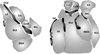The basolateral amygdala in reward learning and addiction - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The basolateral amygdala in reward learning and addiction
Kate M Wassum et al. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Oct.
Abstract
Sophisticated behavioral paradigms partnered with the emergence of increasingly selective techniques to target the basolateral amygdala (BLA) have resulted in an enhanced understanding of the role of this nucleus in learning and using reward information. Due to the wide variety of behavioral approaches many questions remain on the circumscribed role of BLA in appetitive behavior. In this review, we integrate conclusions of BLA function in reward-related behavior using traditional interference techniques (lesion, pharmacological inactivation) with those using newer methodological approaches in experimental animals that allow in vivo manipulation of cell type-specific populations and neural recordings. Secondly, from a review of appetitive behavioral tasks in rodents and monkeys and recent computational models of reward procurement, we derive evidence for BLA as a neural integrator of reward value, history, and cost parameters. Taken together, BLA codes specific and temporally dynamic outcome representations in a distributed network to orchestrate adaptive responses. We provide evidence that experiences with opiates and psychostimulants alter these outcome representations in BLA, resulting in long-term modified action.
Keywords: Amphetamine; Basolateral amygdala; Discounting; Opiate; Orbitofrontal cortex; Outcome devaluation; Reversal learning.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest. There is nothing to disclose nor are there any conflicts of interest.
Figures
Figure 1. Amygdala and reward
Pubmed search terms “amygdala” and “reward” or “amygdala” and “fear” from 1960–2014, excluding 2015. A steeper rise in the number of publications on the amygdala in appetitive behavior now accounts for approximately half of the reports in the 2010s.
Figure 2. Rodent and monkey amygdala nuclei
Coronal sections of amygdala nuclei in the mouse and the macaque monkey. Modified from John et al. 2013.
Figure 3. An adapted model of reward procurement for the integration of incentive value, reward history, and costs by the basolateral amygdala (BLA)
According to this model, a signal of subjective reward intensity (RI), which we call incentive value, gets integrated from the past into the present (a vertical line denotes past and present). In the present, there is an integration of cost parameters (risk, delay, effort). The evidence we review suggests this integration occurs dynamically in the BLA, as part of a distributed network. The putative product of BLA signaling (to areas like the dorsomedial striatum, nucleus accumbens, and orbitofrontal cortex) is a position on the “reward mountain” (A through E). The mountain is a scalar representation of “cost” and “payoff.” Modified from Breton et al. 2014.
Similar articles
- The Medial Orbitofrontal Cortex-Basolateral Amygdala Circuit Regulates the Influence of Reward Cues on Adaptive Behavior and Choice.
Lichtenberg NT, Sepe-Forrest L, Pennington ZT, Lamparelli AC, Greenfield VY, Wassum KM. Lichtenberg NT, et al. J Neurosci. 2021 Aug 25;41(34):7267-7277. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0901-21.2021. Epub 2021 Jul 16. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34272313 Free PMC article. - Neural Representations of Unconditioned Stimuli in Basolateral Amygdala Mediate Innate and Learned Responses.
Gore F, Schwartz EC, Brangers BC, Aladi S, Stujenske JM, Likhtik E, Russo MJ, Gordon JA, Salzman CD, Axel R. Gore F, et al. Cell. 2015 Jul 2;162(1):134-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.027. Cell. 2015. PMID: 26140594 Free PMC article. - Dissociable roles for the basolateral amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex in decision-making under risk of punishment.
Orsini CA, Trotta RT, Bizon JL, Setlow B. Orsini CA, et al. J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 28;35(4):1368-79. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3586-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25632115 Free PMC article. - Amygdala-cortical collaboration in reward learning and decision making.
Wassum KM. Wassum KM. Elife. 2022 Sep 5;11:e80926. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80926. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36062909 Free PMC article. Review. - Ventral striatal control of appetitive motivation: role in ingestive behavior and reward-related learning.
Kelley AE. Kelley AE. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004 Jan;27(8):765-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2003.11.015. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004. PMID: 15019426 Review.
Cited by
- Multidimensional processing in the amygdala.
Gothard KM. Gothard KM. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Oct;21(10):565-575. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0350-y. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32839565 Free PMC article. Review. - Linking RDoC and HiTOP: A new interface for advancing psychiatric nosology and neuroscience.
Michelini G, Palumbo IM, DeYoung CG, Latzman RD, Kotov R. Michelini G, et al. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021 Jun;86:102025. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2021.102025. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33798996 Free PMC article. Review. - Dose mediates the protracted effects of adolescent THC exposure on reward and stress reactivity in males relevant to perturbation of the basolateral amygdala transcriptome.
Ferland JN, Ellis RJ, Rompala G, Landry JA, Callens JE, Ly A, Frier MD, Uzamere TO, Hurd YL. Ferland JN, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Jun;28(6):2583-2593. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01467-0. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 35236956 - Importin α3 (KPNA3) Deficiency Augments Effortful Reward-Seeking Behavior in Mice.
Aomine Y, Sakurai K, Macpherson T, Ozawa T, Miyamoto Y, Yoneda Y, Oka M, Hikida T. Aomine Y, et al. Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 30;16:905991. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.905991. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35844217 Free PMC article. - Occasion setting.
Fraser KM, Holland PC. Fraser KM, et al. Behav Neurosci. 2019 Apr;133(2):145-175. doi: 10.1037/bne0000306. Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30907616 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Aggleton JP, Passingham RE. An assessment of the reinforcing properties of foods after amygdaloid lesions in rhesus monkeys. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1982;96(1):71–77. - PubMed
- Aggleton JP. The amygdala: a functional analysis. second ed. New York: Oxford UP; 2000.
- Balleine BW, Dickinson A. The role of incentive learning in instrumental outcome revaluation by sensory-specific satiety. Learn. Behav. 1998;26(1):46–59.
- Balleine BW, Garner C, Gonzalez F, Dickinson A. Motivational control of heterogeneous instrumental chains. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 1995;21:203–217.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources