Formin-like2 regulates Rho/ROCK pathway to promote actin assembly and cell invasion of colorectal cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Formin-like2 regulates Rho/ROCK pathway to promote actin assembly and cell invasion of colorectal cancer
Yuanfeng Zeng et al. Cancer Sci. 2015 Oct.
Retraction in
Abstract
Formin-like2 (FMNL2) is a member of the diaphanous-related formins family, which act as effectors and upstream modulators of Rho GTPases signaling and control the actin-dependent processes, such as cell motility or invasion. FMNL2 has been identified as promoting the motility and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma (CRC). However, whether FMNL2 regulates Rho signaling to promote cancer cell invasion remains unclear. In this study, we demonstrated an essential role for FMNL2 in the activations of Rho/ROCK pathway, SRF transcription or actin assembly, and subsequent CRC cell invasion. FMNL2 could activate Rho/ROCK pathway, and required ROCK to promote CRC cell invasion. Moreover, FMNL2 promoted the formation of filopodia and stress fiber, and activated the SRF transcription in a Rho-dependent manner. We also demonstrated that FMNL2 was necessary for LPA-induced invasion, RhoA/ROCK activation, actin assembly and SRF activation. FMNL2 was an essential component of LPA signal transduction toward RhoA by directly interacting with LARG. LARG silence inhibited RhoA/ROCK pathway and CRC cell invasion. Collectively, these data indicate that FMNL2, acting as upstream of RhoA by interacting with LARG, can promote actin assembly and CRC cell invasion through a Rho/ROCK-dependent mechanism.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; FMNL2; LARG; Rho/ROCK signaling; invasion.
© 2015 The Authors. Cancer Science published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Figure 1
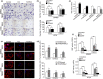
Formin-like2 (FMNL2) regulates Rho/ROCK pathway and requires ROCK to promote cell invasion. (a) Expression of FMNL2 in FMNL2-expressing and FMNL2-silencing cells by western blot. (b) The levels of active GTP-bound RhoA, RhoB, RhoC, Rac1 and Cdc42 and their total proteins in FMNL2-expressing and FMNL2-depleting cells by western blot. (c) Expressions of Cofilin, LIMK, MLC and their phosphorylation levels in FMNL2-expressing and FMNL2-depleting cells by western blot. (d) The levels of RhoA-GTP, p-Cofilin, p-LIMK, p-MLC in FMNL2-expressing cells treated with C3 transferase. (e) The levels of RhoA-GTP, p-Cofilin, p-LIMK, p-MLC in FMNL2-expressing cells treated with Y27632. GAPDH was shown as a control.
Figure 2
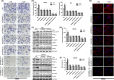
Formin-like2 (FMNL2) promotes actin assembly and SRF activation in a Rho-dependent manner. (a, b) The effects of C3 transferase and Y27632 on FMNL2-induced cell invasion by Boyden chamber. The morphological comparison of cancer cells penetrating the artificial basement membrane is also shown. Scale bars represent 50 μm. (c, d) The effects of C3 transferase and Y27632 on FMNL2-induced F-actin contents stained by phalloidin. Scale bars represent 5 μm. (e) Luciferase activities of the transcription factor serum response factor (SRF) in FMNL2-expressing and FMNL2-depleting cells by luciferase activity assay. (f) The effects of C3 transferase and SRF knockdown on FMNL2-induced SRF transcription. **P < 0.01.
Figure 3
Formin-like2 (FMNL2) is necessary for LPA-induced invasion, actin assembly, RhoA/ROCK and serum response factor (SRF) activations. (a, b) The effects of FMNL2 and mDial1 on lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-induced cell invasion by Boyden chamber. The morphological comparison of cancer cells penetrating the artificial basement membrane is also shown. Scale bars represent 50 μm. (c) The levels of RhoA-GTP, p-Cofilin, p-LIMK, p-MLC in FMNL2-depleting cells under the treatment of LPA. GAPDH is shown as a control. (d, e) F-actin contents in FMNL2 and mDial1-depleting cells under the treatment of LPA. Scale bars represent 5 μm. (f) Luciferase activities of the transcription factor SRF in FMNL2 and mDial1-depleting cells under the treatment of LPA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Figure 4
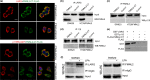
Formin-like2 (FMNL2) directly interacts with LARG. (a) Immuenofluorescence analysis of co-localization of FMNL2 with LARG or p115RhoGEF in SW480/FMNL2 and HT29/FMNL2 cells. Scale bars represent 5 μm. (b) The interaction between LARG and FMNL2 in SW620 and HT29/FMNL2 cells by Co-IP. (c, d) The interaction between FMNL2 and p115RhoGEF in SW620 and HT29/FMNL2 cells by Co-IP. (e) The interaction between FMNL2 and LARG in vitro by GST pull-down assay. (f) The endogenous interaction between FMNL2 and LARG in SW620 cells under the treatment of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) by Co-IP.
Figure 5
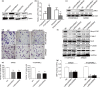
LARG is necessary for RhoA/ROCK activation and colorectal carcinoma (CRC) cell invasion induced by FMNL2. (a, b) Expression of LARG in FMNL2-expressing HT29 cells and FMNL2-depleting SW620 cells. (c) Expression of LARG in LARG-silencing cells by western blot. (d, e) The effect of LARG silence on the invasion of SW620 and HT29/FMNL2 cells by Boyden chamber. The morphological comparison of cancer cells penetrating the artificial basement membrane is also shown. Scale bars represent 50 μm. (f) The levels of RhoA-GTP, p-LIMK and p-MLC in LARG-silencing SW620 and HT29/FMNL2 cells. GAPDH was shown as a control. (g) Luciferase activities of the transcription factor SRF in LARG-silencing SW620 and HT29/FMNL2 cells. *P <0.05, **P <0.01.
Similar articles
- Formin-like 3 regulates RhoC/FAK pathway and actin assembly to promote cell invasion in colorectal carcinoma.
Zeng YF, Xiao YS, Liu Y, Luo XJ, Wen LD, Liu Q, Chen M. Zeng YF, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep 14;24(34):3884-3897. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3884. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30228782 Free PMC article. - Positive feedback between Dia1, LARG, and RhoA regulates cell morphology and invasion.
Kitzing TM, Sahadevan AS, Brandt DT, Knieling H, Hannemann S, Fackler OT, Grosshans J, Grosse R. Kitzing TM, et al. Genes Dev. 2007 Jun 15;21(12):1478-83. doi: 10.1101/gad.424807. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17575049 Free PMC article. - Endothelin A receptor drives invadopodia function and cell motility through the β-arrestin/PDZ-RhoGEF pathway in ovarian carcinoma.
Semprucci E, Tocci P, Cianfrocca R, Sestito R, Caprara V, Veglione M, Castro VD, Spadaro F, Ferrandina G, Bagnato A, Rosanò L. Semprucci E, et al. Oncogene. 2016 Jun 30;35(26):3432-42. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.403. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26522724 - Functions of Rho family of small GTPases and Rho-associated coiled-coil kinases in bone cells during differentiation and mineralization.
Strzelecka-Kiliszek A, Mebarek S, Roszkowska M, Buchet R, Magne D, Pikula S. Strzelecka-Kiliszek A, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 May;1861(5 Pt A):1009-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28188861 Review. - Rho signaling, ROCK and mDia1, in transformation, metastasis and invasion.
Narumiya S, Tanji M, Ishizaki T. Narumiya S, et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009 Jun;28(1-2):65-76. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9170-7. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009. PMID: 19160018 Review.
Cited by
- Simulated microgravity inhibits osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via depolymerizing F-actin to impede TAZ nuclear translocation.
Chen Z, Luo Q, Lin C, Kuang D, Song G. Chen Z, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 22;6:30322. doi: 10.1038/srep30322. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27444891 Free PMC article. - The Aging Vasculature: Glucose Tolerance, Hypoglycemia and the Role of the Serum Response Factor.
Aberdeen H, Battles K, Taylor A, Garner-Donald J, Davis-Wilson A, Rogers BT, Cavalier C, Williams ED. Aberdeen H, et al. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2021 May 17;8(5):58. doi: 10.3390/jcdd8050058. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2021. PMID: 34067715 Free PMC article. Review. - Geometry and network connectivity govern the mechanics of stress fibers.
Kassianidou E, Brand CA, Schwarz US, Kumar S. Kassianidou E, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 7;114(10):2622-2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606649114. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28213499 Free PMC article. - CHG: A Systematically Integrated Database of Cancer Hallmark Genes.
Zhang D, Huo D, Xie H, Wu L, Zhang J, Liu L, Jin Q, Chen X. Zhang D, et al. Front Genet. 2020 Feb 5;11:29. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00029. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32117445 Free PMC article. - Model-based unsupervised learning informs metformin-induced cell-migration inhibition through an AMPK-independent mechanism in breast cancer.
Athreya AP, Kalari KR, Cairns J, Gaglio AJ, Wills QF, Niu N, Weinshilboum R, Iyer RK, Wang L. Athreya AP, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 18;8(16):27199-27215. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16109. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423712 Free PMC article.
References
- Kedrin D, van Rheenen J, Hernandez L, Condeelis J, Segall JE. Cell motility and cytoskeletal regulation in invasion and metastasis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12:143–52. - PubMed
- Faix J, Grosse R. Staying in shape with formins. Dev Cell. 2006;10:693–706. - PubMed
- Eisenmann KM, Harris ES, Kitchen SM, et al. Dia-interacting protein modulates formin-mediated actin assembly at the cell cortex. Curr Biol. 2007;17:579–91. - PubMed
- Sahai E. Mechanisms of cancer cell invasion. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15:87–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous