SAR405, a PIK3C3/Vps34 inhibitor that prevents autophagy and synergizes with MTOR inhibition in tumor cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
SAR405, a PIK3C3/Vps34 inhibitor that prevents autophagy and synergizes with MTOR inhibition in tumor cells
Benoit Pasquier. Autophagy. 2015.
Abstract
Autophagy plays an important role in cancer and it has been suggested that it functions not only as a tumor suppressor pathway to prevent tumor initiation, but also as a prosurvival pathway that helps tumor cells endure metabolic stress and resist death triggered by chemotherapeutic agents. We recently described the discovery of inhibitors of PIK3C3/Vps34 (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, catalytic subunit type 3), the lipid kinase component of the class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PtdIns3K). This PtdIns3K isoform has attracted significant attention in recent years because of its role in autophagy. Following chemical optimization we identified SAR405, a low molecular mass kinase inhibitor of PIK3C3, highly potent and selective with regard to other lipid and protein kinases. We demonstrated that inhibiting the catalytic activity of PIK3C3 disrupts vesicle trafficking from late endosomes to lysosomes. SAR405 treatment also inhibits autophagy induced either by starvation or by MTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) inhibition. Finally our results show that combining SAR405 with everolimus, the FDA-approved MTOR inhibitor, results in a significant synergy on the reduction of cell proliferation using renal tumor cells. This result indicates a potential therapeutic application for PIK3C3 inhibitors in cancer.
Keywords: MTOR; PIK3C3/Vps34; autophagy; renal cell carcinoma; vesicle trafficking.
Figures
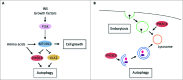
Figure 1.
(A) Signaling pathways that regulate autophagy. In fed conditions, insulin (INS) and/or growth factors, MTOR complex 1 (MTORC1) is activated via a known signaling pathway including class I PI3K and negatively regulates downstream kinases such as PIK3C3 and ULK1 (unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1) leading to a prevention of autophagy. In this condition, MTORC1 is also a key regulator of cell growth. Under starvation, the activity of MTORC1 is suppressed releasing the inhibition of PIK3C3 and ULK1 and allowing the induction of the autophagy machinery. (B) Cellular functions of PIK3C3. The process of autophagy starts with the generation of autophagosomes that then fuse with the lysosome allowing the degradation of the autophagosome contents. Our results using SAR405 demonstrated that PIK3C3 has a dual role during the initial steps of autophagy, with the generation of autophagosomes, and also during endocytosis between late endosomes to lysosomes.
Similar articles
- A highly potent and selective Vps34 inhibitor alters vesicle trafficking and autophagy.
Ronan B, Flamand O, Vescovi L, Dureuil C, Durand L, Fassy F, Bachelot MF, Lamberton A, Mathieu M, Bertrand T, Marquette JP, El-Ahmad Y, Filoche-Romme B, Schio L, Garcia-Echeverria C, Goulaouic H, Pasquier B. Ronan B, et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2014 Dec;10(12):1013-9. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1681. Epub 2014 Oct 19. Nat Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25326666 - Development of in vitro PIK3C3/VPS34 complex protein assay for autophagy-specific inhibitor screening.
Kim TM, Baek JH, Kim JH, Oh MS, Kim J. Kim TM, et al. Anal Biochem. 2015 Jul 1;480:21-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2015.04.004. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Anal Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25862085 - Binding of Avibirnavirus VP3 to the PIK3C3-PDPK1 complex inhibits autophagy by activating the AKT-MTOR pathway.
Zhang Y, Hu B, Li Y, Deng T, Xu Y, Lei J, Zhou J. Zhang Y, et al. Autophagy. 2020 Sep;16(9):1697-1710. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1704118. Epub 2019 Dec 29. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31885313 Free PMC article. - Differential regulatory functions of three classes of phosphatidylinositol and phosphoinositide 3-kinases in autophagy.
Yu X, Long YC, Shen HM. Yu X, et al. Autophagy. 2015;11(10):1711-28. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1043076. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 26018563 Free PMC article. Review. - MTOR, PIK3C3, and autophagy: Signaling the beginning from the end.
Munson MJ, Ganley IG. Munson MJ, et al. Autophagy. 2015;11(12):2375-6. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1106668. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 26565689 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The dual role of autophagy in acute myeloid leukemia.
Seo W, Silwal P, Song IC, Jo EK. Seo W, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2022 May 7;15(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01262-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35526025 Free PMC article. Review. - Modulation of Neuro-Inflammatory Signals in Microglia by Plasma Prekallikrein and Neuronal Cell Debris.
Jaffa AA, Jaffa MA, Moussa M, Ahmed IA, Karam M, Aldeen KS, Al Sayegh R, El-Achkar GA, Nasrallah L, Yehya Y, Habib A, Ziyadeh FN, Eid AH, Kobeissy FH, Jaffa AA. Jaffa AA, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;12:743059. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.743059. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867349 Free PMC article. - Targeting autophagy with SAR405 alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.
Sun X, Du J, Meng H, Liu F, Yang N, Deng S, Wan H, Ye D, Song E, Zeng H. Sun X, et al. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Dec;39(6):3255-3267. doi: 10.1007/s10565-023-09831-8. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37768392 - P5CR1 protein expression and the effect of gene-silencing on lung adenocarcinoma.
She Y, Mao A, Li F, Wei X. She Y, et al. PeerJ. 2019 May 14;7:e6934. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6934. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31143549 Free PMC article. - Autophagy and multidrug resistance in cancer.
Li YJ, Lei YH, Yao N, Wang CR, Hu N, Ye WC, Zhang DM, Chen ZS. Li YJ, et al. Chin J Cancer. 2017 Jun 24;36(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0219-2. Chin J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28646911 Free PMC article. Review.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous