Treatment with IL-10 producing B cells in combination with E2 ameliorates EAE severity and decreases CNS inflammation in B cell-deficient mice - PubMed (original) (raw)
Treatment with IL-10 producing B cells in combination with E2 ameliorates EAE severity and decreases CNS inflammation in B cell-deficient mice
Jun Zhang et al. Metab Brain Dis. 2015 Oct.
Abstract
Clinical improvement during pregnancy in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients suggests that sex hormones exert potent regulatory effects on autoimmune function. Our previous studies demonstrated that estrogen- (17β-estradiol; E2) mediated protection against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a mouse model for MS, hinges on the B cells, leading to elevated numbers of IL-10 secreting CD1d(hi)CD5(+) B regulatory cells (Bregs) in wild type mice. Our data show that co-administration of E2 and IL-10(+) B cells ameliorates EAE disease severity and limits CNS infiltrating leukocytes in B cell deficient mice. Additionally, treatment with E2 and Bregs reduces demyelination and dramatically decreases the proportion of CD11b(+)CD45(hi) activated microglia/macrophages found in the CNS of immunized animals compared to vehicle, E2 or Breg cells alone. Furthermore, mice given E2 and Bregs exhibit increased numbers of peripheral programmed death-1 positive CD4(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs) and up-regulation of programmed death receptor-ligand-1 and CD80 expression on monocytes. Our study suggests IL-10 producing Bregs have powerful therapeutic potential as an agent against EAE when augmented with E2 treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
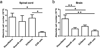
Fig. 1. IL-10 producing B cells and E2 ameliorate EAE and decrease spinal cord inflammation in µMT−/− mice
Spinal cords from each group were collected 24 days post-immunization, fixed in PFA, and embedded in paraffin for sectioning. Ten µm transverse sections from different regions of the spinal cord from each of the groups were stained with Hematoxylin & Eosin to enumerate infiltrating leukocytes (Fig. 1a) and with Luxol Fast Blue to visualize extent of demyelination (Fig. 1b). Arrows denote foci of inflammation. Magnification was 50× and 200× (inset). Sections are representative of 2 experiments (n = 3 mice/group/experiment).
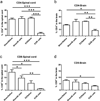
Fig. 2. IL-10 producing B cells and E2 treatment reduce infiltration of leukocytes into the CNS of µMT−/− mice
Mononuclear cells were isolated from CNS tissues and total live cell numbers from spinal cords (Fig. 2a) and brains (Fig. 2b) were counted on a hemocytometer. Data shown are representative of 4 independent experiments consisting of 6 mice per group (mean ± SEM). Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA followed by Newman-Kuels post hoc test. Significant differences between sample means are indicated (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001)
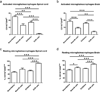
Fig. 3. Administration of IL-10 producing B cells in combination with E2 treatment decreased activation of microglia/macrophages in the CNS
CD11b+CD45hi activated microglia/macrophages (Fig. 3a, 3b) and CD11b+CD45low resting microglia/macrophages (Fig. 3c, 3d) were determined in individual spinal cords and brains. Data shown are representative of 4 independent experiments consisting of 6 mice per group (mean ± SEM). Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA followed by Newman-Kuels post hoc test. Significant differences between sample means are indicated (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001)
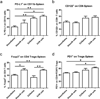
Fig. 4. Lower infiltration of proinflammatory immune cells in the CNS with IL-10 producing B cells plus E2 treatment
Frequencies of CD4+ (Fig. 4a, 4b) and CD8+ T cells (Fig. 4c, 4d) were determined in individual spinal cords and brains and indicate the percentages of total gated live leukocytes (n=6). Data are representative of 4 independent experiments consisting of 6 mice per group (mean ± SEM). Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA followed by Newman-Kuels post hoc test. Significant differences between sample means are indicated (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001)
Fig. 5. Activation and pro-inflammatory state of CD11b+ monocytes
Expression of the monocyte activation markers I-Ab (Fig. 5a) and CD80 (Fig. 5b) were determined on CD11b+ splenocytes from the various treatment groups. Fig. 5c: TNF-α producing CD11b+ monocytes. Data are representative of 4 independent experiments consisting of 6 mice per group (mean ± SEM). Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA followed by Newman-Kuels post hoc test. Significant differences between sample means are indicated (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001)
Fig. 6. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway molecules are up-regulated in µMT−/− mice that receive IL-10 producing B cells and E2
PD-L1 expression was assessed on splenic CD11b+ monocytes (Fig. 6a); CD122, on splenic CD8+ T cells (Fig. 6b); Foxp3, on splenic CD4+ T cells (Fig. 6c) and PD-1, on splenic CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Fig. 6d). Data are representative from 4 independent experiments consisting of 6 mice per group (mean ± SEM). Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA followed by Newman-Kuels post hoc test. Significant differences between sample means are indicated (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001)
Similar articles
- IL-10 producing B cells partially restore E2-mediated protection against EAE in PD-L1 deficient mice.
Zhang J, Benedek G, Bodhankar S, Lapato A, Vandenbark AA, Offner H. Zhang J, et al. J Neuroimmunol. 2015 Aug 15;285:129-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jun 11. J Neuroimmunol. 2015. PMID: 26198929 Free PMC article. - Estrogen-induced protection against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is abrogated in the absence of B cells.
Bodhankar S, Wang C, Vandenbark AA, Offner H. Bodhankar S, et al. Eur J Immunol. 2011 Apr;41(4):1165-75. doi: 10.1002/eji.201040992. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21413005 Free PMC article. - B cell regulation of CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells and IL-10 via B7 is essential for recovery from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Mann MK, Maresz K, Shriver LP, Tan Y, Dittel BN. Mann MK, et al. J Immunol. 2007 Mar 15;178(6):3447-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.6.3447. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17339439 - A potential role for estrogen in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis.
Offner H, Polanczyk M. Offner H, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Nov;1089:343-72. doi: 10.1196/annals.1386.021. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17261780 Review.
Cited by
- IRAK-M suppresses the activation of microglial NLRP3 inflammasome and GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis through inhibiting IRAK1 phosphorylation during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Wang Y, Pei S, Liu Z, Ding Y, Qian T, Wen H, Hsu SW, Zhou Z, Zhang J, Wang H. Wang Y, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2023 Feb 10;14(2):103. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05621-6. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36765034 Free PMC article. - PD-L1 is required for estrogen-induced protection against severe EAE in IL-10 deficient mice1.
Offner H, Lockwood D, Meza-Romero R, Vandenbark AA. Offner H, et al. Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Feb;38(2):589-599. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-01129-8. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 36454506 Free PMC article. - Toll-Like Receptor Signaling and Immune Regulatory Lymphocytes in Periodontal Disease.
Gu Y, Han X. Gu Y, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 8;21(9):3329. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093329. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32397173 Free PMC article. Review. - Protective effects of Vitex agnus-castus in ovariectomy mice following permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Alimohamadi R, Fatemi I, Naderi S, Hakimizadeh E, Rahmani MR, Allahtavakoli M. Alimohamadi R, et al. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Sep;22(9):1097-1101. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.31692.7625. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31807255 Free PMC article. - Estrogen-induced compensatory mechanisms protect IL-10-deficient mice from developing EAE.
Seifert HA, Gerstner G, Kent G, Vandenbark AA, Offner H. Seifert HA, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Oct 29;16(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1588-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31665042 Free PMC article.
References
- Abramsky O. Pregnancy and multiple sclerosis. Annals of neurology. 1994;36(Suppl):S38–S41. - PubMed
- Becher B, Antel JP. Comparison of phenotypic and functional properties of immediately ex vivo and cultured human adult microglia. Glia. 1996;18:1–10. - PubMed
- Blair PA, Norena LY, Flores-Borja F, Rawlings DJ, Isenberg DA, Ehrenstein MR, Mauri C. CD19(+)CD24(hi)CD38(hi) B cells exhibit regulatory capacity in healthy individuals but are functionally impaired in systemic Lupus. Erythematosus patients Immunity. 2010;32:129–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous