A systematic review of the management of acute pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
A systematic review of the management of acute pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis
A M Giladi et al. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2015 Sep.
Abstract
Pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis (PFT) is an aggressive closed-space infection that can result in severe morbidity. Although surgical treatment of pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis has been widely described, the role of antibiotic therapy is inadequately understood. We conducted a literature review of studies reporting on acute pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis management. A total of 28 case series articles were obtained, all of which used surgical intervention with varied use of antibiotics. Inconsistencies among the studies limited summative statistical analysis. Our results showed that use of antibiotics as a component of therapy resulted in improved range of motion outcomes (54% excellent vs. 14% excellent), as did using catheter irrigation rather than open washout (71% excellent vs. 26% excellent). These studies showed benefits of early treatment of pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis and of systemic antibiotic use. As broad-spectrum antibiotics have changed the management of other infectious conditions, we must more closely evaluate consistent antibiotic use in pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis management.
Level of evidence: Therapeutic, Level III.
Keywords: Acute flexor tenosynovitis; antibiotic usage; bacterial; pyogenic; surgical drainage; treatment.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Figures
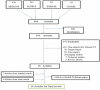
Figure 1
Flow chart of database search for treatment of acute flexor tenosynovitis
Similar articles
- Comparison of Open Drainage Versus Closed Catheter Irrigation for Treatment of Suppurative Flexor Tenosynovitis.
Born TR, Wagner ER, Kakar S. Born TR, et al. Hand (N Y). 2017 Nov;12(6):579-584. doi: 10.1177/1558944716675131. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Hand (N Y). 2017. PMID: 29091483 Free PMC article. - Treatment of digital pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis: single open debridement, irrigation, and primary wound closure followed by antibiotic therapy.
Hohendorff B, Sauer H, Biber F, Franke J, Spies CK, Müller LP, Ries C. Hohendorff B, et al. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017 Jan;137(1):141-145. doi: 10.1007/s00402-016-2587-5. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017. PMID: 27787635 - Pyogenic Flexor Tenosynovitis: Evaluation and Management.
Goyal K, Speeckaert AL. Goyal K, et al. Hand Clin. 2020 Aug;36(3):323-329. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2020.03.005. Hand Clin. 2020. PMID: 32586458 Review. - Corticosteroids as an adjunct to antibiotics and surgical drainage for the treatment of pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis.
Draeger RW, Singh B, Bynum DK, Dahners LE. Draeger RW, et al. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010 Nov 17;92(16):2653-62. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.I.01205. Epub 2010 Oct 15. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010. PMID: 20952605 - Closed Continuous Irrigation With Lidocaine and Immediate Mobilization for Treatment of Pyogenic Tenosynovitis.
Knackstedt R, Tyler J, Bernard S. Knackstedt R, et al. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2017 Sep;21(3):114-115. doi: 10.1097/BTH.0000000000000164. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2017. PMID: 28727585 Review.
Cited by
- Local cefuroxime tissue concentrations in the hand after single and repeated administration to 16 patients undergoing trapeziectomy: a randomized controlled trial.
Jørgensen AR, Hanberg P, Bue M, Hartig-Andreasen C, Jørgensen NP, Stilling M. Jørgensen AR, et al. Acta Orthop. 2024 Sep 6;95:498-504. doi: 10.2340/17453674.2024.41343. Acta Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39240016 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Infectious Extensor Tenosynovitis of the Hallucis Longus Tendon: A Case Report.
St Clair JW, Bragg K, Mattingly JL, Collado J, Beel BC, Siddiqui AA, James CL. St Clair JW, et al. Cureus. 2024 May 15;16(5):e60384. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60384. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38883076 Free PMC article. - Delayed debridement affects prognosis in patients with purulent flexor tenosynovitis: a retrospective cohort and multivariate analyses.
Fujihara Y, Sakai A, Niwa S, Ota H, Kumagai H. Fujihara Y, et al. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 May;144(5):2437-2441. doi: 10.1007/s00402-024-05269-7. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 38492063 - Tenosynovitis of hand: Causes and complications.
Muthu S, Annamalai S, Kandasamy V. Muthu S, et al. World J Clin Cases. 2024 Feb 6;12(4):671-676. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i4.671. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38322687 Free PMC article. - A neonate with multiple hand flexor tendon ruptures due to methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus sepsis: a case report.
Nakamuara T, Iwai M, Inoue T, Irie H, Karasugi T, Seki A, Hamaguchi M, Kuraoka S, Mizukami T, Nakamura K. Nakamuara T, et al. BMC Pediatr. 2023 Feb 9;23(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-03871-z. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36759790 Free PMC article.
References
- Bauman JT, Millon SJ, Tanner SL. The outpatient treatment of pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2005;14:92–5. - PubMed
- Boles SD, Schmidt CC. Pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis. Hand Clin. 1998;14:567–78. - PubMed
- Clark DC. Common acute hand infections. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68:2167–76. - PubMed
- Clarkson PPA. General and Plastic Surgery of the hand. Blackwell scientific publication; Oxford: 1963.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials