Group 2 innate lymphoid cells utilize the IRF4-IL-9 module to coordinate epithelial cell maintenance of lung homeostasis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells utilize the IRF4-IL-9 module to coordinate epithelial cell maintenance of lung homeostasis
A Mohapatra et al. Mucosal Immunol. 2016 Jan.
Abstract
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) have an important role in acute allergic lung inflammation. Given their distribution and function, lung ILC2s are hypothesized to coordinate epithelial responses to the external environment; however, how barrier surveillance is linked to ILC2 activation remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate that alveolar type II cells are the main source of interleukin (IL)-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) generated in response to chitin or migratory helminths. IL-33 and TSLP synergistically induce an interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4)-IL-9 program in ILC2s, and autocrine IL-9 promotes rapid IL-5 and IL-13 production required for optimal epithelial responses in the conducting airways. Thus, ILC2s link alveolar function to regulation of airway flow, revealing a key interaction between resident lymphoid and structural cells that might underlie similar organizational hierarchies in other organs.
Figures
Figure 1
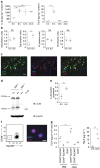
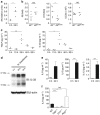
Alveolar type II (ATII) cells are the source of interleukin (IL)-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in response to chitin. (a) ELISA of IL-33 (left) and TSLP (right) from whole lung homogenates of mice at indicated times after chitin administration. (b) Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR analysis of Il33, Tslp, Il2, and Il7 expression from whole lung RNA of mice 6 h after chitin challenge. Values normalized to 18s expression and graphed as fold increase over the mean of the 0 h mice. (c) Immunohistochemistry of naive mouse lungs. Original magnification, × 200. Scale bar, 50 μm. (d) Western blot analysis of whole lung homogenates of mice at indicated times after chitin. “rIL-33” is recombinant protein (Ser109-Ile266; R&D Systems). IB, immunoblot. (e) Ratio of 20-kDa anti-IL-33-reactive band pixel density to total IL-33 pixel density (sum of 20-kDa band and 35-kDa band densities) in each lane, compiled from three independent experiments. (f) Flow cytometry (left) and immunocytochemistry (right) of post-sort ATII cells (DAPIlo CD45lo CD11blo CD31lo EpCAM+) isolated from lungs of mice 3 h after chitin. Original magnification, × 200. Scale bar, 10 μm. (g) ELISA of TSLP in lung populations sorted from mice 3 h after PBS or chitin (left) and in supernatants from MLE12 cells cultured with 40 ng ml−1 phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate for the indicated times (right), compiled from four independent experiments, respectively. Where applicable: *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0005 and NS, not significant (two-tailed _t_-test). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments with 2–4 mice per exposure (a,f) or at least two independent experiments with 3 mice per exposure (b–d). DAPI, 4',6-diamidine-2'-phenylindole dihydrochloride; SPC, surfactant protein C.
Figure 2
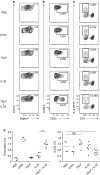
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and interleukin (IL)-33 cooperatively activate group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) in vivo. Mice were analyzed 12 h after administration of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), chitin, 1 μg rTSLP (recombinant TSLP), 50 ng rIL-33, or rTSLP+rIL-33. (a–c) Flow cytometry of eosinophils (a; pre-gate: DAPIlo CD11clo) and ILC2s (b, c; pre-gate: DAPIlo CD11clo CD11blo thy1.2+ CD8lo B220lo NK1.1lo CD4lo) from the lungs of wild-type mice (a,b) or Il5 red5/red5 mice (c). Numbers near gates represent percentage of live cells (DAPIlo CD11clo CD11b+ SSChi Siglec-F+ α4β7lo; a) or mean fluorescence intensity (b,c). (d) Eosinophils (left) and ILC2s (right) graphed as a percentage of live cells, gated as in a and b, respectively. Where applicable: *P<0.05, ***P<0.0005, and NS, not significant (two-tailed _t_-test). Representative flow cytometry data from two independent experiments with 2–4 mice per exposure is shown in a–c, with compiled results in d.
Figure 3
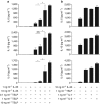
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) synergizes with interleukin (IL)-33 to stimulate group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s). Lung ILC2s were sorted from wild-type mice and cultured for 3 days. Expression of IL-5, IL-13, and IL-9 in supernatants after stimulation with IL-33 and/or TSLP (a) or with IL-33 and either TSLP, IL-7, or IL-2 (b) was assessed by cytometric bead array. Where applicable: *P<0.05 and NS, not significant (two-tailed _t_-test). Data are representative of at least three independent sorts of cells pooled from multiple mice. Bars represent mean+standard deviation. The mean is the average of duplicate or triplicate wells per condition.
Figure 4
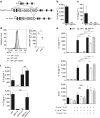
Group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2)-derived interleukin (IL)-9 requires interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) and amplifies cell-intrinsic cytokine production in vitro. (a) Gene targeting schematic for generation of the Il9 9er allele. (b) Expression of IL-9 by cytometric bead array (CBA) in supernatants from 4-day “Th9” cultures of naïve CD4+ T cells sorted from Il9 +/+ and Il9 9er/9er mice. (c) Expression of IL-9 by CBA in supernatants from 3-day cultures of lung ILC2s with 0.1 ng ml−1 rTSLP and 10 ng ml−1 rIL-33, sorted from wild-type (WT), Irf4 −/−, and Il9 9er/9er mice. (d) IRF4 expression (left) in ILC2s and CD4+ CD25+ T cells from the lungs of naive Irf4 +/+ and Irf4 −/− mice, as assessed by flow cytometry; median fluorescence intensities (MFIs) of IRF4 staining in ILC2s are graphed at right. (e) Expression of IL-5 and IL-13 by CBA in supernatants from 3-day cultures of lung ILC2s with the indicated cytokines, sorted from WT, Irf4 −/−, and Il9 9er/9er mice. Number of LiveDeadlo cells by FACS recovered at the end of culture is graphed below. (f) Expression of IL-5 and IL-9 by CBA in supernatants from 3-day cultures of lung ILC2s with 0.1 ng ml−1 rTSLP and 10 ng ml−1 rIL-33. Wells contained 5,000 cells of the indicated genotype or 10,000 cells (last column, 5,000 per genotype). Where applicable: *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0005, and NS, not significant (two-tailed _t_-test). ND, not detected. Bars represent mean+standard deviation. The mean is the average of duplicate or triplicate wells per condition, with individual wells seeded with cells from a single mouse (c, e) or a pool of mice (b, f). Data in b, c, e and f are representative of at least two independent sorts with 2–4 mice per genotype; in d, of at least two independent experiments with at least 3 mice per genotype.
Figure 5
Early interleukin (IL)-9 augments rapid group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) cytokine expression in response to chitin or N. brasiliensis challenge. (a) Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) analysis of whole lung RNA from mice at the indicated times after chitin, normalized to 18 s expression, and graphed in arbitrary units. (b) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Il5 (left) and Il13 (middle) expression and enumeration of ILC2s by flow cytometry (right) in the lungs of Il9 +/+ or Il9 9er/9er mice 25 h after chitin. RT-PCR values are normalized to 18 s expression and presented as fold increase over normalized values in unexposed mice (not shown). (c) ELISA of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and IL-33 from bronchoalveolar lavages (BALs) of mice at the indicated times after N. brasiliensis infection. (d) Western blot analysis of whole lung homogenates from mice at the indicated times after challenge with N. brasiliensis or chitin. IB, immunoblot. (e) Cytometric bead array (CBA) analysis of IL-9, IL-5, and IL-13 in BALs from mice at the indicated times after N. brasiliensis infection. (f) CBA analysis of BALs from mice of the indicated genotypes 24 h after N. brasiliensis infection. Where applicable: *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0005 and NS, not significant (two-tailed _t_-test). Data in a are compiled from two independent experiments; in b–d, representative of two experiments with 2–5 mice per exposure. Data in e and f are compiled from three independent experiments, with each data point representing BALs pooled from 3–5 mice; bars represent mean+standard deviation. ND, not detected.
Figure 6
Interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) and interleukin (IL)-9 are required for the rapid, group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2)-mediated lung epithelial response to N. brasiliensis. Wild-type (WT), Irf4 −/−, and Il9 9er/9er mice were infected with N. brasiliensis, and lungs were harvested 3 days later. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of eosinophils (DAPIlo CD11clo CD11b+ SSChi Siglec-F+; left) and ILC2s (DAPIlo CD11clo CD11blo CD8lo B220lo thy1.2+ CD5lo CD4lo CD45+ CD25+; right). (b) Cytometric bead array analysis of supernatants from 16 h, ex vivo cultures of lung ILC2s sorted from infected mice of the indicated genotypes. (c) Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR analysis of whole lung RNA for expression of Il5, Il13, and IL-13 target genes, normalized to 18s expression and graphed in arbitrary units. Where applicable: *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0005, and NS, not significant (two-tailed _t_-test). Data are representative of at least two experiments with 2–4 mice per genotype.
Similar articles
- Experimental asthma persists in IL-33 receptor knockout mice because of the emergence of thymic stromal lymphopoietin-driven IL-9+ and IL-13+ type 2 innate lymphoid cell subpopulations.
Verma M, Liu S, Michalec L, Sripada A, Gorska MM, Alam R. Verma M, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Sep;142(3):793-803.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.10.020. Epub 2017 Nov 10. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29132961 Free PMC article. - Nematode-Infected Mice Acquire Resistance to Subsequent Infection With Unrelated Nematode by Inducing Highly Responsive Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Lung.
Yasuda K, Adachi T, Koida A, Nakanishi K. Yasuda K, et al. Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 19;9:2132. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02132. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30283458 Free PMC article. - Interleukin-33 Induces the Enzyme Tryptophan Hydroxylase 1 to Promote Inflammatory Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell-Mediated Immunity.
Flamar AL, Klose CSN, Moeller JB, Mahlakõiv T, Bessman NJ, Zhang W, Moriyama S, Stokic-Trtica V, Rankin LC, Putzel GG, Rodewald HR, He Z, Chen L, Lira SA, Karsenty G, Artis D. Flamar AL, et al. Immunity. 2020 Apr 14;52(4):606-619.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.02.009. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32160524 Free PMC article. - Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s): The spotlight in asthma pathogenesis and lung tissue injury.
Sadik S, Lu Y, Zhu S, Cai J, Mi LL. Sadik S, et al. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021 Mar 1;49(2):208-216. doi: 10.15586/aei.v49i2.29. eCollection 2021. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021. PMID: 33641310 Review. - Lung ILC2s link innate and adaptive responses in allergic inflammation.
Martinez-Gonzalez I, Steer CA, Takei F. Martinez-Gonzalez I, et al. Trends Immunol. 2015 Mar;36(3):189-95. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Trends Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25704560 Review.
Cited by
- Dendritic cells in lung immunopathology.
Cook PC, MacDonald AS. Cook PC, et al. Semin Immunopathol. 2016 Jul;38(4):449-60. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0571-3. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Semin Immunopathol. 2016. PMID: 27256370 Free PMC article. Review. - The absence of IL-9 reduces allergic airway inflammation by reducing ILC2, Th2 and mast cells in murine model of asthma.
Li Y, Lan F, Yang Y, Xu Y, Chen Y, Qin X, Lv Z, Wang W, Ying S, Zhang L. Li Y, et al. BMC Pulm Med. 2022 May 6;22(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-01976-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35524325 Free PMC article. - Interleukin-7 Receptor Alpha in Innate Lymphoid Cells: More Than a Marker.
Sheikh A, Abraham N. Sheikh A, et al. Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 11;10:2897. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02897. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31921158 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeted deletion of the TSLP receptor reveals cellular mechanisms that promote type 2 airway inflammation.
Kabata H, Flamar AL, Mahlakõiv T, Moriyama S, Rodewald HR, Ziegler SF, Artis D. Kabata H, et al. Mucosal Immunol. 2020 Jul;13(4):626-636. doi: 10.1038/s41385-020-0266-x. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Mucosal Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32066836 Free PMC article.
References
- 4Spits, H. et al. Innate lymphoid cells - a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13, 145–149 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007334/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI026918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI119944/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL107202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI030663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI113143/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI026918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI026918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128903/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI030663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI_/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials