Assessing FOXO1A as a potential susceptibility locus for type 2 diabetes and obesity in American Indians - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2015 Oct;23(10):1960-5.
doi: 10.1002/oby.21236. Epub 2015 Sep 4.
Affiliations
- PMID: 26337673
- PMCID: PMC4586407
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.21236
Assessing FOXO1A as a potential susceptibility locus for type 2 diabetes and obesity in American Indians
Yunhua L Muller et al. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2015 Oct.
Abstract
Objective: A prior genome-wide association study (GWAS) in Pima Indians identified variation within FOXO1A that modestly associated with early-onset (onset age < 25 years) type 2 diabetes (T2D). FOXO1A encodes the forkhead transcription factor involved in pancreatic β-cell growth and hypothalamic energy balance; therefore, FOXO1A was analyzed as a candidate gene for T2D and obesity in a population-based sample of 7,710 American Indians.
Methods: Tag SNPs in/near FOXO1A (minor allele frequency ≥ 0.05) were analyzed for association with T2D at early onset (n = 1,060) and all ages (n = 7,710) and with insulin secretion (n = 298). SNPs were also analyzed for association with maximum body mass index (BMI) in adulthood (n = 5,918), maximum BMI z-score in childhood (n = 5,350), and % body fat (n = 555).
Results: An intronic SNP rs2297627 associated with early-onset T2D [OR = 1.34 (1.13-1.58), P = 8.7 × 10(-4)] and T2D onset at any age [OR = 1.19 (1.09-1.30), P = 1 × 10(-4) ]. The T2D risk allele also associated with lower acute insulin secretion (β = 0.88, as a multiplier, P = 0.02). Another intronic SNP (rs1334241, D' = 0.99, r(2) = 0.49 with rs2297627) associated with maximum adulthood BMI (β = 1.02, as a multiplier, P = 3 × 10(-5)), maximum childhood BMI z-score (β = 0.08, P = 3 × 10(-4)), and % body fat (β = 0.83%, P = 0.04).
Conclusions: Common variation in FOXO1A may modestly affect risk for T2D and obesity in American Indians.
© 2015 The Obesity Society.
Figures
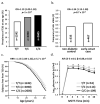
Figure 1. Association data for rs2297627
Association with prevalence of T2D at any age (a); risk allele frequency distribution in early-onset T2D case and control groups (b); Kaplan-Meier survival curve for time to T2D onset (c) and plasma insulin concentrations in response to a 25-g intravenous glucose bolus (IVGTT) (d). The p value and OR for T2D at any age are adjusted for age, sex, birth year and heritage. The p value and OR for early-onset T2D (case-control analysis) are adjusted for sex and birth year and heritage. Cox proportional hazards model is used to determine the hazard rate ratio (HRR) for association with age of T2D onset including sex, birth-year, American/European ancestry and self-reported Pima heritage as covariates. Data for plasma insulin and glucose concentrations are given as adjusted mean±SE by genotypes. AIR (mean insulin increment from 3-5 min) is log10-transformed before analyses to approximate a normal distribution, and beta is exponentiated to obtain the effect per risk allele, expressed as a multiplier. The_p_ value and beta for AIR are adjusted for age, sex, % body fat and rate of glucose disappearance during insulin-stimulation. The p value and beta for plasma glucose concentrations are adjusted for age, sex and % body fat.
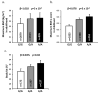
Figure 2. Association data for rs1334241
Maximum BMI in adulthood (a), maximum BMI z-score in childhood (b) and % body fat in adulthood (c). Adult BMI is the maximum BMI (kg/m2) from a non-diabetic examination recorded at age ≥15 years. Childhood BMI z-score is the maximum sex- and age-specific z-score identified between the ages of 5 and 20 years. Data are given as adjusted mean±SE by genotypes. Adult BMI is loge−transformed before analyses to approximate a normal distribution, and beta is exponentiated to obtain the effect estimate for each risk allele, expressed as a multiplier. Beta and_p_ values for adult BMI and childhood BMI z-score are adjusted for age, sex, birth year and heritage. Beta and p values for % body fat are adjusted for age, sex and heritage.
Similar articles
- A cis-eQTL in PFKFB2 is associated with diabetic nephropathy, adiposity and insulin secretion in American Indians.
Muller YL, Piaggi P, Hanson RL, Kobes S, Bhutta S, Abdussamad M, Leak-Johnson T, Kretzler M, Huang K, Weil EJ, Nelson RG, Knowler WC, Bogardus C, Baier LJ. Muller YL, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2015 May 15;24(10):2985-96. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv040. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25662186 Free PMC article. - Common genetic variation in and near the melanocortin 4 receptor gene (MC4R) is associated with body mass index in American Indian adults and children.
Muller YL, Thearle MS, Piaggi P, Hanson RL, Hoffman D, Gene B, Mahkee D, Huang K, Kobes S, Votruba S, Knowler WC, Bogardus C, Baier LJ. Muller YL, et al. Hum Genet. 2014 Nov;133(11):1431-41. doi: 10.1007/s00439-014-1477-6. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 25103139 Free PMC article. - Assessing variation across 8 established East Asian loci for type 2 diabetes mellitus in American Indians: Suggestive evidence for new sex-specific diabetes signals in GLIS3 and ZFAND3.
Muller YL, Piaggi P, Chen P, Wiessner G, Okani C, Kobes S, Knowler WC, Bogardus C, Hanson RL, Baier LJ. Muller YL, et al. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017 May;33(4). doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2869. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 27862917 - Insights into the Genetic Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes from Genome-Wide Association Studies of Obesity-Related Traits.
Karaderi T, Drong AW, Lindgren CM. Karaderi T, et al. Curr Diab Rep. 2015 Oct;15(10):83. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0648-8. Curr Diab Rep. 2015. PMID: 26363598 Free PMC article. Review. - The genetics of bipolar disorder with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Miola A, De Filippis E, Veldic M, Ho AM, Winham SJ, Mendoza M, Romo-Nava F, Nunez NA, Gardea Resendez M, Prieto ML, McElroy SL, Biernacka JM, Frye MA, Cuellar-Barboza AB. Miola A, et al. J Affect Disord. 2022 Sep 15;313:222-231. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.06.084. Epub 2022 Jun 30. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 35780966 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Chlorogenic Acid Targeting of the AKT PH Domain Activates AKT/GSK3β/FOXO1 Signaling and Improves Glucose Metabolism.
Gao J, He X, Ma Y, Zhao X, Hou X, Hao E, Deng J, Bai G. Gao J, et al. Nutrients. 2018 Sep 23;10(10):1366. doi: 10.3390/nu10101366. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30249058 Free PMC article. - FoxO integration of insulin signaling with glucose and lipid metabolism.
Lee S, Dong HH. Lee S, et al. J Endocrinol. 2017 May;233(2):R67-R79. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0002. Epub 2017 Feb 17. J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28213398 Free PMC article. Review. - Myeloid FoxO1 depletion attenuates hepatic inflammation and prevents nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Lee S, Usman TO, Yamauchi J, Chhetri G, Wang X, Coudriet GM, Zhu C, Gao J, McConnell R, Krantz K, Rajasundaram D, Singh S, Piganelli J, Ostrowska A, Soto-Gutierrez A, Monga SP, Singhi AD, Muzumdar R, Tsung A, Dong HH. Lee S, et al. J Clin Invest. 2022 Jul 15;132(14):e154333. doi: 10.1172/JCI154333. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35700043 Free PMC article. - SIRT1 rs10823108 and FOXO1 rs17446614 responsible for genetic susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy.
Zhao Y, Wei J, Hou X, Liu H, Guo F, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Qu Y, Gu J, Zhou Y, Jia X, Qin G, Feng L. Zhao Y, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 31;7(1):10285. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10612-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28860538 Free PMC article. - Characterization of Exome Variants and Their Metabolic Impact in 6,716 American Indians from the Southwest US.
Kim HI, Ye B, Gosalia N; Regeneron Genetics Center; Köroğlu Ç, Hanson RL, Hsueh WC, Knowler WC, Baier LJ, Bogardus C, Shuldiner AR, Van Hout CV. Kim HI, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Aug 6;107(2):251-264. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.06.009. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 32640185 Free PMC article.
References
- Kim HJ, Kobayashi M, Sasaki T, Kikuchi O, Amano K, Kitazumi T, et al. Overexpression of FoxO1 in the hypothalamus and pancreas causes obesity and glucose intolerance. Endocrinology. 2012;153:659–671. - PubMed
- Kim MS, Pak YK, Jang PG, Namkoong C, Choi YS, Won JC, et al. Role of hypothalamic Foxo1 in the regulation of food intake and energy homeostasis. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:901–906. - PubMed
- Knowler WC, Pettitt DJ, Saad MF, Bennett PH. Diabetes mellitus in the Pima Indians: incidence, risk factors and pathogenesis. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1990;6:1–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous