One-year efficacy and safety of a fixed combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: results of a 26-week extension to a 26-week main trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2015 Oct;17(10):965-73.
doi: 10.1111/dom.12498. Epub 2015 Jul 1.
Affiliations
- PMID: 25980900
- PMCID: PMC4744775
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.12498
Clinical Trial
One-year efficacy and safety of a fixed combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: results of a 26-week extension to a 26-week main trial
S C L Gough et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015 Oct.
Abstract
Aims: To confirm, in a 26-week extension study, the sustained efficacy and safety of a fixed combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with either insulin degludec or liraglutide alone, in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: Insulin-naïve adults with type 2 diabetes randomized to once-daily IDegLira, insulin degludec or liraglutide, in addition to metformin ± pioglitazone, continued their allocated treatment in this preplanned 26-week extension of the DUAL I trial.
Results: A total of 78.8% of patients (1311/1663) continued into the extension phase. The mean glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) concentration at 52 weeks was reduced from baseline by 1.84% (20.2 mmol/mol) for the IDegLira group, 1.40% (15.3 mmol/mol) for the insulin degludec group and 1.21% (13.2 mmol/mol) for the liraglutide group. Of the patients on IDegLira, 78% achieved an HbA1c of <7% (53 mmol/mol) versus 63% of the patients on insulin degludec and 57% of those on liraglutide. The mean fasting plasma glucose concentration at the end of the trial was similar for IDegLira (5.7 mmol/l) and insulin degludec (6.0 mmol/l), but higher for liraglutide (7.3 mmol/l). At 52 weeks, the daily insulin dose was 37% lower with IDegLira (39 units) than with insulin degludec (62 units). IDegLira was associated with a significantly greater decrease in body weight (estimated treatment difference, -2.80 kg, p < 0.0001) and a 37% lower rate of hypoglycaemia compared with insulin degludec. Overall, all treatments were well tolerated and no new adverse events or tolerability issues were observed for IDegLira.
Conclusions: These 12-month data, derived from a 26-week extension of the DUAL I trial, confirm the initial 26-week main phase results and the sustainability of the benefits of IDegLira compared with its components in glycaemic efficacy, safety and tolerability.
Keywords: diabetes therapy; hypoglycaemia; insulin degludec; liraglutide.
© 2015 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
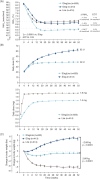
Figure 1
(A) Mean glycated haemoglobin (
HbA1c
) concentration over time, by treatment group. Mean values with error bars [standard error of the mean (s.e.m.)] based on the full analysis set (
FAS
) and
LOCF
‐imputed data. p values from an analysis of covariance (
ancova
) model. Dashed lines (‐‐):
A
merican
D
iabetes
A
ssociation
HbA1c
target <7.0%;
I
nternational
D
iabetes
F
ederation
HbA1c
target ≤6.5%. (B) Mean daily doses of insulin degludec and liraglutide components of treatment, over time. Mean values with error bars (s.e.m.) based on safety analysis set and
LOCF
‐imputed data; n for each treatment based on
FAS
; week 52 dose is observed dose based on
FAS
. (C) Change in mean body weight over time, by treatment group. Mean values with error bars (s.e.m.) based on
FAS
and
LOCF
‐imputed data. Estimated treatment differences and p values are from an
ancova
model.
EOT
, end of trial;
IDeg
, insulin degludec;
IDegLira
, insulin degludec/liraglutide combination;
Lira
, liraglutide. Results at 26 weeks are from the main phase of the
DUAL I
trial and have been reported previously 5).
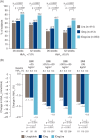
Figure 2
(A) Percentage of subjects reaching a glycated haemoglobin (
HbA1c
) target of <7.0 or ≤6.5% at 26 and 52 weeks, by treatment group. Values based on full analysis set (
FAS
) and
LOCF
‐imputed data; p values are from a logistic regression model.
HbA1c
target <7.0% (53 mmol/mol) is from
A
merican
D
iabetes
A
ssociation and
HbA1c
target ≤6.5% (48 mmol/mol) is from the
I
nternational
D
iabetes
F
ederation. (B)
HbA1c
reduction at 52 weeks by treatment group, stratified by baseline
BMI
. Data are mean from observed values based on
FAS
and
LOCF
‐imputed data; p values from
ancova
model. n, number of subjects contributing to the analysis. IDeg, insulin degludec;
IDegLira
, insulin degludec/liraglutide combination;
Lira
, liraglutide. Results at 26 weeks are from the main phase of the
DUAL I
trial and have been reported previously 5.
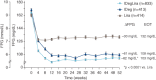
Figure 3
Fasting plasma glucose (
FPG
) from 0 to 52 weeks by treatment group. Mean values with error bars (standard error of the mean) based on full analysis set and
LOCF
‐imputed data; p value is from an analysis of covariance model.
IDeg
, insulin degludec;
IDegLira
, insulin degludec/liraglutide combination;
Lira
, liraglutide. Results at 26 weeks are from the main phase of the
DUAL I
trial and have been reported previously 5.
Similar articles
- Safety and efficacy of IDegLira titrated once weekly versus twice weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic drugs: DUAL VI randomized clinical trial.
Harris SB, Kocsis G, Prager R, Ridge T, Chandarana K, Halladin N, Jabbour S. Harris SB, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Jun;19(6):858-865. doi: 10.1111/dom.12892. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 28124817 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Superior efficacy with a fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with insulin degludec and liraglutide in insulin-naïve Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes in a phase 3, open-label, randomized trial.
Kaku K, Araki E, Tanizawa Y, Ross Agner B, Nishida T, Ranthe M, Inagaki N. Kaku K, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Dec;21(12):2674-2683. doi: 10.1111/dom.13856. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019. PMID: 31407845 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Efficacy and safety of a fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with its components given alone: results of a phase 3, open-label, randomised, 26-week, treat-to-target trial in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes.
Gough SC, Bode B, Woo V, Rodbard HW, Linjawi S, Poulsen P, Damgaard LH, Buse JB; NN9068-3697 (DUAL-I) trial investigators. Gough SC, et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014 Nov;2(11):885-93. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70174-3. Epub 2014 Sep 1. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25190523 Clinical Trial. - The Clinical Use of a Fixed-Dose Combination of Insulin Degludec and Liraglutide (Xultophy 100/3.6) for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes.
Harris K, Nealy KL. Harris K, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;52(1):69-77. doi: 10.1177/1060028017726348. Epub 2017 Aug 11. Ann Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 28799414 Review. - Efficacy and safety of fixed-ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Vedtofte L, Knop FK, Vilsbøll T. Vedtofte L, et al. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017 Mar;16(3):387-396. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2017.1288715. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017. PMID: 28150516 Review.
Cited by
- Effectiveness, Simplification and Persistence of IDegLira in Poorly Controlled People with Type 2 Diabetes: A 4-Year Follow-Up Real-World Study.
Di Loreto C, Celleno R, Pezzuto D, Ambrosi F, Bellavita S, Biagini M, Passeri M, Del Sindaco P. Di Loreto C, et al. Diabetes Ther. 2024 Jun;15(6):1313-1331. doi: 10.1007/s13300-024-01564-z. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Diabetes Ther. 2024. PMID: 38605275 Free PMC article. - Degree of obesity and gastrointestinal adverse reactions influence the weight loss effect of liraglutide in overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes.
Zhou F, Jiang L, Guo J, Fan Y, Pan Q, Li T, Sun X, Li P. Zhou F, et al. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2023 Mar 18;14:20406223231161516. doi: 10.1177/20406223231161516. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2023. PMID: 36950020 Free PMC article. - Real-world effectiveness of IDegLira compared with intensified conventional insulin therapy in adults with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study.
Szépkúti S, Bandur S, Kovács G, Ferenci T, Svébis MM, Turbucz P, Tabák ÁG. Szépkúti S, et al. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Sep 14;22(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01139-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 36104712 Free PMC article. - Preserved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of insulin degludec and liraglutide when administered as insulin degludec/liraglutide in a Chinese population.
Liu H, Luo B, Chen X, Ingwersen SH, Jia T, Vestergård Jacobsen L, Hu P. Liu H, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2022 Apr;13(4):652-656. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13716. Epub 2021 Dec 28. J Diabetes Investig. 2022. PMID: 34797962 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Cost-Effectiveness of iGlarLixi in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Suboptimally Controlled on Basal Insulin Plus Metformin in the UK.
McCrimmon RJ, Falla E, Sha JZ, Alsaleh AJO, Lew E, Hudson R, Baxter M, Palmer K. McCrimmon RJ, et al. Diabetes Ther. 2021 Dec;12(12):3217-3230. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01159-y. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Diabetes Ther. 2021. PMID: 34714523 Free PMC article.
References
- Eng C, Kramer CK, Zinman B, Retnakaran R. Glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonist and basal insulin combination treatment for the management of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Lancet 2014; 384: 2228–2234. - PubMed
- Goldenberg R. Insulin plus incretin agent combination therapy in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Curr Med Res Opin 2014; 30: 431–445. - PubMed
- Gough SC, Bode B, Woo V et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed‐ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with its components given alone: results of a phase 3, open‐label, randomised, 26‐week, treat‐to‐target trial in insulin‐naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014; 2: 885–893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical