Randomized placebo-controlled dose-ranging and pharmacodynamics study of roxadustat (FG-4592) to treat anemia in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD) patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2015 Oct;30(10):1665-73.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv302. Epub 2015 Aug 3.
Affiliations
- PMID: 26238121
- PMCID: PMC4569392
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfv302
Clinical Trial
Randomized placebo-controlled dose-ranging and pharmacodynamics study of roxadustat (FG-4592) to treat anemia in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD) patients
Anatole Besarab et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015 Oct.
Abstract
Background: Roxadustat (FG-4592) is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor that stimulates erythropoiesis. This Phase 2a study tested efficacy (Hb response) and safety of roxadustat in anemic nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD) subjects.
Methods: NDD-CKD subjects with hemoglobin (Hb) ≤11.0 g/dL were sequentially enrolled into four dose cohorts and randomized to roxadustat or placebo two times weekly (BIW) or three times weekly (TIW) for 4 weeks, in an approximate roxadustat:placebo ratio of 3:1. Efficacy was assessed by (i) mean Hb change (ΔHb) from baseline (BL) and (ii) proportion of Hb responders (ΔHb ≥ 1.0 g/dL). Pharmacodynamic evaluation was performed in a subset of subjects. Safety was evaluated by adverse event frequency/severity.
Results: Of 116 subjects receiving treatment, 104 completed 4 weeks of dosing and 96 were evaluable for efficacy. BL characteristics for roxadustat and placebo groups were comparable. In roxadustat-treated subjects, Hb levels increased from BL in a dose-related manner in the 0.7, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 mg/kg groups. Maximum ΔHb within the first 6 weeks was significantly higher in the 1.5 and 2.0 mg/kg groups than in the placebo subjects. Hb responder rates were dose dependent and ranged from 30% in the 0.7 mg/kg BIW group to 100% in the 2.0 mg/kg BIW and TIW groups versus 13% in placebo.
Conclusions: Roxadustat transiently and moderately increased endogenous erythropoietin and reduced hepcidin. Adverse events were similar in the roxadustat and placebo groups. Roxadustat produced dose-dependent increases in blood Hb among anemic NDD-CKD patients in a placebo-controlled trial.
Clinical trials registration: Clintrials.gov #NCT00761657.
Keywords: HIF-PHI; anemia; chronic kidney disease; erythropoietin; hepcidin.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
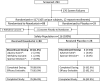
FIGURE 1:
Patient disposition. *The AEs in the roxadustat arm were acute prostatitis (in the 1.0 mg/kg TIW group) and elevated liver enzymes (in the 2.0 mg/kg BIW group). One placebo patient was discontinued because of SAEs of acute pericarditis and renal failure.
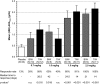
FIGURE 2:
Mean maximum change from BL in Hb (ΔHbmax) and % subjects achieved Hb response, defined as Hb increase by ≥1 g/dL (EE population). Mean (SD) BL Hb was 10.1 (0.7) g/dL for roxadustat subjects and 10.1 (0.6) g/dL for placebo subjects. Pooled placebo data used. Time to response was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method, estimable for groups with >50% response. Nonresponders were censored at Day 42. *From an intergroup _t_-test compared with placebo; n.s.: not significant.
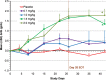
FIGURE 3:
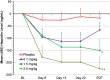
Mean change from BL in Hb (ΔHb) in TIW cohorts (EE population). Mean (SD) BL Hb was 10.1 (0.7) g/dL for roxadustat TIW subjects and 10.1 (0.6) g/dL for placebo subjects. Last-observation-carried-forward (LOCF) method was used to impute missing values. *P < 0.01 intergroup two-sample _t_-tests comparing roxadustat change from BL with placebo change from BL. End of treatment (EOT) for TIW was Day 26.
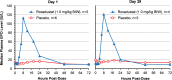
FIGURE 4:
Changes in median plasma EPO on first and final days of treatment. Data are for the PK/PD population (subjects with complete dataset only).
FIGURE 5:
Mean change from BL in serum hepcidin (EE population). Data from BIW and TIW groups were pooled for each dose level. Serum hepcidin was not measured in the roxadustat 1.0 mg/kg dose group. LOCF method was used to impute missing data. *P = 0.048, **P = 0.0013, intergroup two-sample _t_-tests comparing roxadustat change from BL with placebo change from BL. EOT was Day 29 (BIW) or Day 26 (TIW).
Similar articles
- Oral Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor Roxadustat (FG-4592) for the Treatment of Anemia in Patients with CKD.
Provenzano R, Besarab A, Sun CH, Diamond SA, Durham JH, Cangiano JL, Aiello JR, Novak JE, Lee T, Leong R, Roberts BK, Saikali KG, Hemmerich S, Szczech LA, Yu KP, Neff TB. Provenzano R, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jun 6;11(6):982-991. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06890615. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27094610 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Phase 2 studies of oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor FG-4592 for treatment of anemia in China.
Chen N, Qian J, Chen J, Yu X, Mei C, Hao C, Jiang G, Lin H, Zhang X, Zuo L, He Q, Fu P, Li X, Ni D, Hemmerich S, Liu C, Szczech L, Besarab A, Neff TB, Peony Yu KH, Valone FH. Chen N, et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017 Aug 1;32(8):1373-1386. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx011. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28371815 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Roxadustat Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Anemia in Japanese Patients Not on Dialysis: A Phase 2, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.
Akizawa T, Iwasaki M, Otsuka T, Reusch M, Misumi T. Akizawa T, et al. Adv Ther. 2019 Jun;36(6):1438-1454. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-00943-4. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 30953333 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Roxadustat (FG-4592) treatment for anemia in dialysis-dependent (DD) and not dialysis-dependent (NDD) chronic kidney disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Liu J, Zhang A, Hayden JC, Bhagavathula AS, Alshehhi F, Rinaldi G, Kontogiannis V, Rahmani J. Liu J, et al. Pharmacol Res. 2020 May;155:104747. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104747. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32171893 - Roxadustat for the treatment of anemia in patients with chronic kidney diseases: a meta-analysis.
Zhang L, Hou J, Li J, Su SS, Xue S. Zhang L, et al. Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jun 11;13(13):17914-17929. doi: 10.18632/aging.203143. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34115611 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Bibliometric analysis of hypoxia inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor in anemia.
Zheng L, Liu M, Zhang Y, Zhang K, Gu Y, Liu D. Zheng L, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 21;13:1005225. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1005225. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36225579 Free PMC article. - Efficacy and safety of roxadustat for the treatment of anemia in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized double-blind controlled clinical trials.
Chen T, Huang J, Dong H, Xu L, Chen C, Tang Y, Huang W. Chen T, et al. Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 4;9:1029432. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1029432. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36466382 Free PMC article. - 3-Hydroxypyruvate Destabilizes Hypoxia Inducible Factor and Induces Angiostasis.
Singh C, Sharma A, Hoppe G, Song W, Bolok Y, Sears JE. Singh C, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Jul 2;59(8):3440-3448. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-24120. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30025089 Free PMC article. - Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Stabilizers in End Stage Kidney Disease: "Can the Promise Be Kept?".
Crugliano G, Serra R, Ielapi N, Battaglia Y, Coppolino G, Bolignano D, Bracale UM, Pisani A, Faga T, Michael A, Provenzano M, Andreucci M. Crugliano G, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12590. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212590. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830468 Free PMC article. Review. - Sustained plasma hepcidin suppression and iron elevation by Anticalin-derived hepcidin antagonist in cynomolgus monkey.
Hohlbaum AM, Gille H, Trentmann S, Kolodziejczyk M, Rattenstetter B, Laarakkers CM, Katzmann G, Christian HJ, Andersen N, Allersdorfer A, Olwill SA, Meibohm B, Audoly LP, Swinkels DW, van Swelm RPL. Hohlbaum AM, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;175(7):1054-1065. doi: 10.1111/bph.14143. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29329501 Free PMC article.
References
- Collins AJ, Ma JZ, Xia A et al. . Trends in anemia treatment with erythropoietin usage and patient outcomes. Am J Kidney Dis 1998; 32: S133–S141 - PubMed
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA et al. . Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 2007; 298: 2038–2047 - PubMed
- Eschbach JW, Egrie JC, Downing MR et al. . Correction of the anemia of end-stage renal disease with recombinant human erythropoietin. Results of a combined phase I and II clinical trial. N Engl J Med 1987; 316: 73–78 - PubMed
- Regidor DL, Kopple JD, Kovesdy CP et al. . Associations between changes in hemoglobin and administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agent and survival in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 1181–1191 - PubMed
- Revicki DA, Brown RE, Feeny DH et al. . Health-related quality of life associated with recombinant human erythropoietin therapy for predialysis chronic renal disease patients. Am J Kidney Dis 1995; 25: 548–554 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical