MicroRNA-137 Negatively Regulates H₂O₂-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis Through CDC42 - PubMed (original) (raw)
MicroRNA-137 Negatively Regulates H₂O₂-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis Through CDC42
Junnan Wang et al. Med Sci Monit. 2015.
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress, inducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis or myocardial ischemia, is the major denominator of many cardiac diseases. In this study, we intended to explore the regulatory function of microRNA-137 (miR-137) in oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Material and methods: Cardiomyocytes were extracted from newborn C57BL/6 mice and cultured in vitro. Apoptosis was induced by H2O2, and evaluated by TUNEL assay. The effect of cardiomyocyte apoptosis on gene expression of miR-137 was evaluated by qRT-PCR. Lentivirus was used to stably down-regulate miR-137, and the subsequent effects of miR-137 down-regulation on cardiomyocyte apoptosis, its targeted gene CDC42, and caspase pathway were evaluated by TUNEL assay, dual-luciferase reporter assay, and Western blot assay, respectively. Finally, CDC42 was down-regulated by siRNA and its effect on miR-137-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis protection was examined.
Results: H2O2 induced significant apoptosis and up-regulated miR-137 in cardiomyocytes, whereas lentivirus-mediated miR-137 down-regulation protected against apoptosis. CDC42 was the direct target gene of miR-137 and proteins of CDC42, caspase-3, and caspase-9 were all regulated by miR-137 down-regulation in cardiomyocyte apoptosis. SiRNA-mediated CDC42 down-regulation reversed the protection of miR-137 down-regulation against cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Conclusions: Our work demonstrated miR-137 and CDC42 are critical regulators in cardiomyocyte apoptosis. It may help to identify the molecular targets to prevent myocardial injury in human patients.
Figures
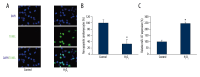
Figure 1
The effect of H2O2 on cardiomyocyte apoptosis and gene expression of miR-137. Cardiomyocytes were extracted from P1–P3 mice and incubated with 100 μM H2O2 for 24 h. (A) Cardiomyocyte apoptosis was evaluated by a TUNEL assay (green). The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (B) The percentages of non-apoptotic cardiomyocytes (DAPI-positive/TUNEL-negative) were compared between Control and H2O2 treatment (* P<0.05). (C) The gene expression levels of miR-137 were also compared between Control and H2O2 treatment (* P<0.05).
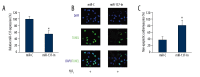
Figure 2
The effect of miR-137 down-regulation on H2O2 -induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes were transfected with lentiviruses of mmu-miR-137 inhibitor (miR-137-In) or its negative control miRNA (miR-C). (A) Twenty-four hours after lentiviral transfection, qRT-PCR was performed to measure the efficacy of lentiviral infection (* P<0.05). (B) Cardiomyocytes were then treated with 100 μM H2O2 for another 24 h, followed by a TUNEL assay to evaluate the effect of miR-137 down-regulation on cardiomyocyte apoptosis. (C) The percentages of non-apoptotic cardiomyocytes (DAPI-positive/TUNEL-negative) were compared between the cardiomyocytes transfected with miR-C and the ones transfected with miR-137-In (* P<0.05).
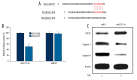
Figure 3
MiR-137 regulated CDC42 and caspase proteins in H2O2 -induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. (A) The putative binding sites of murine miR-137 on wild-type (WT) CDC42 3′-UTR was highlighted. A mutated (Mut) CDC42 3′-UTR sequence was generated for the application of luciferase assay. (B) In a dual-luciferase reporter assay, HEK293T cells were transfected with firefly luciferase reporter inserted with WT CDC42 3′-UTR (CDC42-WT), or the reporter inserted with Mut CDC42 3′-UTR (CDC42-WT). Also, cells were co-transfected with either miR-137 mimics or its negative control miRNA (miR-NC). Twenty-four hours after transfection, relative luciferase activities were evaluated and normalized to the values in cells transfected with CDC42-MU (* P<0.05). (C) Cardiomyocytes were transfected with either miR-C or miR-137-In lentiviruses for 24 h, followed by another 24 h treatment of 100 μM H2O2. Western blotting analysis was used to compare the protein expression levels of CDC42, caspase-3 and caspase-9.
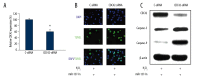
Figure 4
CDC42 down-regulation reversed the effect of miR-137 on H2O2-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. (A) Cardiomyocytes were transfected with CDC42 specific siRNA (CDC42-siRNA) or its negative control siRNA (C-siRNA) for 24 h. QRT-PCR was used to evaluate the transfection efficiency (* P<0.05). (B) Cardiomyocytes were transfected with miR-137-In for 24 h, followed by another 24 h transfection of either CDC42-siRNA or C-siRNA. Then, cardiomyocytes were treated with 100 μM H2O2 for 24 h, followed by a TUNEL assay to evaluate the effect of CDC42 down-regulation on cardiomyocyte apoptosis. (C) Western blotting analysis was ALSO used to compare the protein expression levels of CDC42, caspase-3 and caspase-9.
Similar articles
- BDNF-mediates Down-regulation of MicroRNA-195 Inhibits Ischemic Cardiac Apoptosis in Rats.
Hang P, Sun C, Guo J, Zhao J, Du Z. Hang P, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2016 Jul 9;12(8):979-89. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.15071. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27489501 Free PMC article. - MiR-381 negatively regulates cardiomyocyte survival by suppressing Notch signaling.
Lu L, Zhang H, Dong W, Peng W, Yang J. Lu L, et al. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2018 Sep;54(8):610-619. doi: 10.1007/s11626-018-0277-z. Epub 2018 Aug 13. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2018. PMID: 30105734 - MiR-208a aggravates H2O2-induced cardiomyocyte injury by targeting APC.
Liu F, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Lu Y, Lu X. Liu F, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 1;864:172668. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172668. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31545986 - Downregulation of microRNA-100 protects H2O2-induced apoptosis in neonatal cardiomyocytes.
Chen A, Li G, Chen L, Guo J, Liu Y. Chen A, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):5491-6. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191255 Free PMC article. - Small molecules, big effects: the role of microRNAs in regulation of cardiomyocyte death.
Skommer J, Rana I, Marques FZ, Zhu W, Du Z, Charchar FJ. Skommer J, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jul 17;5(7):e1325. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.287. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25032848 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- MicroRNA-15a - cell division cycle 42 signaling pathway in pathogenesis of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease.
Tang WJ, Peng KY, Tang ZF, Wang YH, Xue AJ, Huang Y. Tang WJ, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Dec 14;24(46):5234-5245. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i46.5234. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30581272 Free PMC article. - Curcumin alleviates LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in mouse microglial BV2 cells by targeting miR-137-3p/NeuroD1.
Gao F, Lei J, Zhang Z, Yang Y, You H. Gao F, et al. RSC Adv. 2019 Nov 25;9(66):38397-38406. doi: 10.1039/c9ra07266g. eCollection 2019 Nov 25. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35540218 Free PMC article. - The MicroRNA Family Both in Normal Development and in Different Diseases: The miR-17-92 Cluster.
Bai X, Hua S, Zhang J, Xu S. Bai X, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2019 Feb 3;2019:9450240. doi: 10.1155/2019/9450240. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30854399 Free PMC article. Review. - Nanomechanical Characteristics of Cervical Cancer and Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Revealed by Atomic Force Microscopy.
Cui Y, Zhang X, You K, Guo Y, Liu C, Fang X, Geng L. Cui Y, et al. Med Sci Monit. 2017 Aug 31;23:4205-4213. doi: 10.12659/msm.903484. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28859048 Free PMC article.
References
- Misra MK, Sarwat M, Bhakuni P, et al. Oxidative stress and ischemic myocardial syndromes. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15(10):RA209–19. - PubMed
- White HD, Chew DP. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 2008;372(9638):570–84. - PubMed
- Ibanez B, Heusch G, Ovize M, Van de Werf F. Evolving Therapies for Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(14):1454–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous