The interaction between epigenetics, nutrition and the development of cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The interaction between epigenetics, nutrition and the development of cancer
Karen S Bishop et al. Nutrients. 2015.
Abstract
Unlike the genome, the epigenome can be modified and hence some epigenetic risk markers have the potential to be reversed. Such modifications take place by means of drugs, diet or environmental exposures. It is widely accepted that epigenetic modifications take place during early embryonic and primordial cell development, but it is also important that we gain an understanding of the potential for such changes later in life. These "later life" epigenetic modifications in response to dietary intervention are the focus of this paper. The epigenetic modifications investigated include DNA methylation, histone modifications and the influence of microRNAs. The epigenotype could be used not only to predict susceptibility to certain cancers but also to assess the effectiveness of dietary modifications to reduce such risk. The influence of diet or dietary components on epigenetic modifications and the impact on cancer initiation or progression has been assessed herein.
Figures
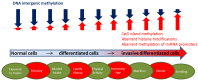
Figure 1
A diagrammatic representation of the extent and type of epigenetic modifications that promote cancer risk and/or progression, and the modifiable (in green ovals) and non-modifiable (in red ovals) factors that may influence these epigenetic modifications.
References
- Burger G.C.E., Sandstead H.R., Drummond J. Starvation in Western Holland: 1945. Lancet. 1945;246:282–283. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(45)90738-0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources