Up-regulation of the Hippo pathway effector TAZ renders lung adenocarcinoma cells harboring EGFR-T790M mutation resistant to gefitinib - PubMed (original) (raw)
Up-regulation of the Hippo pathway effector TAZ renders lung adenocarcinoma cells harboring EGFR-T790M mutation resistant to gefitinib
Wei Xu et al. Cell Biosci. 2015.
Abstract
Background: The T790M mutation of epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a major cause of the acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKIs) treatment for lung cancer patients. The Hippo pathway effector, TAZ, has emerged as a key player in organ growth and tumorigenesis, including lung cancer.
Results: In this study, we have discovered high TAZ expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells harboring dual mutation and TAZ depletion sensitized their response to EGFR-TKIs. Mechanistically, knockdown of TAZ in T790M-induced resistant cells leaded to reduced anchorage-independent growth in vitro, tumor formation and resistance to gefitinib in vivo, correlated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and suppressed migration and invasion. Furthermore, we confirmed CTGF and AXL, novel EMT markers and potential therapeutic targets for overcoming EGFR inhibitor resistance, as directly transcriptional targets of TAZ.
Conclusions: Taken together, this study suggests that expression of TAZ is an intrinsic mechanism of T790M-induced resistance in response to EGFR-TKIs. Combinational targeting on both EGFR and TAZ may enhance the efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in acquired resistance of NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR; EMT; Gefitinib; Lung adenocarcinoma; TAZ.
Figures
Figure 1
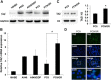
Enhanced expression of TAZ in gefitinib-resistant cell. (A) Lysates derived from human bronchial epithelial cell line 16HBE, lung adenocarcinoma cell lines A549, cisplatin-resistant A549/DDP, gefitinib-sensitive PC9 and gefitinib-resistant PC9/GR were analyzed by western blot using anti-TAZ antibodies. The levels of GAPDH were detected as loading controls. (B) Relative mRNAs of TAZ in lung cancer cell lines were examined by real-time PCR. The endogenous b-actin RNA was used as the internal control. (C) Nuclear fractions in PC9 and PC9/GR cell lines were analyzed by western blot. The levels of histone H3 were detected as loading controls. Densitometric evaluation of TAZ:H3 ratios is illustrated in graph beside. Data are shown as means ± SEM. n=3. Statistical analyses were carried out using Student’s t-test. Significance: * P<0.05. (D) Confocal microscopy of immunofluorescent staining of TAZ in PC9 and PC9/GR cells. Scale bar = 100 mm for original picture and 25 mm for inset. Dapi was used to stain nuclei.
Figure 2
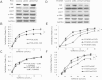
Effect of TAZ on the sensitivity of NSCLC cells to gefitinib. (A) Protein lysate extracted from PC9 cells expressing pEX2-TAZ were subjected to western blot by using anti-TAZ, anti-pAkt, anti-tAkt, anti-pERK and anti-tERK antibodies, respectively. (B) Overexpression of TAZ descreased gefitinib sensitivity in PC9 cells. Cells were transfected and then exposed to various doses of gefitinib for 48 h and viability was accessed by MTT assay as described in Methods. The inhibition rate was calculated according to the following formula: inhibition ratio (%) = [1- A490 (experimental group)/A490 (Control group)] × 100. (C) LY294002, as a inhibition of Akt signaling, abolished TAZ-driven descreased sensitivity to gefitinib of PC9 cell. (D) shRNAs against different regions of TAZ mRNA (shTAZ1 and shTAZ2) were expressed in PC9/GR cells. Expressions of TAZ, pAkt, tAkt, pERK and tERK were detected by western blot. (E) enhanced sensitivity of PC9/GR cells to gefitinib after TAZ knockdown. (F) Enhanced sensitivity to gefitinib after TAZ knockdown were detected in H1975 cells. Procedures and conditions for inhibition rate are described as in (B). Results are expressed as means ± SEM from three independent experiments (*P<0.05). Statistical analyses were carried out using Student’s t-test.
Figure 3
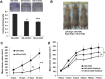
TAZ knockdown in PC9/GR cells suppresses anchorage-independent growth, tumorigenesis and resistant to gefitinib in vivo. (A) Two hundred stable GR-shNC, GR-shTAZ1 and GR-shTAZ2 cells were plated onto 6-well plates and a colony formation assay was assessed and photographed. The rate of colony formation was calculated as follows: colony-forming rate = (average colony number/ plated single cell number) × 100%. The colony-forming rates of GR-shTAZ cells were reduced drastically compared with control group. Results are expressed as means ± SEM from three independent experiments (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001). (B) PC9/GR cells with stable expression of shTAZ2 and shNC were inoculated subcutaneously into right and left flanks of nude mice (n = 6 per group), respectively. Representative photographs of nude mice 29 days after inoculation are shown. (C) Tumor growth curve is indicated. (D) Mice bearing PC9/GR xenografts were treated daily with gefitinib at indicated doses. Data represent means ± SEM (*P<0.05, **P<0.01). Statistical analyses were carried out using Student’s t-test.
Figure 4
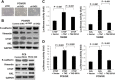
TAZ mediates EMT of gefitinib-resistant PC9/GR. (A) TAZ knockdown in PC9/GR cells resulted in a morphology change in PC9/GR by a light microscope. The spindle form of the PC9/GR-shNC cells changed to a round shape. The cell density of the clusters was obviously enhanced in the PC9/GR-shTAZ cells. (B) Cell lysates from PC9/GR and PC9 cells expressing vector, shTAZ and PEX2-TAZ were separated and probed with antibodies for epithelial marker and mesenchymal markers as indicated. TAZ knockdown in PC9/GR cells increased E-cadherin and decreased vimentin, CTGF and AXL. All data were normalized to GAPDH. (C) Luciferase reporter assay in 16HBE cells with TAZ or TAZ-S51A overexpression. 16HBE cells co-transfected with pGL3-CTGF/pGL3-AXL and pEX2-TAZ showed significantly elevated reporter activity compared with controls. Meanwhile, cells co-transfected with pEX2-TAZ-S51A, which disrupts the TEAD binding, exhibited decreased luciferase activity compared with pEX2-TAZ. Cells were harvested 48 h after transfection for measurement of luciferase activity in all experiments. (D) Luciferase reporter assay in PC9/GR cells. Total amounts of DNA and RNA were kept constant. Results are expressed as means ± SEM from three independent experiments. Statistical analyses were carried out using Student’s t-test.
Figure 5
Knockdown of TAZ in PC9/GR suppresses cell migration and invasion. (A) Wound-healing migration assay for PC9/GR cells expressing shNC, shTAZ1 or shTAZ2. The healing of wounds by migrated cells at time 0 and 24 h was imaged. PC9/GR cells expressing shNC migrated faster than PC9/GR cells knocking down TAZ. (B,C) The migration (B) and invasion (C) of control, PC9/GR cells expressing shNC, shTAZ1 or shTAZ2 were assessed by transwell assay and matrigel invasion assay. The migration and invasiveness of TAZ-knocked-down PC9/GR cells decreased 52% - 63% and 53% - 62%, respectively, compared with control cells. Results are expressed as means ± SEM from three independent experiments (** P<0.01, *** P<0.001). Statistical analyses were carried out using Student’s t-test.
Similar articles
- Gossypol overcomes EGFR-TKIs resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting YAP/TAZ and EGFRL858R/T790M.
Xu J, Zhu GY, Cao D, Pan H, Li YW. Xu J, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jul;115:108860. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108860. Epub 2019 May 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31055235 - AT-101 enhances gefitinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR T790M mutations.
Zhao R, Zhou S, Xia B, Zhang CY, Hai P, Zhe H, Wang YY. Zhao R, et al. BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 18;16:491. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2519-3. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27431492 Free PMC article. - Long non-coding RNA UCA1 induces non-T790M acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs by activating the AKT/mTOR pathway in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.
Cheng N, Cai W, Ren S, Li X, Wang Q, Pan H, Zhao M, Li J, Zhang Y, Zhao C, Chen X, Fei K, Zhou C, Hirsch FR. Cheng N, et al. Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 15;6(27):23582-93. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4361. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26160838 Free PMC article. - Next-generation EGFR/HER tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations: a review of the evidence.
Wang X, Goldstein D, Crowe PJ, Yang JL. Wang X, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Sep 6;9:5461-73. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S94745. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27660463 Free PMC article. Review. - Addressing epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in non-small cell lung cancer.
Noda S, Kanda S. Noda S, et al. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2016;10(5):547-56. doi: 10.1586/17476348.2016.1164603. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2016. PMID: 26959310 Review.
Cited by
- Targeting YAP/TAZ-TEAD protein-protein interactions using fragment-based and computational modeling approaches.
Kaan HYK, Sim AYL, Tan SKJ, Verma C, Song H. Kaan HYK, et al. PLoS One. 2017 Jun 1;12(6):e0178381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178381. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28570566 Free PMC article. - [Research Progress of the Role of EMT in EGFR-TKIs Resistance of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].
Yu L, Huang S, Lv W, He Z, Hu J. Yu L, et al. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018 Dec 20;21(12):907-911. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2018.12.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30591098 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese. - TRIB3 confers radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by stabilizing TAZ.
Zhou S, Liu S, Lin C, Li Y, Ye L, Wu X, Jian Y, Dai Y, Ouyang Y, Zhao L, Liu M, Song L, Xi M. Zhou S, et al. Oncogene. 2020 Apr;39(18):3710-3725. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1245-0. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32157210 - Molecular Pathways: Hippo Signaling, a Critical Tumor Suppressor.
Sebio A, Lenz HJ. Sebio A, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;21(22):5002-7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0411. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26384319 Free PMC article. - Role of YAP/TAZ transcriptional regulators in resistance to anti-cancer therapies.
Kim MH, Kim J. Kim MH, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Apr;74(8):1457-1474. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2412-x. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27826640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bell DW, Gore I, Okimoto RA, Godin-Heymann N, Sordella R, Mulloy R, Sharma SV, Brannigan BW, Mohapatra G, Settleman J, Haber DA. Inherited susceptibility to lung cancer may be associated with the T790M drug resistance mutation in EGFR. Nat Genet. 2005;37(12):1315–1316. doi: 10.1038/ng1671. - DOI - PubMed
- Yoshida T, Zhang G, Smith MA, Lopez AS, Bai Y, Li J, Fang B, Koomen J, Rawal B, Fisher KJ, Chen AY, Kitano M, Morita Y, Yamaguchi H, Shibata K, Okabe T, Okamoto I, Nakagawa K, Haura EB. Tyrosine Phosphoproteomics Identifies Both Codrivers and Cotargeting Strategies for T790M-Related EGFR-TKI Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(15):4059–4074. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1559. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous