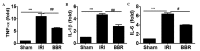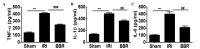Berberine attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by suppressing the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling - PubMed (original) (raw)
Berberine attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by suppressing the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling
Zhu Qin-Wei et al. Exp Ther Med. 2016 Mar.
Abstract
Berberine (BBR), an isoquinoline alkaloid originally isolated from the Chinese herb Coptis chinensis (Huanglian), exhibits anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. Since myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is associated with an excessive immune response, the current study was conducted to investigate the impact of BBR on myocardial I/R injury, a common disorder in clinical settings. Preconditioning of Sprague-Dawley rats with BBR (100 mg/kg/day, by gavage) for 14 days prior to the induction of I/R significantly attenuated myocardial I/R injury as manifested by a reduction in the incidence of ventricular arrhythmia and the amelioration of myocardial histological changes. These effects were found to be associated with the suppression of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathway and the subsequent reduction of the expression of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-α in the serum and myocardial tissue. These results indicate that BBR has the potential be an effective alternative therapy for the prevention and treatment of myocardial I/R injury in clinical practice.
Keywords: berberine; inflammation; myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury; phosphoinositide 3-kinase; protein kinase B.
Figures
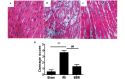
Figure 1.
Histological analysis of myocardial tissues. Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining results for myocardial sections in rats of the (A) sham (B) ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) and (C) berberine (BBR) groups (magnification, ×200). (D) Semi-quantitative analysis of H&E staining in the rats (n=3 per group). ***P<0.001, ##P<0.01.
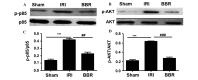
Figure 2.
Administration of BBR inhibited the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling. The phosphorylated proteins were measured by western blotting to assess the activity of p85 and AKT. Representative western blots for (A) p85 and p-p85 and (B) AKT and p-AKT. Quantitative analysis of (C) p-p85 and (D) AKT activities. The relative activity for p85 and AKT was assessed as a ratio between the phosphorylated form and all forms of the protein (n=10 rats/group). ***P<0.001, ##P<0.01; ###P<0.001. BBR, berberine; IRI, ischemia/reperfusion injury; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; p, phospho.
Figure 3.
BBR treatment suppresses I/R-induced cytokine expression in the myocardium. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was employed to evaluate the expression of inflammatory cytokines in the myocardial tissue. The expression levels of (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-1β and (C) IL-6 were examined after 4 h of myocardial I/R insult. ***P<0.001, ##P<0.01, #P<0.05. Ten rats were included in each study group. BBR, berberine; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; IRI, I/R injury; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin.
Figure 4.
BBR treatment suppresses IR-induced cytokine expression in the serum. ELISA was employed to assess the expression of inflammatory cytokines in the serum. The expression levels of (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-1β and (C) IL-6 were determined after 4 h myocardial I/R insult. ***P<0.001, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001. Ten rats were included in each study group. BBR, berberine; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; IRI, I/R injury; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; Il, interleukin; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Similar articles
- Berberine protects rat heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury via activating JAK2/STAT3 signaling and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Zhao GL, Yu LM, Gao WL, Duan WX, Jiang B, Liu XD, Zhang B, Liu ZH, Zhai ME, Jin ZX, Yu SQ, Wang Y. Zhao GL, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016 Mar;37(3):354-67. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.136. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016. PMID: 26806299 Free PMC article. - Protective effect of berberine against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury: role of Notch1/Hes1-PTEN/Akt signaling.
Yu L, Li F, Zhao G, Yang Y, Jin Z, Zhai M, Yu W, Zhao L, Chen W, Duan W, Yu S. Yu L, et al. Apoptosis. 2015 Jun;20(6):796-810. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1122-4. Apoptosis. 2015. PMID: 25824534 - Neuroprotective Properties of Berberine: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications.
Tian E, Sharma G, Dai C. Tian E, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;12(10):1883. doi: 10.3390/antiox12101883. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37891961 Free PMC article. Review. - Cytokine storm-calming property of the isoquinoline alkaloids in Coptis chinensis Franch.
Lan Y, Wang H, Wu J, Meng X. Lan Y, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 6;13:973587. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.973587. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36147356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Coptidis rhizoma and its main bioactive components: recent advances in chemical investigation, quality evaluation and pharmacological activity.
Meng FC, Wu ZF, Yin ZQ, Lin LG, Wang R, Zhang QW. Meng FC, et al. Chin Med. 2018 Mar 7;13:13. doi: 10.1186/s13020-018-0171-3. eCollection 2018. Chin Med. 2018. PMID: 29541156 Free PMC article. Review. - LDK378 improves micro- and macro-circulation via alleviating STING-mediated inflammatory injury in a Sepsis rat model induced by Cecal ligation and puncture.
Ge W, Hu Q, Fang X, Liu J, Xu J, Hu J, Liu X, Ling Q, Wang Y, Li H, Gao M, Jiang L, Yang Z, Tang W. Ge W, et al. J Inflamm (Lond). 2019 Feb 18;16:3. doi: 10.1186/s12950-019-0208-0. eCollection 2019. J Inflamm (Lond). 2019. PMID: 30820191 Free PMC article. - Protective effects of berberine in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome mediated via the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Yu J, Ding C, Hua Z, Jiang X, Wang C. Yu J, et al. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021 May;47(5):1789-1803. doi: 10.1111/jog.14730. Epub 2021 Mar 11. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021. PMID: 33709493 Free PMC article. - Immune and Metabolic Regulation Mechanism of Dangguiliuhuang Decoction against Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis.
Cao H, Tuo L, Tuo Y, Xia Z, Fu R, Liu Y, Quan Y, Liu J, Yu Z, Xiang M. Cao H, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jul 7;8:445. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00445. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28736524 Free PMC article.
References
- Yan X, Qiu W, Jia B, Zhong H, Li X, Chen Z. Myocardial protection by interferon-γ late preconditioning during cardiopulmonary bypass-associated myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in pigs. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:2145–2152. - PubMed
- Lassaletta AD, Elmadhun NY, Zanetti AV, Feng J, Anduaga J, Gohh RY, Sellke FW, Bianchi C. Rapamycin treatment of healthy pigs subjected to acute myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury attenuates cardiac functions and increases myocardial necrosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97:901–907. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2013.09.059. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources