VFDB 2016: hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis--10 years on - PubMed (original) (raw)
VFDB 2016: hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis--10 years on
Lihong Chen et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016.
Abstract
The virulence factor database (VFDB, http://www.mgc.ac.cn/VFs/) is dedicated to providing up-to-date knowledge of virulence factors (VFs) of various bacterial pathogens. Since its inception the VFDB has served as a comprehensive repository of bacterial VFs for over a decade. The exponential growth in the amount of biological data is challenging to the current database in regard to big data analysis. We recently improved two aspects of the infrastructural dataset of VFDB: (i) removed the redundancy introduced by previous releases and generated two hierarchical datasets--one core dataset of experimentally verified VFs only and another full dataset including all known and predicted VFs and (ii) refined the gene annotation of the core dataset with controlled vocabularies. Our efforts enhanced the data quality of the VFDB and promoted the usability of the database in the big data era for the bioinformatic mining of the explosively growing data regarding bacterial VFs.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
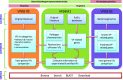
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the relationship between previous releases of virulence factor database (VFDB). R1 forms the base and core of the database, whereas R2 and R3 provided a comparative genomics platform and expanded the data contents in terms of genomes and pathogens (illustrated by the horizontal bars on the top), respectively.
Similar articles
- VFDB: a reference database for bacterial virulence factors.
Chen L, Yang J, Yu J, Yao Z, Sun L, Shen Y, Jin Q. Chen L, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 1;33(Database issue):D325-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki008. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15608208 Free PMC article. - VFDB 2022: a general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors.
Liu B, Zheng D, Zhou S, Chen L, Yang J. Liu B, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 7;50(D1):D912-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1107. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34850947 Free PMC article. - VFDB 2012 update: toward the genetic diversity and molecular evolution of bacterial virulence factors.
Chen L, Xiong Z, Sun L, Yang J, Jin Q. Chen L, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D641-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr989. Epub 2011 Nov 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22067448 Free PMC article. - Genome-enabled perspectives on the composition, evolution, and expression of virulence determinants in bacterial plant pathogens.
Lindeberg M. Lindeberg M. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2012;50:111-32. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-081211-173022. Epub 2012 May 1. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2012. PMID: 22559066 Review. - Bacterial genomics and pathogen evolution.
Raskin DM, Seshadri R, Pukatzki SU, Mekalanos JJ. Raskin DM, et al. Cell. 2006 Feb 24;124(4):703-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.002. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16497582 Review.
Cited by
- Genome-wide comparative analysis of clinical and environmental strains of the opportunistic pathogen Paracoccus yeei (Alphaproteobacteria).
Szuplewska M, Sentkowska D, Lasek R, Decewicz P, Hałucha M, Funk Ł, Chmielowska C, Bartosik D. Szuplewska M, et al. Front Microbiol. 2024 Nov 6;15:1483110. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1483110. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39568992 Free PMC article. - From acute to persistent infection: revealing phylogenomic variations in Salmonella Agona.
Waters EV, Lee WWY, Ismail Ahmed A, Chattaway MA, Langridge GC. Waters EV, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2024 Oct 31;20(10):e1012679. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012679. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39480892 Free PMC article. - Segatella clades adopt distinct roles within a single individual's gut.
Xiao X, Singh A, Giometto A, Brito IL. Xiao X, et al. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Oct 27;10(1):114. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00590-w. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 39465298 Free PMC article. - The Challenging Life of Mutators: How Pseudomonas aeruginosa Survives between Persistence and Evolution in Cystic Fibrosis Lung.
Rossitto M, Fox V, Vrenna G, Tuccio Guarna Assanti V, Essa N, Lepanto MS, Raimondi S, Agosta M, Cortazzo V, Fini V, Granaglia A, Montemitro E, Cutrera R, Perno CF, Bernaschi P. Rossitto M, et al. Microorganisms. 2024 Oct 11;12(10):2051. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12102051. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39458360 Free PMC article. - Genomic Analysis of Aeromonas salmonicida ssp. salmonicida Isolates Collected During Multiple Clinical Outbreaks Supports Association with a Single Epidemiological Unit.
Wojnarowski K, Cholewińska P, Steinbauer P, Lautwein T, Hussein W, Streb LM, Palić D. Wojnarowski K, et al. Pathogens. 2024 Oct 17;13(10):908. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13100908. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39452779 Free PMC article.
References
- van Oosten M., Hahn M., Crane L.M., Pleijhuis R.G., Francis K.P., van Dijl J.M., van Dam G.M. Targeted imaging of bacterial infections: advances, hurdles and hopes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015;39:892–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources