XL888 Limits Vemurafenib-Induced Proliferative Skin Events by Suppressing Paradoxical MAPK Activation - PubMed (original) (raw)
XL888 Limits Vemurafenib-Induced Proliferative Skin Events by Suppressing Paradoxical MAPK Activation
Manali Phadke et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Oct.
No abstract available
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
G. Gibney has served as a consultant for BMS, Genentech and Novartis. V. Sondak has served as a consultant for Merck, OncoSec, MabVax, Polynoma and Genentech. J. Weber has received honoraria from Genentech and GSK. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
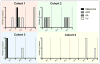
Figure 1. Incidence of secondary skin lesions by dose cohort of XL888
Chart shows the incidence of hyperproliferative/neoplastic skin lesions (melanoma, SCC: squamous cell carcinoma, KA: keratoacanthoma, and VV: verucca vulgaris, stratified by XL888 dose cohort (cohort 1: 30mg; cohort 2: 45mg; cohort 3: 90mg; cohort 4: 135mg). Data shows number of lesions of each type for each individual patient. Cohort had 7 total events (3/3 patients), cohort 2 had 6 total events (2/3 patients), cohort 3 had 3 total events (2/3 patients) and cohort 4 had 3 total events (2/6 patients).
Figure 2. XL888 suppresses paradoxical MAPK signaling in _NRAS_-mutant melanoma and _HRAS_-transformed NIH3T3 cells
a: XL888 prevents the paradoxical MAPK signaling in 3 NRAS mutant melanoma cell lines. IPC-298, M245 and WM1366 cell lines were treated with vemurafenib (1 μM, 72 hrs) in the absence and presence of XL888 (300 nM). Western blots show total CRAF, phospho-ERK and total ERK. b: XL888 (300 nM) suppressed vemurafenib-driven (1 μM, 72 hrs) paradoxical MAPK signaling in NIH3T3 cells transduced with HRAS Q61L.
Comment in
- The Broad Stroke of Hsp90 Inhibitors: Painting over the RAF Inhibitor Paradox.
Vido MJ, Aplin AE. Vido MJ, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Oct;135(10):2355-2357. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.239. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26358385 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- The Broad Stroke of Hsp90 Inhibitors: Painting over the RAF Inhibitor Paradox.
Vido MJ, Aplin AE. Vido MJ, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Oct;135(10):2355-2357. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.239. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26358385 Free PMC article. - Pharmacodynamic effects and mechanisms of resistance to vemurafenib in patients with metastatic melanoma.
Trunzer K, Pavlick AC, Schuchter L, Gonzalez R, McArthur GA, Hutson TE, Moschos SJ, Flaherty KT, Kim KB, Weber JS, Hersey P, Long GV, Lawrence D, Ott PA, Amaravadi RK, Lewis KD, Puzanov I, Lo RS, Koehler A, Kockx M, Spleiss O, Schell-Steven A, Gilbert HN, Cockey L, Bollag G, Lee RJ, Joe AK, Sosman JA, Ribas A. Trunzer K, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2013 May 10;31(14):1767-74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.44.7888. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23569304 Clinical Trial. - Cutaneous manifestations of vemurafenib therapy for metastatic melanoma.
Owen JL, Lopez IE, Desai SR. Owen JL, et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015 May;14(5):509-10. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25942671 - The discovery of vemurafenib for the treatment of BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma.
Kim A, Cohen MS. Kim A, et al. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016 Sep;11(9):907-16. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2016.1201057. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27327499 Free PMC article. Review. - Vemurafenib in patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive advanced melanoma.
Ravnan MC, Matalka MS. Ravnan MC, et al. Clin Ther. 2012 Jul;34(7):1474-86. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.06.009. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Clin Ther. 2012. PMID: 22742884 Review.
Cited by
- Targeting CDK2 overcomes melanoma resistance against BRAF and Hsp90 inhibitors.
Azimi A, Caramuta S, Seashore-Ludlow B, Boström J, Robinson JL, Edfors F, Tuominen R, Kemper K, Krijgsman O, Peeper DS, Nielsen J, Hansson J, Egyhazi Brage S, Altun M, Uhlen M, Maddalo G. Azimi A, et al. Mol Syst Biol. 2018 Mar 5;14(3):e7858. doi: 10.15252/msb.20177858. Mol Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29507054 Free PMC article. - The Broad Stroke of Hsp90 Inhibitors: Painting over the RAF Inhibitor Paradox.
Vido MJ, Aplin AE. Vido MJ, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Oct;135(10):2355-2357. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.239. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26358385 Free PMC article. - 17-AAG inhibits vemurafenib-associated MAP kinase activation and is synergistic with cellular immunotherapy in a murine melanoma model.
Joshi SS, Jiang S, Unni E, Goding SR, Fan T, Antony PA, Hornyak TJ. Joshi SS, et al. PLoS One. 2018 Feb 26;13(2):e0191264. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191264. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29481571 Free PMC article. - Inhibitors of HSP90 in melanoma.
Mielczarek-Lewandowska A, Hartman ML, Czyz M. Mielczarek-Lewandowska A, et al. Apoptosis. 2020 Feb;25(1-2):12-28. doi: 10.1007/s10495-019-01577-1. Apoptosis. 2020. PMID: 31659567 Free PMC article. Review. - Discrete cytosolic macromolecular BRAF complexes exhibit distinct activities and composition.
Diedrich B, Rigbolt KT, Röring M, Herr R, Kaeser-Pebernard S, Gretzmeier C, Murphy RF, Brummer T, Dengjel J. Diedrich B, et al. EMBO J. 2017 Mar 1;36(5):646-663. doi: 10.15252/embj.201694732. Epub 2017 Jan 16. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 28093501 Free PMC article.
References
- Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380:358–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources