Mastocytosis: a mutated KIT receptor induced myeloproliferative disorder - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Mastocytosis: a mutated KIT receptor induced myeloproliferative disorder
Anindya Chatterjee et al. Oncotarget. 2015.
Abstract
Although more than 90% systemic mastocytosis (SM) patients express gain of function mutations in the KIT receptor, recent next generation sequencing has revealed the presence of several additional genetic and epigenetic mutations in a subset of these patients, which confer poor prognosis and inferior overall survival. A clear understanding of how genetic and epigenetic mutations cooperate in regulating the tremendous heterogeneity observed in these patients will be essential for designing effective treatment strategies for this complex disease. In this review, we describe the clinical heterogeneity observed in patients with mastocytosis, the nature of relatively novel mutations identified in these patients, therapeutic strategies to target molecules downstream from activating KIT receptor and finally we speculate on potential novel strategies to interfere with the function of not only the oncogenic KIT receptor but also epigenetic mutations seen in these patients.
Keywords: KIT mutations; alternative targets in mastocytosis; mastocytosis; myeloproliferative disorder; signaling pathways in mastocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
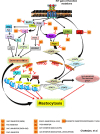
Figure 1. Targeting various downstream signaling pathways from mutated KIT D816V receptors are depicted
PI3K mediated activation of RAS-MAPK-JNK pathway, AKT-ERK and ATK-mTORC2 pathway leads to survival of neoplastic MCs. Recent studies highlight newer pathways mediated by SHP2, FAK, ROCK are described with corresponding inhibitors that hold promise. (1) SHP2 and P13K/GAB2 induced AKT/ERK activation can be inhibited using SHP2 specific inhibitor IIBO8, (2) FAK/TIAM1/RAC1/PAK1 mediated nuclear translocation of active STAT5 in SM patients can be inhibited by targeting FAK and PAK1 (4) with inhibitors, (3) PI3K mediated activation of RAC1 via VAV1 can be targeted using novel RAC1 inhibitor Ehop-016, (5) PI3K/RHOA mediated activation of ROCK1 can be targeted by inhibitor H-1152 against ROCK1, (6) targeting PI3K using inhibitors that have shown promise in other malignancies [69], (7) targeting AKT (GSK2141795), (8) inhibiting JAK with Roxolitinib, Lestaurtinib, Pacritinib, and (9) targeting epigenetic regulators ASXL1, DNMT3A and TET2 by 5-azacytidine (5′-AZA) and 5-aza-2′ deoxycytidine (Decitabine/DAC).
Similar articles
- C-kit activating mutation in a neonate with in-utero presentation of systemic mastocytosis associated with myeloproliferative disorder.
Kuint J, Bielorai B, Gilat D, Birenbaum E, Amariglio N, Rechavi G. Kuint J, et al. Br J Haematol. 1999 Sep;106(3):838-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1999.01683.x. Br J Haematol. 1999. PMID: 10468886 No abstract available. - Detection of the KITD816V mutation in myelodysplastic and/or myeloproliferative neoplasms and acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes predicts concurrent systemic mastocytosis.
Craig JW, Hasserjian RP, Kim AS, Aster JC, Pinkus GS, Hornick JL, Steensma DP, Coleman Lindsley R, DeAngelo DJ, Morgan EA. Craig JW, et al. Mod Pathol. 2020 Jun;33(6):1135-1145. doi: 10.1038/s41379-019-0447-x. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Mod Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31896808 - A transgenic zebrafish model expressing KIT-D816V recapitulates features of aggressive systemic mastocytosis.
Balci TB, Prykhozhij SV, Teh EM, Da'as SI, McBride E, Liwski R, Chute IC, Leger D, Lewis SM, Berman JN. Balci TB, et al. Br J Haematol. 2014 Oct;167(1):48-61. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12999. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Br J Haematol. 2014. PMID: 24989799 - Recent advances in the understanding of mastocytosis: the role of KIT mutations.
Orfao A, Garcia-Montero AC, Sanchez L, Escribano L; REMA. Orfao A, et al. Br J Haematol. 2007 Jul;138(1):12-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06619.x. Br J Haematol. 2007. PMID: 17555444 Review. - KIT and mastocytosis.
Lim KH, Pardanani A, Tefferi A. Lim KH, et al. Acta Haematol. 2008;119(4):194-8. doi: 10.1159/000140630. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Acta Haematol. 2008. PMID: 18566536 Review.
Cited by
- Detection of KIT Mutations in Systemic Mastocytosis: How, When, and Why.
Cilloni D, Maffeo B, Savi A, Danzero AC, Bonuomo V, Fava C. Cilloni D, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 10;25(20):10885. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010885. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456668 Free PMC article. Review. - MASTering systemic mastocytosis: Lessons learned from a large patient cohort.
Tse KY, Chen W, Puttock EJ, Chowdhury S, Miller K, Powell D, Lampson B, Yuen C, Cattie D, Green T, Sullivan E, Zeiger RS. Tse KY, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2024 Jul 27;3(4):100316. doi: 10.1016/j.jacig.2024.100316. eCollection 2024 Nov. J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2024. PMID: 39234417 Free PMC article. - Radiation-associated cutaneous mastocytosis: a case report and review of the literature.
Aaron Trando, Austin KM, Hinds B, Jeong AR, Goodman AM. Aaron Trando, et al. Acta Oncol. 2024 Aug 14;63:685-688. doi: 10.2340/1651-226X.2024.40595. Acta Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39143718 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available. - Genetic Changes in Mastocytes and Their Significance in Mast Cell Tumor Prognosis and Treatment.
Zmorzynski S, Kimicka-Szajwaj A, Szajwaj A, Czerwik-Marcinkowska J, Wojcierowski J. Zmorzynski S, et al. Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;15(1):137. doi: 10.3390/genes15010137. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275618 Free PMC article. Review. - Acute mast cell leukemia without KIT D816V mutation and lack of CD2 and CD25-a case report of rare entity.
Zaremba-Pataj E, Patkowska E, Krzywdzińska A, Szumera-Ciećkiewicz A, Chlebowska-Tuz J. Zaremba-Pataj E, et al. J Hematop. 2023 Mar;16(1):39-47. doi: 10.1007/s12308-022-00526-3. Epub 2023 Jan 20. J Hematop. 2023. PMID: 38175371
References
- Pardanani A. Systemic mastocytosis in adults: 2013 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. American journal of hematology. 2013;88:612–624. - PubMed
- Wang SA, Hutchinson L, Tang G, Chen SS, Miron PM, Huh YO, Jones DM, Bueso-Ramos C, Verstovsek S, Medeiros LJ, Miranda RN. Systemic mastocytosis with associated clonal hematological non-mast cell lineage disease: clinical significance and comparison of chomosomal abnormalities in SM and AHNMD components. American journal of hematology. 2013;88:219–224. - PMC - PubMed
- Miettinen M, Lasota J. KIT (CD117): a review on expression in normal and neoplastic tissues, and mutations and their clinicopathologic correlation. Applied immunohistochemistry & molecular morphology : AIMM / official publication of the Society for Applied Immunohistochemistry. 2005;13:205–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL081111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA173852/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL077177/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA173852/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA134777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL081111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077177/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources