Black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its constituent (thymoquinone): a review on antimicrobial effects - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2014 Dec;17(12):929-38.
Affiliations
- PMID: 25859296
- PMCID: PMC4387228
Review
Black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its constituent (thymoquinone): a review on antimicrobial effects
Fatemeh Forouzanfar et al. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014 Dec.
Abstract
Nigella sativa seeds have wide therapeutic effects and have been reported to have significant effects against many ailments such as skin diseases, jaundice, gastrointestinal problems, anorexia, conjunctivitis, dyspepsia, rheumatism, diabetes, hypertension, intrinsic hemorrhage, paralysis, amenorrhea, anorexia, asthma, cough, bronchitis, headache, fever, influenza and eczema. Thymoquinone (TQ) is one of the most active constituent and has different beneficial properties. Focus on antimicrobial effects, different extracts of N. sativa as well as TQ, have a broad antimicrobial spectrum including Gram-negative, Gram-positive bacteria, viruses, parasites, schistosoma and fungi. The effectiveness of N. sativa seeds and TQ is variable and depends on species of target microorganisms. The present review paper tries to describe all antimicrobial activities that have been carried out by various researchers.
Keywords: Antifungal; Antimicrobial; Antiparasite; Antischistosoma; Antivirus; Nigella sativa; Thymoquinone Antibacterial.
Figures
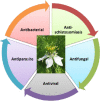
Figure 1
Different effects of Nigella sativa against microorganisms
Similar articles
- A glance at black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent, thymoquinone, in ischemia: a review.
Oskouei Z, Akaberi M, Hosseinzadeh H. Oskouei Z, et al. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Dec;21(12):1200-1209. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.31703.7630. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30627362 Free PMC article. Review. - Review on Clinical Trials of Black Seed (Nigella sativa ) and Its Active Constituent, Thymoquinone.
Tavakkoli A, Mahdian V, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H. Tavakkoli A, et al. J Pharmacopuncture. 2017 Sep;20(3):179-193. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2017.20.021. Epub 2017 Sep 30. J Pharmacopuncture. 2017. PMID: 30087794 Free PMC article. Review. - Gastrointestinal effects of Nigella sativa and its main constituent, thymoquinone: a review.
Shakeri F, Gholamnezhad Z, Mégarbane B, Rezaee R, Boskabady MH. Shakeri F, et al. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2016 Jan-Feb;6(1):9-20. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2016. PMID: 27247918 Free PMC article. Review. - Black Cumin (Nigella sativa) and Its Active Constituent, Thymoquinone: An Overview on the Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Effects.
Amin B, Hosseinzadeh H. Amin B, et al. Planta Med. 2016 Jan;82(1-2):8-16. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1557838. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Planta Med. 2016. PMID: 26366755 Review. - A Review on Possible Therapeutic Effect of Nigella sativa and Thymoquinone in Neurodegenerative Diseases.
Samarghandian S, Farkhondeh T, Samini F. Samarghandian S, et al. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2018;17(6):412-420. doi: 10.2174/1871527317666180702101455. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29962349 Review.
Cited by
- Antimicrobial Properties and Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Compounds in Nigella sativa: A Review.
Abbas M, Gururani MA, Ali A, Bajwa S, Hassan R, Batool SW, Imam M, Wei D. Abbas M, et al. Molecules. 2024 Oct 17;29(20):4914. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204914. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459282 Free PMC article. Review. - Inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa oil loaded to liposomal nanocarriers on Candida parapsilosis isolates.
Ghiaee Shamloo A, Zarrinfar H, Jaafari MR, Yadegari MH. Ghiaee Shamloo A, et al. Iran J Microbiol. 2024 Aug;16(4):560-568. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v16i4.16316. Iran J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39267937 Free PMC article. - Integrative network pharmacology, molecular docking, and dynamic simulation analysis of a polyherbal formulation for potential therapeutic impact on prostate cancer.
Vikhar Danish Ahmad A, Ayaz Ali S, Yasar Q, Sakle NS, Mukhtar Khan M. Vikhar Danish Ahmad A, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Jul 11;10(14):e34531. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34531. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39114070 Free PMC article. - The Combination of 3-Hydrazinoquinoxaline-2-Thiol with Thymoquinone Demonstrates Synergistic Activity Against Different Candida Strains.
Bazuhair MA, Alsieni M, Abdullah H, Mokhtar JA, Attallah D, Abujamel TS, Alkuwaity KK, Niyazi HA, Niyazi HA, AbdulMajed H, Juma N, Al-Rabia MW, Alfadil A, Ibrahem K. Bazuhair MA, et al. Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Jun 6;17:2289-2298. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S464287. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38860227 Free PMC article. - Thymoquinone is a natural antibiofilm and pathogenicity attenuating agent in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Al-Rabia MW, Asfour HZ, Alhakamy NA, Abdulaal WH, Ibrahim TS, Abbas HA, Salem IM, Hegazy WAH, Nazeih SI. Al-Rabia MW, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Apr 4;14:1382289. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1382289. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38638827 Free PMC article.
References
- Goreja WG. New York, NY: Amazing Herbs Press; 2003. Black seed: nature's miracle remedy.
- Khan MR. Chemical composition and medicinal properties of Nigella sativa Linn. Inflammo-pharmacology. 1999;7:13–35. - PubMed
- Tembhurne SV, Feroz S, Sakarkar DM. A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa (kalonji) seeds. J Med Plants Res. 2014;8:166–167.
- Staphylakis PK, Gegiou D. The sterols of Nigella sativa seed oil. Phytochemistry. 1986;25:761–763.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources