. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2024 Jun;9(2):99-109. doi: 10.1177/23971983241235708. Epub 2024 Mar 13. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2024. PMID: 38910595 - Use of exercise tests in screening for pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: A systematic literature review.
Madigan S, Proudman S, Schembri D, Davies H, Adams R. Madigan S, et al. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2024 Feb;9(1):50-58. doi: 10.1177/23971983231199148. Epub 2023 Oct 2. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2024. PMID: 38333530 Free PMC article. - Connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary hypertension: A comprehensive review.
Khangoora V, Bernstein EJ, King CS, Shlobin OA. Khangoora V, et al. Pulm Circ. 2023 Dec 11;13(4):e12276. doi: 10.1002/pul2.12276. eCollection 2023 Oct. Pulm Circ. 2023. PMID: 38088955 Free PMC article. Review. - 2023 Taiwan Society of Cardiology (TSOC) and Taiwan College of Rheumatology (TCR) Joint Consensus on Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.
Huang WC, Hsieh SC, Wu YW, Hsieh TY, Wu YJ, Li KJ, Charng MJ, Chen WS, Sung SH, Tsao YP, Ho WJ, Lai CC, Cheng CC, Tsai HC, Hsu CH, Lu CH, Chiu YW, Shen CY, Wu CH, Liu FC, Lin YH, Yeh FC, Liu WS, Lee HT, Wu SH, Chang CC, Chu CY, Hou CJ, Tsai CY. Huang WC, et al. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2023 Mar;39(2):213-241. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202303_39(2).20230117A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2023. PMID: 36911549 Free PMC article.
References
- Galiè N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur Heart J. 2009;30:2493–537. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp297. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical