Altered lysosomal proteins in neural-derived plasma exosomes in preclinical Alzheimer disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Altered lysosomal proteins in neural-derived plasma exosomes in preclinical Alzheimer disease
Edward J Goetzl et al. Neurology. 2015.
Abstract
Objective: Diverse autolysosomal proteins were quantified in neurally derived blood exosomes from patients with Alzheimer disease (AD) and controls to investigate disordered neuronal autophagy.
Methods: Blood exosomes obtained once from patients with AD (n = 26) or frontotemporal dementia (n = 16), other patients with AD (n = 20) both when cognitively normal and 1 to 10 years later when diagnosed, and case controls were enriched for neural sources by anti-human L1CAM antibody immunoabsorption. Extracted exosomal proteins were quantified by ELISAs and normalized with the CD81 exosomal marker.
Results: Mean exosomal levels of cathepsin D, lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP-1), and ubiquitinylated proteins were significantly higher and of heat-shock protein 70 significantly lower for AD than controls in cross-sectional studies (p ≤ 0.0005). Levels of cathepsin D, LAMP-1, and ubiquitinylated protein also were significantly higher for patients with AD than for patients with frontotemporal dementia (p ≤ 0.006). Step-wise discriminant modeling of the protein levels correctly classified 100% of patients with AD. Exosomal levels of all proteins were similarly significantly different from those of matched controls in 20 patients 1 to 10 years before and at diagnosis of AD (p ≤ 0.0003).
Conclusions: Levels of autolysosomal proteins in neurally derived blood exosomes distinguish patients with AD from case controls and appear to reflect the pathology of AD up to 10 years before clinical onset. These preliminary results confirm in living patients with AD the early appearance of neuronal lysosomal dysfunction and suggest that these proteins may be useful biomarkers in large prospective studies.
© 2015 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
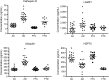
Figure 1. Levels of plasma exosomal proteins in patients with AD, FTD, and cognitively normal case controls
The horizontal line in each cluster here and in figure 2 depicts the mean for that set. AC = Alzheimer normal control; AD = Alzheimer disease; FTC = frontotemporal normal control; FTD = frontotemporal dementia; HSP70 = heat-shock protein 70; LAMP-1 = lysosome-associated membrane protein 1.
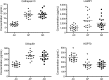
Figure 2. Sequential levels of plasma exosomal proteins in patients with AD measured first at a time of normal cognition (preclinical, AP) and later at the time of development of aMCI or dementia (AD), as contrasted with cognitively normal control participants (AC) matched to individuals in their preclinical phase
AC = Alzheimer normal control; AD = Alzheimer disease; aMCI = amnestic mild cognitive impairment; AP = preclinical Alzheimer disease; FTC = frontotemporal normal control; FTD = frontotemporal dementia; HSP70 = heat-shock protein 70; LAMP-1 = lysosome-associated membrane protein 1.
Similar articles
- Identification of preclinical Alzheimer's disease by a profile of pathogenic proteins in neurally derived blood exosomes: A case-control study.
Fiandaca MS, Kapogiannis D, Mapstone M, Boxer A, Eitan E, Schwartz JB, Abner EL, Petersen RC, Federoff HJ, Miller BL, Goetzl EJ. Fiandaca MS, et al. Alzheimers Dement. 2015 Jun;11(6):600-7.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2014.06.008. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Alzheimers Dement. 2015. PMID: 25130657 Free PMC article. - Dysfunctionally phosphorylated type 1 insulin receptor substrate in neural-derived blood exosomes of preclinical Alzheimer's disease.
Kapogiannis D, Boxer A, Schwartz JB, Abner EL, Biragyn A, Masharani U, Frassetto L, Petersen RC, Miller BL, Goetzl EJ. Kapogiannis D, et al. FASEB J. 2015 Feb;29(2):589-96. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-262048. Epub 2014 Oct 23. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25342129 Free PMC article. - Decreased synaptic proteins in neuronal exosomes of frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
Goetzl EJ, Kapogiannis D, Schwartz JB, Lobach IV, Goetzl L, Abner EL, Jicha GA, Karydas AM, Boxer A, Miller BL. Goetzl EJ, et al. FASEB J. 2016 Dec;30(12):4141-4148. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600816R. Epub 2016 Sep 6. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 27601437 Free PMC article. - Emergence of exosomal miRNAs as a diagnostic biomarker for Alzheimer's disease.
Van Giau V, An SS. Van Giau V, et al. J Neurol Sci. 2016 Jan 15;360:141-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 4. J Neurol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26723991 Review. - Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as promising biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease.
Chen JJ, Yang G, Yan QQ, Zhao J, Li S. Chen JJ, et al. Rev Neurosci. 2019 Dec 18;31(1):77-87. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2019-0001. Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31318699 Review.
Cited by
- Dual role of brain-derived extracellular vesicles in dementia-related neurodegenerative disorders: cargo of disease spreading signals and diagnostic-therapeutic molecules.
Natale F, Fusco S, Grassi C. Natale F, et al. Transl Neurodegener. 2022 Nov 27;11(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s40035-022-00326-w. Transl Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 36437458 Free PMC article. Review. - Profiling Inflammatory Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid: An Optimized Diagnostic Model for Parkinson's Disease.
Vacchi E, Burrello J, Burrello A, Bolis S, Monticone S, Barile L, Kaelin-Lang A, Melli G. Vacchi E, et al. Biomedicines. 2021 Feb 25;9(3):230. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9030230. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33669043 Free PMC article. - Clinical applications for exosomes: Are we there yet?
Perocheau D, Touramanidou L, Gurung S, Gissen P, Baruteau J. Perocheau D, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2021 Jun;178(12):2375-2392. doi: 10.1111/bph.15432. Epub 2021 May 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33751579 Free PMC article. Review. - "Liquid Biopsy" of White Matter Hyperintensity in Functionally Normal Elders.
Elahi FM, Casaletto KB, Altendahl M, Staffaroni AM, Fletcher E, Filshtein TJ, Glymour MM, Miller BL, Hinman JD, DeCarli C, Goetzl EJ, Kramer JH. Elahi FM, et al. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Nov 9;10:343. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00343. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30483114 Free PMC article. - Connecting Exosomes and Connexins.
Gemel J, Kilkus J, Dawson G, Beyer EC. Gemel J, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Apr 4;11(4):476. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040476. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30987321 Free PMC article.
References
- Schwagerl AL, Mohan PS, Cataldo AM, Vonsattel JP, Kowall NW, Nixon RA. Elevated levels of the endosomal-lysosomal proteinase cathepsin D in cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer disease. J Neurochem 1995;64:443–446. - PubMed
- Nixon RA, Cataldo AM. Lysosomal system pathways: genes to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2006;9:277–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous