An Update on Sinonasal Round Cell Undifferentiated Tumors - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
An Update on Sinonasal Round Cell Undifferentiated Tumors
Alessandro Franchi. Head Neck Pathol. 2016 Mar.
Abstract
The sinonasal cavities host a wide variety of undifferentiated malignancies with round cell morphology, including neoplasms of epithelial, mesenchymal, neuroectodermal, and hematolymphoid lineage. The differential diagnosis may be difficult, especially in small biopsy material, due to overlapping morphology, but their correct classification is clinically relevant. The aim of this review is to provide practical guidelines for the differential diagnosis of these malignancies, with emphasis on recently described entities and special reference to the role of ancillary techniques.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Immunohistochemistry; Molecular biology; Nasal cavity; Paranasal sinuses; Undifferentiated tumors.
Figures
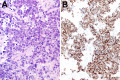
Fig. 1
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma. a The tumor consists of a proliferation of undifferentiated round cells, with a high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio. Mitotic figures and apoptotic bodies are present. Tumor cells are positive for cytokeratin 8 (b)
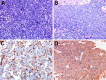
Fig. 2
Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the maxillary sinus (a). The tumor is composed of closely packed cells with inconspicuous cytoplasm and nuclei with dense chromatin. In sinonasal large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, neoplastic cells have larger nuclei with prominent nucleoli (b). These malignancies are positive for cytokeratins, often with a dot-like paranuclear pattern (c) and synaptophysin (d)
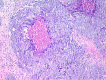
Fig. 3
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma with comedo necrosis
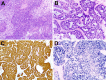
Fig. 4
HPV-related carcinoma with adenoid cystic-like features presents areas of solid growth of basaloid cells (a) and cribriform areas (b). P16 is diffusely positive (c), and high risk HPV can be detected by in situ hybridization (d)
Fig. 5
Sinonasal melanoma presenting with round cell undifferentiated morphology (a). The tumor is positive for HMB45 (b)
Fig. 6
High grade olfactory neuroblastoma is characterized by a solid growth pattern, moderate pleomorphism (a), and presence of necrosis (b). The tumor is positive for synaptophysin (c), while cytokeratin AE1/AE3 is negative (d). Positive non-neoplastic epithelium is visible on the left
Similar articles
- "Undifferentiated" small round cell tumors of the sinonasal tract: differential diagnosis update.
Iezzoni JC, Mills SE. Iezzoni JC, et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005 Dec;124 Suppl:S110-21. doi: 10.1309/59RBT2RK6LQE4YHB. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16468421 Review. - Sinonasal tumors: a clinicopathologic update of selected tumors.
Slootweg PJ, Ferlito A, Cardesa A, Thompson LD, Hunt JL, Strojan P, Takes RP, Triantafyllou A, Woolgar JA, Rinaldo A, Devaney KO, Barnes L. Slootweg PJ, et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Jan;270(1):5-20. doi: 10.1007/s00405-012-2025-4. Epub 2012 May 18. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 22610012 Review. - [Undifferentiated malignant round cell tumors of the sinonasal tract and nasopharynx].
Casiraghi O, Lefèvre M. Casiraghi O, et al. Ann Pathol. 2009 Sep;29(4):296-312. doi: 10.1016/j.annpat.2009.09.004. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Ann Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19900635 French. - Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Sinonasal Undifferentiated Carcinoma.
Abdelmeguid AS, Bell D, Hanna EY. Abdelmeguid AS, et al. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;84:168-184. doi: 10.1159/000457936. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32731236 Review. - Sinonasal small round blue cell tumors: An approach to diagnosis.
Simons SA, Bridge JA, Leon ME. Simons SA, et al. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2016 Mar;33(2):91-103. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2015.09.010. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26585346 Review.
Cited by
- Variable Expression of S100 Protein in Sinonasal Malignant Mucosal Melanoma: A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall.
Xu X, Palsgrove D, Kurian E, Yan S, Oliai BR, Bishop JA. Xu X, et al. Head Neck Pathol. 2020 Dec;14(4):929-935. doi: 10.1007/s12105-020-01158-8. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Head Neck Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32239440 Free PMC article. - CD3+ CD56+ EBER1+ atypical extraosseous plasmacytoma of the nasal cavity.
Ando Y, Maeshima AM, Fukuhara S, Makita S, Munakata W, Suzuki T, Maruyama D, Taniguchi H, Izutsu K. Ando Y, et al. Int J Hematol. 2018 Sep;108(3):344-347. doi: 10.1007/s12185-018-2438-y. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Int J Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29572766 - Undifferentiated sinonasal malignant melanoma: A case report.
Du J, Huang LL, Xu A, Zhang AL, Kong X, Ding M, Hu W, Guo ZL, Zhong W, Sun SB, Li H, Chen J, Shen Q, Xu LL, Wu HB. Du J, et al. Oncol Lett. 2018 Jul;16(1):580-584. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8662. Epub 2018 May 8. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29930718 Free PMC article. - Positron emission computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging features of sinonasal small round blue cell tumors.
Ozturk K, Gencturk M, Caicedo-Granados E, Li F, Cayci Z. Ozturk K, et al. Neuroradiol J. 2020 Feb;33(1):48-56. doi: 10.1177/1971400919873895. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Neuroradiol J. 2020. PMID: 31460836 Free PMC article. - Newly Described Tumor Entities in Sinonasal Tract Pathology.
Bishop JA. Bishop JA. Head Neck Pathol. 2016 Mar;10(1):23-31. doi: 10.1007/s12105-016-0688-7. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Head Neck Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26830406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources