Multifaceted roles of cysteinyl leukotrienes in eliciting eosinophil granule protein secretion - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Multifaceted roles of cysteinyl leukotrienes in eliciting eosinophil granule protein secretion
Renata Baptista-dos-Reis et al. Biomed Res Int. 2015.
Abstract
Cysteinyl leukotrienes (cysLTs) are cell membrane-impermeant lipid mediators that play major roles in the pathogenesis of eosinophilic inflammation and are recognized to act via at least 2 receptors, namely, cysLT1 receptor (cysLT1R) and cysLT2 receptor (cysLT2R). Eosinophils, which are granulocytes classically associated with host defense against parasitic helminthes and allergic conditions, are distinguished from leukocytes by their dominant population of cytoplasmic crystalloid (also termed secretory, specific, or secondary) granules that contain robust stores of diverse preformed proteins. Human eosinophils are the main source of cysLTs and are recognized to express both cysLTs receptors (cysLTRs) on their surface, at the plasma membrane. More recently, we identified the expression of cysLTRs in eosinophil granule membranes and demonstrated that cysLTs, acting via their granule membrane-expressed receptors, elicit secretion from cell-free human eosinophil granules. Herein, we review the multifaceted roles of cysLTs in eliciting eosinophil granule protein secretion. We discuss the intracrine and autocrine/paracrine secretory responses evoked by cysLTs in eosinophils and in cell-free extracellular eosinophil crystalloid granules. We also discuss the importance of this finding in eosinophil immunobiology and speculate on its potential role(s) in eosinophilic diseases.
Figures
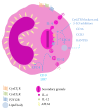
Figure 1
CysLTs are intracrine signals regulating eosinophils' IL-4 secretion by piecemeal degranulation.IL-4 release induced by IL-16, eotaxin, and RANTES is dependent on the intracrine action of lipid body-generated LTC4. Inhibitors of 5-lypoxigenase (5-LO) and/or cysteinyl leukotriene receptors (cysLTRs) blocked intracellular LTC4 production and consequently IL-4 release from eosinophils. The cross-linking of LIR7- or CD9-induced perinuclear-generated LTC4, however IL-12 secretion induced by LIR7 or CD9 is independent of 5-LO metabolites. CysLT1R = cysLT1 receptor; cysLT2R = cysLT2 receptor, P2Y12R = purinergic P2Y12 receptor, and APLM = arachidonyl phospholipids and lipoxygenase machinery.
Figure 2
Stimulating cell-free eosinophil granules with the agonists LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4 elicited the secretion of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) but not eosinophil-derived cytokines or chemokines from the granules. Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor (cysLTR) or P2Y12 receptor (P2Y12R) blockers inhibited ECP secretion after LTC4/LTD4/LTE4 stimulation of cell-free eosinophil granules.
Similar articles
- Cysteinyl Leukotrienes in Eosinophil Biology: Functional Roles and Therapeutic Perspectives in Eosinophilic Disorders.
Thompson-Souza GA, Gropillo I, Neves JS. Thompson-Souza GA, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017 Jul 18;4:106. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2017.00106. eCollection 2017. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28770202 Free PMC article. Review. - Cysteinyl leukotrienes acting via granule membrane-expressed receptors elicit secretion from within cell-free human eosinophil granules.
Neves JS, Radke AL, Weller PF. Neves JS, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Feb;125(2):477-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.029. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20159258 Free PMC article. - Eosinophils and cysteinyl leukotrienes.
Bandeira-Melo C, Weller PF. Bandeira-Melo C, et al. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2003 Aug-Sep;69(2-3):135-43. doi: 10.1016/s0952-3278(03)00074-7. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2003. PMID: 12895596 Review. - Eosinophil crystalloid granules: structure, function, and beyond.
Muniz VS, Weller PF, Neves JS. Muniz VS, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2012 Aug;92(2):281-8. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0212067. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22672875 Free PMC article. Review. - Intracrine cysteinyl leukotriene receptor-mediated signaling of eosinophil vesicular transport-mediated interleukin-4 secretion.
Bandeira-Melo C, Woods LJ, Phoofolo M, Weller PF. Bandeira-Melo C, et al. J Exp Med. 2002 Sep 16;196(6):841-50. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020516. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 12235216 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- 1,4-dihydroxy quininib modulates the secretome of uveal melanoma tumour explants and a marker of oxidative phosphorylation in a metastatic xenograft model.
Slater K, Bosch R, Smith KF, Jahangir CA, Garcia-Mulero S, Rahman A, O'Connell F, Piulats JM, O'Neill V, Horgan N, Coupland SE, O'Sullivan J, Gallagher WM, Villanueva A, Kennedy BN. Slater K, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 9;9:1036322. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1036322. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36698840 Free PMC article. - Effect of TGF-β1 on eosinophils to induce cysteinyl leukotriene E4 production in aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease.
Choi Y, Sim S, Lee DH, Lee HR, Ban GY, Shin YS, Kim YK, Park HS. Choi Y, et al. PLoS One. 2021 Aug 26;16(8):e0256237. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256237. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34437574 Free PMC article. - The clinical profile of benralizumab in the management of severe eosinophilic asthma.
Menzella F, Lusuardi M, Galeone C, Facciolongo N, Zucchi L. Menzella F, et al. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016 Dec;10(6):534-548. doi: 10.1177/1753465816667659. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016. PMID: 27612492 Free PMC article. Review. - Persistent Eosinophilic Inflammation in Adult Asthmatics with High Serum and Urine Levels of Leukotriene E4.
Ban GY, Kim SH, Park HS. Ban GY, et al. J Asthma Allergy. 2021 Oct 12;14:1219-1230. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S325499. eCollection 2021. J Asthma Allergy. 2021. PMID: 34675552 Free PMC article. - Mepolizumab for severe refractory eosinophilic asthma: evidence to date and clinical potential.
Menzella F, Lusuardi M, Galeone C, Taddei S, Facciolongo N, Zucchi L. Menzella F, et al. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2016 Nov;7(6):260-277. doi: 10.1177/2040622316659863. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2016. PMID: 27803792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources