Long-read, whole-genome shotgun sequence data for five model organisms - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1038/sdata.2014.45. eCollection 2014.
Paul Peluso 1, Primo Babayan 1, P Jane Yeadon 2, Charles Yu 3, William W Fisher 3, Chen-Shan Chin 1, Nicole A Rapicavoli 1, David R Rank 1, Joachim Li 4, David E A Catcheside 2, Susan E Celniker 3, Adam M Phillippy 5, Casey M Bergman 6, Jane M Landolin 1
Affiliations
- PMID: 25977796
- PMCID: PMC4365909
- DOI: 10.1038/sdata.2014.45
Long-read, whole-genome shotgun sequence data for five model organisms
Kristi E Kim et al. Sci Data. 2014.
Abstract
Single molecule, real-time (SMRT) sequencing from Pacific Biosciences is increasingly used in many areas of biological research including de novo genome assembly, structural-variant identification, haplotype phasing, mRNA isoform discovery, and base-modification analyses. High-quality, public datasets of SMRT sequences can spur development of analytic tools that can accommodate unique characteristics of SMRT data (long read lengths, lack of GC or amplification bias, and a random error profile leading to high consensus accuracy). In this paper, we describe eight high-coverage SMRT sequence datasets from five organisms (Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Neurospora crassa, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Drosophila melanogaster) that have been publicly released to the general scientific community (NCBI Sequence Read Archive ID SRP040522). Data were generated using two sequencing chemistries (P4C2 and P5C3) on the PacBio RS II instrument. The datasets reported here can be used without restriction by the research community to generate whole-genome assemblies, test new algorithms, investigate genome structure and evolution, and identify base modifications in some of the most widely-studied model systems in biological research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests. K.E.K., P.P., P.B., C.-S.C., N.A.R., D.R.R., and J.M.L. are employees of Pacific Biosciences of California, Inc., a company commercializing DNA sequencing technologies.
Figures
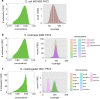
Figure 1. Mapped Subread Concordance and Coverage.
The distribution of mapped subread concordances and mapped subread coverages are plotted for E. coli MG1655 P4C2 (a), S. cerevisiae 9464 P4C2 (b), and D. melanogaster ISO1 P5C3 (c). The coverage distribution is similar among all chromosomes in S. cerevisiae, whereas the coverage distribution is half in chrX (50X) compared to the autosomes (100X) in D. melanogaster. ChrU and chrUextra are assembled contigs that could not be placed to physical chromosomes, and have very low coverages in general.
Similar articles
- Assembling large genomes with single-molecule sequencing and locality-sensitive hashing.
Berlin K, Koren S, Chin CS, Drake JP, Landolin JM, Phillippy AM. Berlin K, et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2015 Jun;33(6):623-30. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3238. Epub 2015 May 25. Nat Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26006009 - Efficient and accurate whole genome assembly and methylome profiling of E. coli.
Powers JG, Weigman VJ, Shu J, Pufky JM, Cox D, Hurban P. Powers JG, et al. BMC Genomics. 2013 Oct 3;14(1):675. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-675. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24090403 Free PMC article. - Nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data.
Chin CS, Alexander DH, Marks P, Klammer AA, Drake J, Heiner C, Clum A, Copeland A, Huddleston J, Eichler EE, Turner SW, Korlach J. Chin CS, et al. Nat Methods. 2013 Jun;10(6):563-9. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2474. Epub 2013 May 5. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23644548 - Advantages of genome sequencing by long-read sequencer using SMRT technology in medical area.
Nakano K, Shiroma A, Shimoji M, Tamotsu H, Ashimine N, Ohki S, Shinzato M, Minami M, Nakanishi T, Teruya K, Satou K, Hirano T. Nakano K, et al. Hum Cell. 2017 Jul;30(3):149-161. doi: 10.1007/s13577-017-0168-8. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Hum Cell. 2017. PMID: 28364362 Free PMC article. Review. - Chromosome-level hybrid de novo genome assemblies as an attainable option for nonmodel insects.
Jaworski CC, Allan CW, Matzkin LM. Jaworski CC, et al. Mol Ecol Resour. 2020 Sep;20(5):1277-1293. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13176. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Mol Ecol Resour. 2020. PMID: 32329220 Review.
Cited by
- Multi-Omics Strategies to Investigate the Biodegradation of Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine in Rhodococcus sp. Strain DN22.
Zhou X, Yao Q, Li N, Xia M, Deng Y. Zhou X, et al. Microorganisms. 2023 Dec 30;12(1):76. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010076. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38257903 Free PMC article. - A comparative evaluation of hybrid error correction methods for error-prone long reads.
Fu S, Wang A, Au KF. Fu S, et al. Genome Biol. 2019 Feb 4;20(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1605-z. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 30717772 Free PMC article. - Complete Genome Sequences and Genome-Wide Characterization of Trichoderma Biocontrol Agents Provide New Insights into their Evolution and Variation in Genome Organization, Sexual Development, and Fungal-Plant Interactions.
Li WC, Lin TC, Chen CL, Liu HC, Lin HN, Chao JL, Hsieh CH, Ni HF, Chen RS, Wang TF. Li WC, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0066321. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00663-21. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34908505 Free PMC article. - Complete Genome Sequence of Lactobacillus nenjiangensis SH-Y15, Isolated from Sauerkraut.
He J, Liu Y, Li F, Wu H, Yang H. He J, et al. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020 Jun 4;9(23):e01473-19. doi: 10.1128/MRA.01473-19. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020. PMID: 32499359 Free PMC article. - Genome Sequencing and Analysis of the Hypocrellin-Producing Fungus Shiraia bambusicola S4201.
Zhao N, Li D, Guo BJ, Tao X, Lin X, Yan SZ, Chen SL. Zhao N, et al. Front Microbiol. 2020 Apr 9;11:643. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00643. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32373091 Free PMC article.
References
Data Citations
- 2014. NCBI Sequence Read Archive. SRP040522
- 2006. GenBank . NC_000913
- 2011. NCBI Assembly . GCF_000146045.2
- 2013. GenBank. AABX00000000.3
- 2011. NCBI Assembly. GCF_000001735.3
References
- Eid J. et al. Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science 323, 133–138 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous