In vitro antibacterial activity of thymol and carvacrol and their effects on broiler chickens challenged with Clostridium perfringens - PubMed (original) (raw)
In vitro antibacterial activity of thymol and carvacrol and their effects on broiler chickens challenged with Clostridium perfringens
Encun Du et al. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2015.
Abstract
Background: In the post-antibiotic era, essential oils (EO) are promising alternatives to growth-promoting antibiotics. The aim of the present study was to investigate the antibacterial activities of an EO product and its components thymol and carvacrol in vitro, and the efficacy of EO to control Clostridium perfringens challenge in broiler chickens.
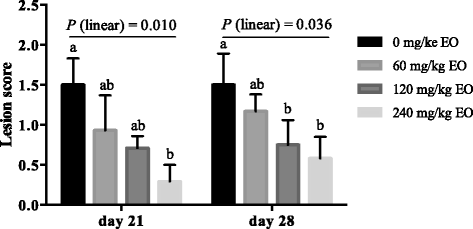
Results: The in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration assay showed strong antibacterial activity of the EO product, thymol, and carvacrol against pathogenic Escherichia coli, C. perfringens, and Salmonella strains, and weak activity towards beneficial Lactobacillus strains. Besides, an additive effect was observed between thymol and carvacrol. The in vivo study was carried out with 448 male broiler chicks following a 4 × 2 factorial arrangement to test the effects of EO supplementation (0, 60, 120, or 240 mg/kg EO in wheat-based diet), pathogen challenge (with or without oral gavage of C. perfringens from day 14 to day 20) and their interactions. Each treatment consisted of eight replicate pens (seven birds/pen). The challenge led to macroscopic gut lesions, and resulted in a significant increase in ileal populations of C. perfringens and Escherichia subgroup (P ≤ 0.05) on day 21. Dietary EO supplementation did not influence C. perfringens numbers, but linearly alleviated intestinal lesions on day 21 and 28 (P = 0.010 and 0.036, respectively), and decreased Escherichia populations in ileum with increased EO dosages (P = 0.027 and 0.071 for day 21 and 28, respectively). For caecum, EO quadratically influenced Lactobacillus populations on day 21 (P = 0.002), and linearly decreased the numbers of total bacteria and Escherichia on day 28 (P = 0.026 and 0.060, respectively). Mean thymol and carvacrol concentrations in the small intestine were 0.21 and 0.20 μg/g in intestinal digesta (wet weight), respectively, for birds fed 60 mg/kg EO, and 0.80 and 0.71 μg/g, respectively, for birds fed 240 mg/kg EO.
Conclusions: These results indicated that dietary EO supplementation could affect intestinal microbiota and alleviate intestinal lesions in broilers, which may contribute in controlling C. perfringens infection in broiler chickens.
Keywords: Broiler chickens; Carvacrol; Clostridium perfringens; Escherichia coli; Essential oils; Thymol.
Figures
Fig. 1
Effects of essential oils on intestinal lesion score of Clostridium perfringens challenged broiler chickens. Values are means of eight replicates per treatment and pooled standard error of the mean. Bars not sharing a common letter differ significantly (P ≤ 0.05). EO, essential oils; P (linear), polynomial contrasts were conducted to determine the linear response of lesion score to dietary EO dosages
Similar articles
- Supplemental thymol and carvacrol increases ileum Lactobacillus population and reduces effect of necrotic enteritis caused by Clostridium perfringes in chickens.
Yin D, Du E, Yuan J, Gao J, Wang Y, Aggrey SE, Guo Y. Yin D, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 4;7(1):7334. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07420-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28779076 Free PMC article. - Effects of thymol and carvacrol supplementation on intestinal integrity and immune responses of broiler chickens challenged with Clostridium perfringens.
Du E, Wang W, Gan L, Li Z, Guo S, Guo Y. Du E, et al. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2016 Mar 22;7:19. doi: 10.1186/s40104-016-0079-7. eCollection 2016. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27006768 Free PMC article. - Pretreatment with probiotics ameliorate gut health and necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens, a substitute to antibiotics.
Rajput DS, Zeng D, Khalique A, Rajput SS, Wang H, Zhao Y, Sun N, Ni X. Rajput DS, et al. AMB Express. 2020 Dec 17;10(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-01153-w. AMB Express. 2020. PMID: 33336284 Free PMC article. Review. - Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Clostridium perfringens: Challenges in No Antibiotics Ever Broiler Production and Potential Solutions.
Fancher CA, Zhang L, Kiess AS, Adhikari PA, Dinh TTN, Sukumaran AT. Fancher CA, et al. Microorganisms. 2020 Oct 6;8(10):1533. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8101533. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33036173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Effects of challenge with Clostridium perfringens, Eimeria and both on ileal microbiota of yellow feather broilers.
Feng X, Li T, Zhu H, Liu L, Bi S, Chen X, Zhang H. Feng X, et al. Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 1;13:1063578. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1063578. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36532499 Free PMC article. - Supplemental thymol and carvacrol increases ileum Lactobacillus population and reduces effect of necrotic enteritis caused by Clostridium perfringes in chickens.
Yin D, Du E, Yuan J, Gao J, Wang Y, Aggrey SE, Guo Y. Yin D, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 4;7(1):7334. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07420-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28779076 Free PMC article. - Effects of dietary supplementation by modified palygorskite and essential oil/palygorskite complex on growth performance and intestinal flora composition of broilers with diarrhea.
Yang QL, Yang L, Qu XY, Xiao DF. Yang QL, et al. Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104379. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104379. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39476614 Free PMC article. - Stress response of Escherichia coli to essential oil components - insights on low-molecular-weight proteins from MALDI-TOF.
Božik M, Cejnar P, Šašková M, Nový P, Maršík P, Klouček P. Božik M, et al. Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 29;8(1):13042. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31255-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30158663 Free PMC article. - Construction and analysis of alginate-based honey hydrogel as an ointment to heal of rat burn wound related infections.
Mirzaei B, Etemadian S, Goli HR, Bahonar S, Gholami SA, Karami P, Farhadi M, Tavakoli R. Mirzaei B, et al. Int J Burns Trauma. 2018 Aug 20;8(4):88-97. eCollection 2018. Int J Burns Trauma. 2018. PMID: 30245913 Free PMC article.
References
- Van der Sluis W. Clostridial enteritis is an often underestimated problem. World Poultry Sci J. 2000;16:42–43.
- Dahiya JP, Wilkie DC, Van Kessel AG, Drew MD. Potential strategies for controlling necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens in post-antibiotic era. Anim Feed Sci Tech. 2006;129:60–88. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2005.12.003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources