Neurogenesis in the Adult Hippocampus - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Neurogenesis in the Adult Hippocampus
Gerd Kempermann et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015.
Abstract
Of the neurogenic zones in the adult brain, adult hippocampal neurogenesis attracts the most attention, because it is involved in higher cognitive function, most notably memory processes, and certain affective behaviors. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is also found in humans at a considerable level and appears to contribute significantly to hippocampal plasticity across the life span, because it is regulated by activity. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis generates new excitatory granule cells in the dentate gyrus, whose axons form the mossy fiber tract that links the dentate gyrus to CA3. It originates from a population of radial glia-like precursor cells (type 1 cells) that have astrocytic properties, express markers of neural stem cells and divide rarely. They give rise to intermediate progenitor cells with first glial (type 2a) and then neuronal (type 2b) phenotype. Through a migratory neuroblast-like stage (type 3), the newborn, lineage-committed cells exit the cell cycle and enter a maturation stage, during which they extend their dendrites into a the molecular layer and their axon to CA3. They go through a period of several weeks, during which they show increased synaptic plasticity, before finally becoming indistinguishable from the older granule cells.
Copyright © 2015 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
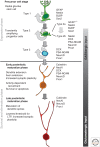
Figure 1.
Developmental stages in the course of adult hippocampal neurogenesis (see text for details). GFAP, Glial fibrillary acidic protein; BLBP, brain lipid-binding protein; DCX, doublecortin; PSA-NCAM, polysialilated neural-cell-adhesion molecule; LTP, long-term potentiation.
Figure 2.
Dendrite development of newborn neurons in the dentate gyrus. Proliferating precursor cells in the subgranular zone (SGZ) were labeled with a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-expressing retrovirus and analyzed at later time points. Here, GFP-positive new granule cells can be seen at ∼2 wk (16 d after injection, left) and 4 wk (28 d after injection, right). During the early postmitotic maturation phase, the cells develop the full morphology of hippocampal granule cells. It is noteworthy that the cells might show a slightly different pace of maturation. After 4 wk, many cells have extended its dendritic tree far into the molecular layer. First dendritic spines can be seen on the dendrites (see Zhao et al. 2006, for details of dendritic development in adult hippocampal neurogenesis). Scale bar, 15 µm. (The figure is contributed by Chunmei Zhao, Salk Institute.)
Similar articles
- Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian dentate gyrus.
Abbott LC, Nigussie F. Abbott LC, et al. Anat Histol Embryol. 2020 Jan;49(1):3-16. doi: 10.1111/ahe.12496. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Anat Histol Embryol. 2020. PMID: 31568602 Review. - Enhanced dendritogenesis and axogenesis in hippocampal neuroblasts of LRRK2 knockout mice.
Paus M, Kohl Z, Ben Abdallah NM, Galter D, Gillardon F, Winkler J. Paus M, et al. Brain Res. 2013 Feb 25;1497:85-100. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.12.024. Epub 2012 Dec 25. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23270607 - p27kip1 Is Required for Functionally Relevant Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Mice.
Hörster H, Garthe A, Walker TL, Ichwan M, Steiner B, Khan MA, Lie DC, Nicola Z, Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Kempermann G. Hörster H, et al. Stem Cells. 2017 Mar;35(3):787-799. doi: 10.1002/stem.2536. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Stem Cells. 2017. PMID: 27790794 - Melatonin Influences Structural Plasticity in the Axons of Granule Cells in the Dentate Gyrus of Balb/C Mice.
Ramírez-Rodríguez GB, Olvera-Hernández S, Vega-Rivera NM, Ortiz-López L. Ramírez-Rodríguez GB, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 25;20(1):73. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010073. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30585191 Free PMC article. - Adult hippocampal neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity and memory: facts and hypotheses.
Bruel-Jungerman E, Rampon C, Laroche S. Bruel-Jungerman E, et al. Rev Neurosci. 2007;18(2):93-114. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2007.18.2.93. Rev Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17593874 Review.
Cited by
- Dementia model mice exhibited improvements of neuropsychiatric symptoms as well as cognitive dysfunction with neural cell transplantation.
Murayama MA, Arimitsu N, Shimizu J, Fujiwara N, Takai K, Okada Y, Hirotsu C, Takada E, Suzuki T, Suzuki N. Murayama MA, et al. Exp Anim. 2021 Aug 6;70(3):387-397. doi: 10.1538/expanim.21-0008. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Exp Anim. 2021. PMID: 33828024 Free PMC article. - Capicua regulates the development of adult-born neurons in the hippocampus.
Hourigan B, Balay SD, Yee G, Sharma S, Tan Q. Hourigan B, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 3;11(1):11725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91168-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34083623 Free PMC article. - IGF1-Stimulated Posttraumatic Hippocampal Remodeling Is Not Dependent on mTOR.
Littlejohn EL, DeSana AJ, Williams HC, Chapman RT, Joseph B, Juras JA, Saatman KE. Littlejohn EL, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 20;9:663456. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.663456. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34095131 Free PMC article. - Sex as a Determinant of Age-Related Changes in the Brain.
Burmistrov DE, Gudkov SV, Franceschi C, Vedunova MV. Burmistrov DE, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 28;25(13):7122. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137122. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000227 Free PMC article. Review. - A Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of the Mouse Hippocampus After Voluntary Exercise.
Methi A, Islam MR, Kaurani L, Sakib MS, Krüger DM, Pena T, Burkhardt S, Liebetanz D, Fischer A. Methi A, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Aug;61(8):5628-5645. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03869-9. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38217668 Free PMC article.
References
- Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M. 2005. Adult neurogenesis: From precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev 85: 523–569. - PubMed
- Aimone JB, Wiles J, Gage FH. 2006. Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat Neurosci 9: 723–727. - PubMed
- Altman J, Bayer SA. 1990a. Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal progenitors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. J Comp Neurol 301: 365–381. - PubMed
- Altman J, Bayer SA. 1990b. Mosaic organization of the hippocampal neuroepithelium and the multiple germinal sources of dentate granule cells. J Comp Neurol 301: 325–342. - PubMed
- Altman J, Das GD. 1965. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol 124: 319–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous