Pharmacologic overview of Withania somnifera, the Indian Ginseng - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Pharmacologic overview of Withania somnifera, the Indian Ginseng
Nawab John Dar et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Dec.
Abstract
Withania somnifera, also called 'Indian ginseng', is an important medicinal plant of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely used, singly or in combination, with other herbs against many ailments in Indian Systems of Medicine since time immemorial. Withania somnifera contains a spectrum of diverse phytochemicals enabling it to have a broad range of biological implications. In preclinical studies, it has shown anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, anti-stress, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, and anti-diabetic properties. Additionally, it has demonstrated the ability to reduce reactive oxygen species, modulate mitochondrial function, regulate apoptosis, and reduce inflammation and enhance endothelial function. In view of these pharmacologic properties, W. somnifera is a potential drug candidate to treat various clinical conditions, particularly related to the nervous system. In this review, we summarize the pharmacologic characteristics and discuss the mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications of the plant and its active constituents.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Anti-arthritic; Anti-bacterial; Anti-cancer; Anti-diabetic; Anti-inflammatory; Anti-stress; Cardio-protective; Parkinson’s disease; Stroke hypoxia; Withania somnifera.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures
Fig. 1
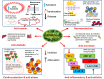
Withania somnifera exerts multiple pharmacologic actions such as neuroprotection (reducing oxidative stress by restoring antioxidant levels, clearance of Aβ levels, attenuating synaptic and dendritic loss and reversing SOD, CAT, GPx, NO and LPO levels), cardio-protection (anti-oxidant balance and activating Nrf-2 and stimulating phase-II detoxification enzymes) anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-stress (inhibiting NFκ-β transcription, MAPK signaling pathways, TNF-α, NO, ROS and IL-8, reducing T-cell population and up-regulating Th1 cytokines), anti-diabetic (stabilizing blood glucose, urine sugar, and glucose-6-phosphate levels significantly), anti-bacterial (inhibiting acid formation, acid tolerance, biofilm formation, spore germination, and hyphal growth) and anti-cancer (cell cycle arrest and activation of p53, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, activation of caspase cascade and PARP-1)
Similar articles
- Pharmacological evaluation of Ashwagandha highlighting its healthcare claims, safety, and toxicity aspects.
Mandlik Ingawale DS, Namdeo AG. Mandlik Ingawale DS, et al. J Diet Suppl. 2021;18(2):183-226. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2020.1741484. Epub 2020 Apr 3. J Diet Suppl. 2021. PMID: 32242751 Review. - Neurodegenerative diseases and Withania somnifera (L.): An update.
Dar NJ, Muzamil Ahmad. Dar NJ, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Jun 28;256:112769. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112769. Epub 2020 Mar 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32240781 Review. - Metabolomic and biotechnological approaches to determine therapeutic potential of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal: A review.
Tripathi N, Shrivastava D, Ahmad Mir B, Kumar S, Govil S, Vahedi M, Bisen PS. Tripathi N, et al. Phytomedicine. 2018 Nov 15;50:127-136. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.08.020. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466971 Review. - Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal - Modern perspectives of an ancient Rasayana from Ayurveda.
Mukherjee PK, Banerjee S, Biswas S, Das B, Kar A, Katiyar CK. Mukherjee PK, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jan 10;264:113157. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113157. Epub 2020 Aug 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32783987 Review. - Review on anticancerous therapeutic potential of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal.
Singh N, Yadav SS, Rao AS, Nandal A, Kumar S, Ganaie SA, Narasihman B. Singh N, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 24;270:113704. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113704. Epub 2020 Dec 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33359918 Review.
Cited by
- SARS-CoV-2 E protein: Pathogenesis and potential therapeutic development.
Zhou S, Lv P, Li M, Chen Z, Xin H, Reilly S, Zhang X. Zhou S, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Mar;159:114242. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114242. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36652729 Free PMC article. Review. - Natural products: a hope for glioblastoma patients.
Vengoji R, Macha MA, Batra SK, Shonka NA. Vengoji R, et al. Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 24;9(31):22194-22219. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25175. eCollection 2018 Apr 24. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29774132 Free PMC article. Review. - Super Critical Fluid Extracted Fatty Acids from Withania somnifera Seeds Repair Psoriasis-Like Skin Lesions and Attenuate Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) Release.
Balkrishna A, Nain P, Chauhan A, Sharma N, Gupta A, Ranjan R, Varshney A. Balkrishna A, et al. Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 25;10(2):185. doi: 10.3390/biom10020185. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31991752 Free PMC article. - Withania somnifera Modulates Radiation-Induced Generation of Lung Cancer Stem Cells via Restraining the Hedgehog Signaling Factors.
Moustafa EM, Abdel Salam HS, Mansour SZ. Moustafa EM, et al. Dose Response. 2022 Feb 24;20(1):15593258221076711. doi: 10.1177/15593258221076711. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. Dose Response. 2022. PMID: 35250409 Free PMC article.
References
- Hepper FN. Old World Withania (Solanaceae): a taxonomic review and key to the species. In: Hawkes JG, Lester RN, Nee M, Estrada N, editors. Solanaceae III: taxonomy, chemistry, evolution. London: Royal Botanic Gardens Kew and Linnean Society of London; 1991.
- Purdie RW, Symon DE, Haegi L. Solanaceae. Flora Aust. 1982;29:184.
- Van Wyk B-E, Wink M. Medicinal plants of the world. Pretoria: Briza Publications; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources