Reduced vascular events in type 2 diabetes by biguanide relative to sulfonylurea: study in a Japanese Hospital Database - PubMed (original) (raw)
Observational Study
Reduced vascular events in type 2 diabetes by biguanide relative to sulfonylurea: study in a Japanese Hospital Database
Makito Tanabe et al. BMC Endocr Disord. 2015.
Abstract
Background: Some oral hypoglycemic agents (OHAs) have been suggested to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We ascertained if OHAs affect CVD risk in a cohort analysis of a multicenter medical-cost accounting database in Japan.
Methods: Data of 4095 and 1273 T2DM patients in study 1 and study 2, respectively, were extracted from the database based on the following conditions: (i) began treatment with a single OHA (sulfonylurea, biguanide, thiazolidinedione, α-glucosidase inhibitor, glinide, or dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor) and continued the medication for ~1-1.4 years; (ii) hemoglobin (Hb)A1c level at baseline was available; (iii) age at baseline was 40-70 years; (iv) presence or absence of CVD history was not considered in study 1, but presence of CVD history was considered in study 2. Effects of OHAs relative to sulfonylurea on CVD risk according to ICD-10 were analysed using Kaplan-Meier curves during 104 weeks.
Results: In study 1 targeting T2DM patients with and without a history of CVD, initial and baseline treatment with a biguanide significantly lowered the risk of CVD compared with that with a sulfonylurea, and was independent of HbA1c control. In study 2, a similar significant preventive effect of a biguanide on CVD risk relative to a sulfonylurea was observed in T2DM patients with history of CVD.
Conclusions: Initial treatment and baseline treatment with a biguanide can reduce CVD risk relative to a sulfonylurea independent of the blood glucose-lowering effect of the biguanide in Japanese T2DM patients.
Figures
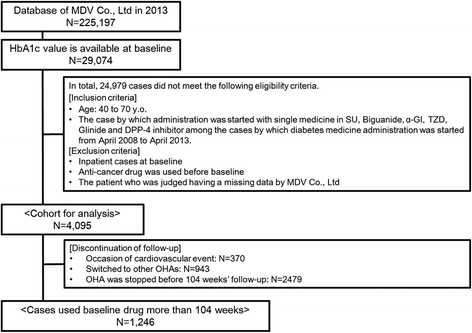
Fig. 1
Outline and flowchart of the protocol for patient selection for analyses of cardiovascular events in study 1
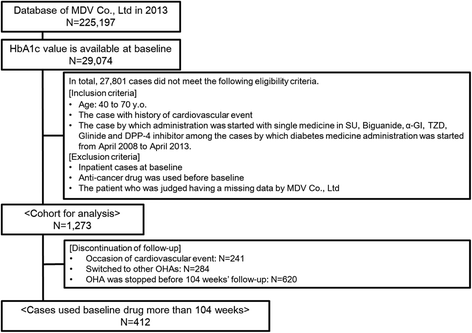
Fig. 2
Outline and flowchart of the protocol for patient selection for analyses of cardiovascular events in study 2
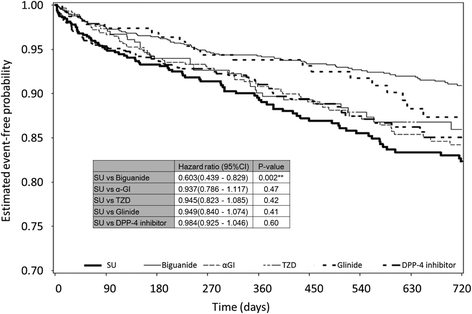
Fig. 3
Kaplan-Meier curve for cardiovascular events during 104 weeks in patients with T2DM with or without a history of cardiovascular events. Number of patients in each drug group is listed in Table 1. Numbers of those in which 104-week follow-up was completed were 629 in SU, 1305 in biguanide, 592 in α-GI, 351 in TZD, 223 in glinide, and 995 in DPP-4 inhibitor groups, respectively (Table 1). Numbers of those in which a cardiovascular event was observed were 80 in SU, 84 in biguanide, 63 in α-GI, 35 in TZD, 21 in glinide, and 87 in DPP-4 inhibitor groups, respectively (Table 3A). Statistical comparison of cardiovascular events during 104 weeks in patients with T2DM with a history of cardiovascular events is shown in the inserted small table. Hazard ratio, Cox proportional hazard model adjusted by sex, age, HbA1c value (NGSP), use or non-use of anti-hypertensive drugs, use or non-use of anti-dyslipidemia drugs. CI indicates a 95 % confidence interval. **P < 0.01
Similar articles
- Prescription of oral hypoglycemic agents for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective cohort study using a Japanese hospital database.
Tanabe M, Motonaga R, Terawaki Y, Nomiyama T, Yanase T. Tanabe M, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2017 Mar;8(2):227-234. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12567. Epub 2016 Sep 15. J Diabetes Investig. 2017. PMID: 27549920 Free PMC article. - Differential cardiovascular outcomes after dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sulfonylurea, and pioglitazone therapy, all in combination with metformin, for type 2 diabetes: a population-based cohort study.
Seong JM, Choi NK, Shin JY, Chang Y, Kim YJ, Lee J, Kim JY, Park BJ. Seong JM, et al. PLoS One. 2015 May 20;10(5):e0124287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124287. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25992614 Free PMC article. - Comparative cardiovascular safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists versus other antidiabetic drugs in routine care: a cohort study.
Patorno E, Everett BM, Goldfine AB, Glynn RJ, Liu J, Gopalakrishnan C, Kim SC. Patorno E, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016 Aug;18(8):755-65. doi: 10.1111/dom.12665. Epub 2016 May 2. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016. PMID: 27003762 - Oral antidiabetic agents: current role in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Krentz AJ, Bailey CJ. Krentz AJ, et al. Drugs. 2005;65(3):385-411. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565030-00005. Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15669880 Review. - Type 2 diabetes: the many facets of care.
Hall MA. Hall MA. Home Healthc Nurse. 2008 Jun;26(6):346-53; quiz 354-5. doi: 10.1097/01.NHH.0000324307.56212.dc. Home Healthc Nurse. 2008. PMID: 18562819 Review.
Cited by
- Semaglutide Adherence and Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Evidence From Real-World Data in Japan.
Masudo C, Horii T, Suzuki R, Mihara K. Masudo C, et al. Cureus. 2025 Mar 13;17(3):e80511. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80511. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40225492 Free PMC article. - The Impact of Cardiac Comorbidity Sequence at Baseline and Mortality Risk in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Population-Based Cohort Study.
Lee S, Huang H, Lee TTL, Chung CT, Chou OHI, Leung KSK, Wai AKC, Wong WT, Liu T, Chang C, Tse G. Lee S, et al. Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 22;12(12):1956. doi: 10.3390/life12121956. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556321 Free PMC article. - Heart failure and chronic kidney disease manifestation and mortality risk associations in type 2 diabetes: A large multinational cohort study.
Birkeland KI, Bodegard J, Eriksson JW, Norhammar A, Haller H, Linssen GCM, Banerjee A, Thuresson M, Okami S, Garal-Pantaler E, Overbeek J, Mamza JB, Zhang R, Yajima T, Komuro I, Kadowaki T. Birkeland KI, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020 Sep;22(9):1607-1618. doi: 10.1111/dom.14074. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020. PMID: 32363737 Free PMC article. - Prescription of oral hypoglycemic agents for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective cohort study using a Japanese hospital database.
Tanabe M, Motonaga R, Terawaki Y, Nomiyama T, Yanase T. Tanabe M, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2017 Mar;8(2):227-234. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12567. Epub 2016 Sep 15. J Diabetes Investig. 2017. PMID: 27549920 Free PMC article.
References
- Roumie CL, Hung AM, Greevy RA, Grijalva CG, Liu X, Murff HJ, Elasy TA, Griffin MR. Comparative effectiveness of sulfonylurea and metformin monotherapy on cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157:601–610. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-157-9-201211060-00003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical