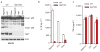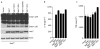NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2016 Feb 18;530(7590):354-7.
doi: 10.1038/nature16959. Epub 2016 Jan 27.
Affiliations
- PMID: 26814970
- PMCID: PMC4810788
- DOI: 10.1038/nature16959
NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux
Yuan He et al. Nature. 2016.
Abstract
Inflammasomes are intracellular protein complexes that drive the activation of inflammatory caspases. So far, four inflammasomes involving NLRP1, NLRP3, NLRC4 and AIM2 have been described that recruit the common adaptor protein ASC to activate caspase-1, leading to the secretion of mature IL-1β and IL-18 proteins. The NLRP3 inflammasome has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several acquired inflammatory diseases as well as cryopyrin-associated periodic fever syndromes (CAPS) caused by inherited NLRP3 mutations. Potassium efflux is a common step that is essential for NLRP3 inflammasome activation induced by many stimuli. Despite extensive investigation, the molecular mechanism leading to NLRP3 activation in response to potassium efflux remains unknown. Here we report the identification of NEK7, a member of the family of mammalian NIMA-related kinases (NEK proteins), as an NLRP3-binding protein that acts downstream of potassium efflux to regulate NLRP3 oligomerization and activation. In the absence of NEK7, caspase-1 activation and IL-1β release were abrogated in response to signals that activate NLRP3, but not NLRC4 or AIM2 inflammasomes. NLRP3-activating stimuli promoted the NLRP3-NEK7 interaction in a process that was dependent on potassium efflux. NLRP3 associated with the catalytic domain of NEK7, but the catalytic activity of NEK7 was shown to be dispensable for activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Activated macrophages formed a high-molecular-mass NLRP3-NEK7 complex, which, along with ASC oligomerization and ASC speck formation, was abrogated in the absence of NEK7. NEK7 was required for macrophages containing the CAPS-associated NLRP3(R258W) activating mutation to activate caspase-1. Mouse chimaeras reconstituted with wild-type, Nek7(-/-) or Nlrp3(-/-) haematopoietic cells showed that NEK7 was required for NLRP3 inflammasome activation in vivo. These studies demonstrate that NEK7 is an essential protein that acts downstream of potassium efflux to mediate NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper
Figures
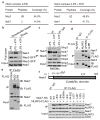
Extended Data Figure 1. Nek7 interacts with NLRP3 upstream of ASC and Caspase-1
a, Immortalized Nlrp3−/− macrophages were infected with lentiviruses containing pHIV vector (Vector) or pHIV-NLRP3-SFP (NLRP3-SFP). Transduced macrophages were sorted by flow cytometry. Cells were treated as indicated. Supernatants (Sup.) and cell lysates (Lys.) were collected and analysed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. b, Immunoblots showing that Nek7, but not Nek6 or Nek9, interacts with NLRP3 in macrophages. NLRP3-associated proteins were pulled down from reconstituted Nlrp3−/− macrophages by streptavidin beads, and analysed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. c, ATP stimulation, but not LPS priming, greatly enhances the Nek7/NLRP3 interaction. d, LPS-primed BMDMs from WT, Asc−/− and Casp1−/−/Casp11−/− were left untreated or treated with 5 mM ATP for 30 min. NLRP3 protein complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-NLRP3 antibody and analysed by immunoblotting. Data are representative of three (a, b) or two (c, d) independent experiments. See Supplementary Fig. 2, 3 for gel source data.
Extended Data Figure 2. Nek7 deficiency does not affect TNF-α release, but abrogates NLRP3 activation induced by cytosolic LPS in macrophages
a, TNF-α secretion from LPS-primed BMDMs treated with ATP, Nigericin, Gramicidin, Poly(dA:dT) or Salmonella. b, TNF-α secretion in LPS-primed BMDMs treated with LLOMe, Silica, Alum, MSU, CPPD or Nano-SiO2. Mock represents macrophages primed with LPS without further stimulations. The amounts of TNF-α release in the absence of LPS priming were below 50 pg/ml in the supernatants. c-e, BMDMs from C57BL/6, Casp11−/−, Nek7−/− (fetal liver chimeras) and Nlrp3−/− mice were primed with LPS for 4 h before transfection with or without LPS with DOTAP. 4 h after transfection, caspase-1 activation (c), IL-1β release (d) and cytotoxicity (e) were analysed. Graphs show the mean ± s.d. of triplicate wells and are representative of three independent experiments. See Supplementary Fig. 3 for gel source data.
Extended Data Figure 3. Nek7 is required for activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages
a–c, Defective NLRP3 inflammasome in Nek7-deficient macrophages. WT and Nek7-deficient macrophages generated by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing were primed with LPS, followed by stimulation with 5 μM nigericin (1 h), 5 mM ATP (30 min) or 200 ng/ml Alum (6 h). Cell lysates were collected and analysed for caspase-1 activation by immunoblotting (a). IL-1β (b) and TNF-α (c) release were analysed by ELISA. ELISA data (b, c) show the mean ± s.d. of triplicate wells. The amounts of TNF-α release in the absence of LPS priming were below 50 pg/ml in the supernatants. Data are representative of three independent experiments. See Supplementary Fig. 3 for gel source data.
Extended Data Figure 4. Nek7 is critical for activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in primary macrophages
a, Nek7 is dispensable for NLRP3 induction and expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome components ASC and caspase-1. BMDMs were treated with control shRNA or Nek7 shRNAs and selected by culture in 3 μg/ml puromycin. Puromycin-resistant macrophages were left unstimulated or stimulated with LPS for 4 h. Cell lysates were collected and analysed by immunoblotting. Actin is shown as a loading control. b–c, Nek7 depletion inhibits activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. BMDMs treated with control shRNA or Nek7 shRNAs were primed with LPS, followed by stimulation with 5 mM ATP (30 min), 5 μM nigericin (1 h) or 500 ng/ml silica (4 h). Supernatants (Sup.) and cell lysates (Lys.) were collected after stimulation and analysed by immunoblotting for caspase-1 activation (b). IL-1β (c) and TNF-α (d) release were analysed by ELISA. ELISA data (c, d) show the mean ± s.d. of triplicate wells. The amounts of TNF-α release in the absence of LPS priming were below 50 pg/ml in the supernatants. Data are representative of three independent experiments. See Supplementary Fig. 3 for gel source data.
Extended Data Figure 5. Nek7 is critical for NLRP3-mediated ASC oligomerization and speck formation in macrophages
a, Representative confocal immunofluorescence images and (b) quantification of endogenous ASC specks (arrows) in macrophages treated with control shRNA- or Nek7 shRNA. Macrophages were primed with LPS and then stimulated with ATP, nigericin, Poly(dA:dT) or Salmonella. After stimulation, cells were fixed and stained for ASC (Green). DAPI was used for staining nuclear DNA (Blue). Data shown represent results from three combined independent experiments in which more than 300 cells were counted in each experiment. Error bars indicate ± s.d. c, Immunoblots showing ASC oligomerization in control shRNA or Nek7 shRNA-treated macrophages. LPS-primed macrophages were treated as indicated. Cell lysates (Triton-X-100 soluble) and BS3-crosslinked pellets (Triton-X-100 insoluble) were analysed by immunoblotting. Mock represents macrophages primed with LPS without further stimulations. Results are representative of two independent experiments. Two-tailed Student’s t-test. * p <0.05. See Supplementary Fig. 3 for gel source data.
Extended Data Figure 6. Nek7 kinase activity is dispensable for activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages
a–c, Immortalized Nek7-deficient macrophages were infected with lentivirus containing empty vector or vector expressing wild type or indicated mutant Nek7. Transduced macrophages were sorted by flow cytometry using GFP as a marker. Macrophages were plated and stimulated with 5 μM nigericin for 1 h after LPS priming. Cell lysates were collected and analysed for caspase-1 activation by immunoblotting (a). IL-1β (b) and TNF-α (c) release were analysed by ELISA. ELISA data (b, c) show the mean ± s.d. of triplicate wells. Data are representative of three independent experiments. See Supplementary Fig. 3 for gel source data.
Extended Data Figure 7. Nek6 and Nek9 are dispensable for activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages
a–c, BMDMs were treated with control shRNA, Nek7 shRNA, Nek6 shRNA or Nek9 shRNA and selected by culture with 3 μg/ml puromycin. Puromycin-resistant cells were plated and primed with LPS, followed by stimulation with 5 mM ATP for 30 min. Cell lysates were collected and analysed for caspase-1 activation by immunoblotting (a). IL-1β (b) and TNF-α (c) release were analysed by ELISA. d, Representative confocal immunofluorescence images and (e) quantification of endogenous ASC specks (arrows) in macrophages. DAPI was used for staining nuclear DNA (Blue). Quantification of ASC speck was from three combined independent experiments in which more than 300 cells were counted in each experiment. Error bars indicate ± s.d. ELISA data (b, c) show the mean ± s.d. of triplicate wells. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Two-tailed Student’s t-test. * p <0.05. See Supplementary Fig. 3 for gel source data.
Extended Data Figure 8. Microtubule depolymerization does not inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the Nek7/NLRP3 interaction in macrophages
a–e, LPS-primed BMDMs were pretreated with vehicle control (DMSO), nocodazole (1, 10, 50 μM) or colchicine (1, 10, 50 μM) for 1 h before stimulation with 5 μM nigericin. Cell lysates were collected and analysed for caspase-1 activation by immunoblotting (a). IL-1β (b) and TNF-α (c) release were analysed by ELISA. Representative confocal immunofluorescence images (d) and (e) quantification of endogenous ASC specks (arrows) in macrophages treated as indicated. Microtubules were stained with anti-α/β tubulin antibody (Red). DAPI was used for staining nuclear DNA (Blue). Data shown in (e) represent results from three combined independent experiments in which more than 300 cells were counted in each experiment. Error bars indicate ± s.d. f, The Nek7/NLRP3 interaction in untreated and treated macrophages was analysed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. ELISA data (b, c) show the mean ± s.d. of triplicate wells. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Two-tailed Student’s t-test. * p <0.05. See Supplementary Fig. 3 for gel source data.
Extended Data Figure 9. Inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) does not inhibit the Nek7/NLRP3 interaction in macrophages
a–b, Reconstituted Immortalized Nlrp3−/− macrophages were primed with LPS for 4 h. Cells were left untreated or treated with indicated concentrations of BTK inhibitor LFM-A13 for 30 min before ATP stimulation. Cell lysates were collected and analysed for caspase-1 activation by immunoblotting (a). Cell lysates were collected and subjected to pull-down with streptavidin beads, and the precipitated protein complex was analysed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (b). Agarose beads were used as a control. Actin is shown as a loading control. Data are representative of two independent experiments. See Supplementary Fig. 3 for gel source data.
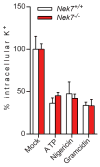
Extended Data Figure 10. Nek7-deficiency does not inhibit potassium efflux induced by NLRP3 stimuli in macrophages
LPS-primed Nek7+/+ and Nek7−/− BMDMs were stimulated as indicated. The intracellular potassium in each condition was analysed. Mock represents macrophages primed with LPS without further stimulation. Graphs show the mean ± s.d. of four technical replicates and are representative of two independent experiments.
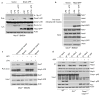
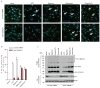
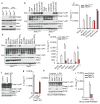
Figure 1. Nek7 interacts with NLRP3
a, Mass spectrometry analysis of NLRP3 and Nek7 peptides after purification of NLRP3-associated proteins. b, NLRP3-SFP was pulled down and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. c, LPS-primed BMDMs were left unstimulated or stimulated with ATP for 30 min. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. d, e, WT or mutant NLRP3 was expressed in HEK 293T cells, immunoprecipitated and analysed by immunoblotting. f, WT or mutant Nek7 was co-expressed with FLAG-tagged NLRP3 in HEK 293T cells, immunoprecipitated and analysed by immunoblotting. Whole cell lysates are shown as the input. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments. See Supplementary Fig. 1 for gel source data.
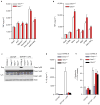
Figure 2. Nek7 deficiency specifically abrogates the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
a, BMDMs were left untreated or stimulated with LPS and cell lysates were immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. b, d, Caspase-1 in the supernatant (Sup.) and cell lysate (Lys.) was analysed in stimulated Nek7+/+ and Nek7−/− macrophages. c, e, IL-1β release was measured. f, g, CRISPR/Cas9-generated Nek7-deficient iBMDMs were transduced with control or pHIV-Nek7 lentivirus, and stimulated with LPS plus nigericin. Caspase-1 activation (f) and IL-1β release (g) were analysed. h, i, Macrophages were transduced with control lentivirus or shRNA lentiviruses targeting Nek7, and stimulated with LPS. Caspase-1 activation (h) and IL-1β release (i) were analysed. IL-1β release data (c, e, g, i) are expressed as mean values. Error bars indicate ± s.d. of triplicate wells. Results are representative of three independent experiments. See Supplementary Fig. 1 for gel source data.
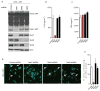
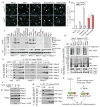
Figure 3. Nek7 is required for NLRP3 oligomerization and ASC speck formation downstream of potassium efflux
a, b, Representative immunofluorescence images and quantification of endogenous ASC specks (arrows). N.D. not detected. Data shown represent results from three combined independent experiments. Scale bars, 10 μm. Error bars indicate ± s.d. c, ASC oligomerization induced by indicated stimuli in Nek7+/+ and Nek7−/− LPS-primed macrophages. d, Indicated LPS-primed macrophages were stimulated with PBS (Mock), ATP or nigericin. Analyses by blue native PAGE or SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotting. e, Cell lysates were separated by a first dimension of blue native PAGE followed by a second dimension of SDS–PAGE. f, g, Nek7/NLRP3 interactions and complex formation in the presence of 5 mM or 50 mM extracellular KCl. h, Proposed model for mechanism of Nek7-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments. See Supplementary Fig. 2 for gel source data.
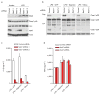
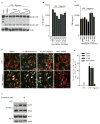
Figure 4. Nek7 is required for activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in vivo
a–c, Mouse serum cytokines IL-1β (a), TNF-α (b) and IL-6 (c) were analysed after intraperitoneal injection of LPS (LPS i.p.). d, IL-1β was analysed in peritoneal lavage fluids after intraperitoneal injection of MSU (MSU i.p.). Each symbol represents one mouse. Mean values are indicated by a horizontal bar. In the absence of LPS or MSU stimulation, the amounts of IL-1β were undetectable. Results are representative of two independent experiments. ns, not significant. *p<0.05; **, p<0.01; *** p<0.001 by Kruskal-Wallis test.
Similar articles
- Caspase-1 autoproteolysis is differentially required for NLRP1b and NLRP3 inflammasome function.
Guey B, Bodnar M, Manié SN, Tardivel A, Petrilli V. Guey B, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 2;111(48):17254-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415756111. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25404286 Free PMC article. - NLRP3 activation and mitosis are mutually exclusive events coordinated by NEK7, a new inflammasome component.
Shi H, Wang Y, Li X, Zhan X, Tang M, Fina M, Su L, Pratt D, Bu CH, Hildebrand S, Lyon S, Scott L, Quan J, Sun Q, Russell J, Arnett S, Jurek P, Chen D, Kravchenko VV, Mathison JC, Moresco EM, Monson NL, Ulevitch RJ, Beutler B. Shi H, et al. Nat Immunol. 2016 Mar;17(3):250-8. doi: 10.1038/ni.3333. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Nat Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26642356 Free PMC article. - A Genome-wide CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) Screen Identifies NEK7 as an Essential Component of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.
Schmid-Burgk JL, Chauhan D, Schmidt T, Ebert TS, Reinhardt J, Endl E, Hornung V. Schmid-Burgk JL, et al. J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 1;291(1):103-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C115.700492. Epub 2015 Nov 9. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26553871 Free PMC article. - Recent advances in the NEK7-licensed NLRP3 inflammasome activation: Mechanisms, role in diseases and related inhibitors.
Zhao N, Li CC, Di B, Xu LL. Zhao N, et al. J Autoimmun. 2020 Sep;113:102515. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102515. Epub 2020 Jul 20. J Autoimmun. 2020. PMID: 32703754 Review. - Biochemical regulation of the inflammasome.
Dowling JK, O'Neill LA. Dowling JK, et al. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Sep;47(5):424-43. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2012.694844. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22681257 Review.
Cited by
- NLRP3 inflammasome activation mechanism and its role in autoimmune liver disease.
Guan Y, Gu Y, Li H, Liang B, Han C, Zhang Y, Liu Q, Wei W, Ma Y. Guan Y, et al. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022 Sep 25;54(11):1577-1586. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022137. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022. PMID: 36148948 Free PMC article. Review. - NLRP3 inflammasome and NLRP3-related autoinflammatory diseases: From cryopyrin function to targeted therapies.
Moltrasio C, Romagnuolo M, Marzano AV. Moltrasio C, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 6;13:1007705. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1007705. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275641 Free PMC article. Review. - The Role of Microglia and the Nlrp3 Inflammasome in Alzheimer's Disease.
Hanslik KL, Ulland TK. Hanslik KL, et al. Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 18;11:570711. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.570711. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33071950 Free PMC article. Review. - Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.
He Y, Hara H, Núñez G. He Y, et al. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016 Dec;41(12):1012-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016. PMID: 27669650 Free PMC article. Review. - Activation and Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome by RNA Viruses.
Choudhury SM, Ma X, Abdullah SW, Zheng H. Choudhury SM, et al. J Inflamm Res. 2021 Mar 26;14:1145-1163. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S295706. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33814921 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Molecular Cell. 2002;10:417–426. - PubMed
- Martinon F, Mayor A, Tschopp J. Annual Review of Immunology. Annual Review of Immunology. 2009;27:229–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK091191/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32DK094775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007517/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI063331/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI063331/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL007517/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063331/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK091191/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK094775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous