Dietary gut microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, and host metabolic regulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Dietary gut microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, and host metabolic regulation
Mayu Kasubuchi et al. Nutrients. 2015.
Abstract
During feeding, the gut microbiota contributes to the host energy acquisition and metabolic regulation thereby influencing the development of metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as acetate, butyrate, and propionate, which are produced by gut microbial fermentation of dietary fiber, are recognized as essential host energy sources and act as signal transduction molecules via G-protein coupled receptors (FFAR2, FFAR3, OLFR78, GPR109A) and as epigenetic regulators of gene expression by the inhibition of histone deacetylase (HDAC). Recent evidence suggests that dietary fiber and the gut microbial-derived SCFAs exert multiple beneficial effects on the host energy metabolism not only by improving the intestinal environment, but also by directly affecting various host peripheral tissues. In this review, we summarize the roles of gut microbial SCFAs in the host energy regulation and present an overview of the current understanding of its physiological functions.
Figures
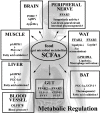
Figure 1
Effects of dietary gut microbial short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) on the regulation of host metabolic functions. SCFAs affect host homeostasis through the stimulation of SCFA receptors, FFAR2, FFAR3, GPR109A and OLFR78.
Similar articles
- The neuropharmacology of butyrate: The bread and butter of the microbiota-gut-brain axis?
Stilling RM, van de Wouw M, Clarke G, Stanton C, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Stilling RM, et al. Neurochem Int. 2016 Oct;99:110-132. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.06.011. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27346602 Review. - Butyrate and propionate protect against diet-induced obesity and regulate gut hormones via free fatty acid receptor 3-independent mechanisms.
Lin HV, Frassetto A, Kowalik EJ Jr, Nawrocki AR, Lu MM, Kosinski JR, Hubert JA, Szeto D, Yao X, Forrest G, Marsh DJ. Lin HV, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035240. Epub 2012 Apr 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22506074 Free PMC article. - Benefits of short-chain fatty acids and their receptors in inflammation and carcinogenesis.
Sivaprakasam S, Prasad PD, Singh N. Sivaprakasam S, et al. Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Aug;164:144-51. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27113407 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of short chain fatty acid producing bacteria on epigenetic regulation of FFAR3 in type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Remely M, Aumueller E, Merold C, Dworzak S, Hippe B, Zanner J, Pointner A, Brath H, Haslberger AG. Remely M, et al. Gene. 2014 Mar 1;537(1):85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.11.081. Epub 2013 Dec 8. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24325907 - [Host energy regulation via SCFAs receptors, as dietary nutrition sensors, by gut microbiota].
Kimura I. Kimura I. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014;134(10):1037-42. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.14-00169. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 25274213 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
- Gut and oral microbiota in gynecological cancers: interaction, mechanism, and therapeutic value.
Wu J, Li J, Yan M, Xiang Z. Wu J, et al. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Oct 10;10(1):104. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00577-7. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 39389989 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of gut microbiota in prostate inflammation and benign prostatic hyperplasia and its therapeutic implications.
Chen J, Chen B, Lin B, Huang Y, Li J, Li J, Chen Z, Wang P, Ran B, Yang J, Huang H, Liu L, Wei Q, Ai J, Cao D. Chen J, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Sep 21;10(19):e38302. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38302. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39386817 Free PMC article. Review. - The interplay between gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and implications for host health and disease.
Hays KE, Pfaffinger JM, Ryznar R. Hays KE, et al. Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2393270. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2393270. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39284033 Free PMC article. Review. - The impact of dysbiosis in oropharyngeal and gut microbiota on systemic inflammatory response and short-term prognosis in acute ischemic stroke with preceding infection.
He Q, Li G, Zhao J, Zhu H, Mo H, Xiong Z, Zhao Z, Chen J, Ning W. He Q, et al. Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 22;15:1432958. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1432958. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39238889 Free PMC article. - The Role of Short Chain Fatty Acids in Inflammation and Body Health.
Du Y, He C, An Y, Huang Y, Zhang H, Fu W, Wang M, Shan Z, Xie J, Yang Y, Zhao B. Du Y, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 5;25(13):7379. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137379. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000498 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources