The Reciprocal Interactions between Polyphenols and Gut Microbiota and Effects on Bioaccessibility - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The Reciprocal Interactions between Polyphenols and Gut Microbiota and Effects on Bioaccessibility
Tugba Ozdal et al. Nutrients. 2016.
Abstract
As of late, polyphenols have increasingly interested the scientific community due to their proposed health benefits. Much of this attention has focused on their bioavailability. Polyphenol-gut microbiota interactions should be considered to understand their biological functions. The dichotomy between the biotransformation of polyphenols into their metabolites by gut microbiota and the modulation of gut microbiota composition by polyphenols contributes to positive health outcomes. Although there are many studies on the in vivo bioavailability of polyphenols, the mutual relationship between polyphenols and gut microbiota is not fully understood. This review focuses on the biotransformation of polyphenols by gut microbiota, modulation of gut microbiota by polyphenols, and the effects of these two-way mutual interactions on polyphenol bioavailability, and ultimately, human health.
Keywords: bioavailability; flavonoids; gut microbiota; health; interactions; microbial metabolism; phenolics; polyphenols.
Figures
Figure 1
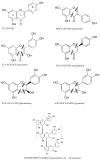
Microbiota heterocyclic C ring cleavage of flavonoids; (|||) positions of the potential C-ring cleavages [42].
Figure 2
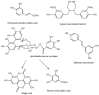
Nonflavonoid-type phenolics that are metabolized by the gut microbiota [42].
Figure 3
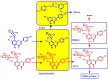
Absorption and metabolism of flavone _C_-monoglycosides (blue arrow) and _C_-multiglycosides (red arrow) [63].
Figure 4
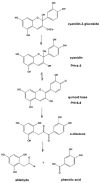
pH-dependent structural changes and degradation of cyanidin-3-glucoside. Reproduced from the original source [94].
Similar articles
- Microbe-bio-Chemical Insight: Reviewing Interactions between Dietary Polyphenols and Gut Microbiota.
Mahajan R, Attri S, Mehta V, Udayabanu M, Goel G. Mahajan R, et al. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(15):1253-1264. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666170208142817. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 27781961 Review. - Interactions of gut microbiota with dietary polyphenols and consequences to human health.
Tomás-Barberán FA, Selma MV, Espín JC. Tomás-Barberán FA, et al. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2016 Nov;19(6):471-476. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000314. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2016. PMID: 27490306 Review. - Bioactivity of dietary polyphenols: The role of metabolites.
Luca SV, Macovei I, Bujor A, Miron A, Skalicka-Woźniak K, Aprotosoaie AC, Trifan A. Luca SV, et al. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(4):626-659. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1546669. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 30614249 Review. - The mutual effect of dietary fiber and polyphenol on gut microbiota: Implications for the metabolic and microbial modulation and associated health benefits.
Cheng B, Feng H, Li C, Jia F, Zhang X. Cheng B, et al. Carbohydr Polym. 2025 Jun 15;358:123541. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.123541. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Carbohydr Polym. 2025. PMID: 40383597 Review. - Benefits of polyphenols on gut microbiota and implications in human health.
Cardona F, Andrés-Lacueva C, Tulipani S, Tinahones FJ, Queipo-Ortuño MI. Cardona F, et al. J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Aug;24(8):1415-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.05.001. J Nutr Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23849454 Review.
Cited by
- Microbiota Modulating Nutritional Approaches to Countering the Effects of Viral Respiratory Infections Including SARS-CoV-2 through Promoting Metabolic and Immune Fitness with Probiotics and Plant Bioactives.
Shinde T, Hansbro PM, Sohal SS, Dingle P, Eri R, Stanley R. Shinde T, et al. Microorganisms. 2020 Jun 18;8(6):921. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8060921. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32570850 Free PMC article. Review. - Does an Apple a Day Also Keep the Microbes Away? The Interplay Between Diet, Microbiota, and Host Defense Peptides at the Intestinal Mucosal Barrier.
Puértolas-Balint F, Schroeder BO. Puértolas-Balint F, et al. Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 9;11:1164. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01164. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32655555 Free PMC article. Review. - Gut/Oral Bacteria Variability May Explain the High Efficacy of Green Tea in Rodent Tumor Inhibition and Its Absence in Humans.
Adami GR, Tangney C, Schwartz JL, Dang KC. Adami GR, et al. Molecules. 2020 Oct 16;25(20):4753. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204753. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33081212 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeting Gut Microbiota with Probiotics and Phenolic Compounds in the Treatment of Atherosclerosis: A Comprehensive Review.
Cruz Neto JPR, de Luna Freire MO, de Albuquerque Lemos DE, Ribeiro Alves RMF, de Farias Cardoso EF, de Moura Balarini C, Duman H, Karav S, de Souza EL, de Brito Alves JL. Cruz Neto JPR, et al. Foods. 2024 Sep 12;13(18):2886. doi: 10.3390/foods13182886. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39335815 Free PMC article. Review. - Food as medicine: targeting the uraemic phenotype in chronic kidney disease.
Mafra D, Borges NA, Lindholm B, Shiels PG, Evenepoel P, Stenvinkel P. Mafra D, et al. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Mar;17(3):153-171. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-00345-8. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 32963366 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials