Fusobacterium nucleatum Osteomyelitis in 3 Previously Healthy Children: A Case Series and Review of the Literature - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Fusobacterium nucleatum Osteomyelitis in 3 Previously Healthy Children: A Case Series and Review of the Literature
Seth W Gregory et al. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2015 Dec.
Abstract
Fusobacterium nucleatum is a rare cause of monomicrobial osteomyelitis in children. We describe the cases of 3 children with F. nucleatum osteomyelitis of the distal femoral epiphysis with concurrent septic arthritis and review 6 other cases reported in the literature. Our report emphasizes the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion for anaerobic osteomyelitis, given its atypical presentation and the unique growth requirements of anaerobic bacteria.
Keywords: anaerobic osteomyelitis; epiphyseal lesion; pediatric.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
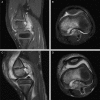
Figure 1.
Sagittal SPGR post-contrast image (A) and T2 axial image (B) showing discrete lesion in the femoral notch in the posteromedial aspect of the knee. Diffuse edema was also noted throughout the notch and medial epiphysis. Repeat MRI after knee arthrotomy and 7 days of piperacillin-tazobactam shows worsening of the osteomyelitis and large joint effusion (C, D).
Similar articles
- Joint and bone infections due to anaerobic bacteria in children.
Brook I. Brook I. Pediatr Rehabil. 2002 Jan-Mar;5(1):11-9. doi: 10.1080/1363849021000007150. Pediatr Rehabil. 2002. PMID: 12396847 Review. - Septic arthritis of the hip due to Fusobacterium nucleatum.
Chryssagi AM, Brusselmans CB, Rombouts JJ. Chryssagi AM, et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2001;20(3):229-31. doi: 10.1007/s100670170072. Clin Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11434480 - Subacute osteomyelitis of the femur due to Fusobacterium nucleatum in a 7-year-old boy.
Budd E, Johnson DS, Thomas E, Sadarangani M. Budd E, et al. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015 Mar;34(3):324-6. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000558. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015. PMID: 25742081 Review. - Osteomyelitis of the pelvis due to Fusobacterium nucleatum.
Beauchamp RD, Cimolai N. Beauchamp RD, et al. Can J Surg. 1991 Dec;34(6):618-20. Can J Surg. 1991. PMID: 1747843 - Diagnosis and treatment of Fusobacterium nucleatum discitis and vertebral osteomyelitis: case report and review of the literature.
Ramos A, Berbari E, Huddleston P. Ramos A, et al. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013 Jan 15;38(2):E120-2. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31827b4d61. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013. PMID: 23132536 Review.
Cited by
- A rapid and sensitive CRISPR-Cas12a for the detection of Fusobacterium nucleatum.
Qu H, Zhang W, Li J, Fu Q, Li X, Wang M, Fu G, Cui J. Qu H, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Feb 6;12(2):e0362923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03629-23. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38197659 Free PMC article. - Fusobacterium nucleatum infection-induced neurodegeneration and abnormal gut microbiota composition in Alzheimer's disease-like rats.
Yan C, Diao Q, Zhao Y, Zhang C, He X, Huang R, Li Y. Yan C, et al. Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 16;16:884543. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.884543. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36188448 Free PMC article. - Fusobacterium nucleatum and colorectal cancer: From phenomenon to mechanism.
Ou S, Wang H, Tao Y, Luo K, Ye J, Ran S, Guan Z, Wang Y, Hu H, Huang R. Ou S, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 29;12:1020583. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1020583. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36523635 Free PMC article. Review. - More Than Just a Periodontal Pathogen -the Research Progress on Fusobacterium nucleatum.
Chen Y, Huang Z, Tang Z, Huang Y, Huang M, Liu H, Ziebolz D, Schmalz G, Jia B, Zhao J. Chen Y, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 3;12:815318. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.815318. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35186795 Free PMC article. Review. - Osteomyelitis of the Distal Phalanx of the Thumb due to Parvimonas micra and Fusobacterium nucleatum: A Case Report.
Tanaka K, Iwasaki T, Kawano M, Kubota Y, Itonaga I, Tsumura H. Tanaka K, et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Aug 7;7(8):ofaa330. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa330. eCollection 2020 Aug. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32851111 Free PMC article.
References
- Conrad DA. Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis. Pediatr Rev 2010; 31:464–71. - PubMed
- Brook I. Joint and bone infections due to anaerobic bacteria in children. Pediatr Rehabil 2002; 5:11–9. - PubMed
- Lewis RP, Sutter VL, Finegold SM. Bone infections involving anaerobic bacteria. Medicine 1978; 57:297–305. - PubMed
- Brook I. Fusobacterial infections in children. J Infect 1994; 28:155–65. - PubMed
- Buckingham SC. Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, and Prevotella. In: Feigin RD, Cherry JD, eds. Feigin and Cherry's Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014: 1825–34.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources