Treatment of dyslipidemia with statins and physical exercises: recent findings of skeletal muscle responses - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2015 Apr;104(4):324-31.
doi: 10.5935/abc.20150005. Epub 2015 Feb 13.
[Article in English, Portuguese]
Affiliations
- PMID: 25993596
- PMCID: PMC4415869
- DOI: 10.5935/abc.20150005
Review
Treatment of dyslipidemia with statins and physical exercises: recent findings of skeletal muscle responses
[Article in English, Portuguese]
Mariana Rotta Bonfim et al. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2015 Apr.
Abstract
Statin treatment in association with physical exercise practice can substantially reduce cardiovascular mortality risk of dyslipidemic individuals, but this practice is associated with myopathic event exacerbation. This study aimed to present the most recent results of specific literature about the effects of statins and its association with physical exercise on skeletal musculature. Thus, a literature review was performed using PubMed and SciELO databases, through the combination of the keywords "statin" AND "exercise" AND "muscle", restricting the selection to original studies published between January 1990 and November 2013. Sixteen studies evaluating the effects of statins in association with acute or chronic exercises on skeletal muscle were analyzed. Study results indicate that athletes using statins can experience deleterious effects on skeletal muscle, as the exacerbation of skeletal muscle injuries are more frequent with intense training or acute eccentric and strenuous exercises. Moderate physical training, in turn, when associated to statins does not increase creatine kinase levels or pain reports, but improves muscle and metabolic functions as a consequence of training. Therefore, it is suggested that dyslipidemic patients undergoing statin treatment should be exposed to moderate aerobic training in combination to resistance exercises three times a week, and the provision of physical training prior to drug administration is desirable, whenever possible.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflict of Interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
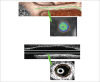
Figure 1
Cholesterol biosynthesis stages and statin action. The enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA into mevalonate; the action of inhibiting this enzyme by statins results in the reduction of cholesterol synthesis, as well as other intermediates (prenylated proteins, dolichols and ubiquinone), which can contribute to muscle injury resulting from statin use. CoA: Coenzyme A; PP: pyrophosphate.
Figure 2
Muscle responses of the association of statins with physical exercise. Strenuous exercises are characterized by acute eccentric exercises, maximum capacity tests and/or competitive activities; moderate exercises are characterized by aerobic training, with or without resistance training, usually performed three times a week for 12 weeks. UP: ubiquitin proteasome.
Similar articles
- Efficacy and safety of statins and exercise combination therapy compared to statin monotherapy in patients with dyslipidaemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Gui YJ, Liao CX, Liu Q, Guo Y, Yang T, Chen JY, Wang YT, Hu JH, Xu DY. Gui YJ, et al. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2017 Jun;24(9):907-916. doi: 10.1177/2047487317691874. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28436720 Review. - [Intense physical exercise, muscle involvement and statin use].
Toussirot E, Michel F, Meneveau N. Toussirot E, et al. Presse Med. 2014 Jun;43(6 Pt 1):726-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2013.11.015. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Presse Med. 2014. PMID: 24630267 French. No abstract available. - Effect of statins on skeletal muscle function.
Parker BA, Capizzi JA, Grimaldi AS, Clarkson PM, Cole SM, Keadle J, Chipkin S, Pescatello LS, Simpson K, White CM, Thompson PD. Parker BA, et al. Circulation. 2013 Jan 1;127(1):96-103. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.136101. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Circulation. 2013. PMID: 23183941 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Effects of statins on skeletal muscle: a perspective for physical therapists.
Di Stasi SL, MacLeod TD, Winters JD, Binder-Macleod SA. Di Stasi SL, et al. Phys Ther. 2010 Oct;90(10):1530-42. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20090251. Epub 2010 Aug 5. Phys Ther. 2010. PMID: 20688875 Free PMC article. Review. - Statin-associated myopathy.
Thompson PD, Clarkson P, Karas RH. Thompson PD, et al. JAMA. 2003 Apr 2;289(13):1681-90. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.13.1681. JAMA. 2003. PMID: 12672737 Review.
Cited by
- Effect of ABCA1-R219K Polymorphism in Serum Lipid Parameters in Patients under Statin Therapy Visiting Tertiary Cardiac Center of Nepal.
Ghimire S, Yadav BK, Shrestha S, Shakya J, Poudel CM, Tuladhar ET, Sharma VK, Raut M, Bhattarai A, Manandhar KD, Pant V, Shrestha D. Ghimire S, et al. J Lab Physicians. 2023 Jul 3;15(4):510-517. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1768630. eCollection 2023 Dec. J Lab Physicians. 2023. PMID: 37780884 Free PMC article. - Effect of the Association of Fixed Oils from Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench, Euterpe oleracea Martius, Bixa orellana Linné and Chronic SM® on Atherogenic Dyslipidemia in Wistar Rats.
Sales PF, Nascimento ALD, Pinheiro FC, Alberto AKM, Teixeira Dos Santos AVTL, Carvalho HO, de Souza GC, Carvalho JCT. Sales PF, et al. Molecules. 2023 Sep 19;28(18):6689. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186689. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764465 Free PMC article. - Corchorus olitorius extract exhibit anti-hyperglycemic and anti-inflammatory properties in rodent models of obesity and diabetes mellitus.
Mokgalaboni K, Phoswa WN. Mokgalaboni K, et al. Front Nutr. 2023 Apr 5;10:1099880. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1099880. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37090773 Free PMC article. Review. - The beneficial effects of exercise on glucose and lipid metabolism during statin therapy is partially mediated by changes of the intestinal flora.
Wang L, Zhou B, Li X, Wang Y, Yang XM, Wang H, Yan J, Dong J. Wang L, et al. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2022;41(3):112-120. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.2021-024. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2022. PMID: 35854693 Free PMC article.
References
- World Health Organization . The World Health Report 2002. Reducing risks, promoting healthy life. Geneva: 2002. - PubMed
- Xavier HT, Izar MC, Neto Faria, JR, Assad MH, Rocha VZ, Sposito AC, Sociedade Brasileira de Cardiologia V Diretriz brasileira de dislipidemias e prevenção da aterosclerose. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2013;101(4) supl. 1:1–22. - PubMed
- Sposito AC, Caramelli B, Fonseca FA, Bertolami MC, Afiune A, Neto, Souza AD, et al. Sociedade Brasileira de Cardiologia IV Diretriz brasileira sobre dislipidemias e prevenção da aterosclerose. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2007;88(supl 1):1–18. - PubMed
- National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002;106(25):3143–3421. - PubMed
- Kokkinos PF, Faselis C, Myers J, Panagiotakos D, Doumas M. Interactive effects of fitness and statin treatment on mortality risk in veterans with dyslipidaemia: a cohort study. Lancet. 2013;381(9864):394–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical