How Do Theories of Cognition and Consciousness in Ancient Indian Thought Systems Relate to Current Western Theorizing and Research? - PubMed (original) (raw)
How Do Theories of Cognition and Consciousness in Ancient Indian Thought Systems Relate to Current Western Theorizing and Research?
Peter Sedlmeier et al. Front Psychol. 2016.
Abstract
Unknown to most Western psychologists, ancient Indian scriptures contain very rich, empirically derived psychological theories that are, however, intertwined with religious and philosophical content. This article represents our attempt to extract the psychological theory of cognition and consciousness from a prominent ancient Indian thought system: Samkhya-Yoga. We derive rather broad hypotheses from this approach that may complement and extend Western mainstream theorizing. These hypotheses address an ancient personality theory, the effects of practicing the applied part of Samkhya-Yoga on normal and extraordinary cognition, as well as different ways of perceiving reality. We summarize empirical evidence collected (mostly without reference to the Indian thought system) in diverse fields of research that allows for making judgments about the hypotheses, and suggest more specific hypotheses to be examined in future research. We conclude that the existing evidence for the (broad) hypotheses is substantial but that there are still considerable gaps in theory and research to be filled. Theories of cognition contained in the ancient Indian systems have the potential to modify and complement existing Western mainstream accounts of cognition. In particular, they might serve as a basis for arriving at more comprehensive theories for several research areas that, so far, lack strong theoretical grounding, such as meditation research or research on aspects of consciousness.
Keywords: Samkhya-Yoga; cognition; consciousness; extraordinary cognition; meditation research.
Figures
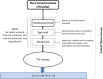
Figure 1
Graphic description of how cognition works according to Samkhya-Yoga.
Similar articles
- Reducing and deducing the structures of consciousness through meditation.
Katyal S. Katyal S. Front Psychol. 2022 Sep 8;13:884512. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.884512. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36160556 Free PMC article. Review. - Theories of consciousness.
Seth AK, Bayne T. Seth AK, et al. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022 Jul;23(7):439-452. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00587-4. Epub 2022 May 3. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35505255 Review. - Unifying biophysical consciousness theories with MaxCon: maximizing configurations of brain connectivity.
Perez Velazquez JL, Mateos DM, Guevara R, Wennberg R. Perez Velazquez JL, et al. Front Syst Neurosci. 2024 Jul 29;18:1426986. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2024.1426986. eCollection 2024. Front Syst Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39135560 Free PMC article. - Recent work on consciousness: philosophical, theoretical, and empirical.
Churchland PM, Churchland PS. Churchland PM, et al. Semin Neurol. 1997 Jun;17(2):179-86. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040928. Semin Neurol. 1997. PMID: 9195661 Review. - Physiological effects of yogic practices and transcendental meditation in health and disease.
Balaji PA, Varne SR, Ali SS. Balaji PA, et al. N Am J Med Sci. 2012 Oct;4(10):442-8. doi: 10.4103/1947-2714.101980. N Am J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 23112963 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Composition of yoga-philosophy based mental traits (Gunas) in major psychiatric disorders: A trans-diagnostic approach.
Bhargav H, Eiman N, Jasti N, More P, Kumar V, Holla B, Arasappa R, Rao NP, Varambally S, Gangadhar BN, Keshavan MS. Bhargav H, et al. Front Psychol. 2023 Feb 1;14:1075060. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1075060. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36818072 Free PMC article. - Rhythmic Chanting and Mystical States across Traditions.
Perry G, Polito V, Thompson WF. Perry G, et al. Brain Sci. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):101. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11010101. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33451163 Free PMC article. - A Correlation Study between Tri-Guna and Emotional Style: A Theoretical Approach toward Developing a Working Model to Integrate Tri-Guna with Affective Neuroscience and Well-Being.
Ravindra PN, Babu P. Ravindra PN, et al. Int J Yoga. 2021 Sep-Dec;14(3):213-221. doi: 10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_52_21. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Int J Yoga. 2021. PMID: 35017863 Free PMC article. - What Is Meditation? Proposing an Empirically Derived Classification System.
Matko K, Sedlmeier P. Matko K, et al. Front Psychol. 2019 Oct 15;10:2276. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02276. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31681085 Free PMC article. - Event-related potential and behavioural differences in affective self-referential processing in long-term meditators versus controls.
Katyal S, Hajcak G, Flora T, Bartlett A, Goldin P. Katyal S, et al. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2020 Apr;20(2):326-339. doi: 10.3758/s13415-020-00771-y. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31981093
References
- Ainslie G. (2001). Breakdown of Will. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press; 10.1017/CBO9781139164191 - DOI
- Alcock J. E. (2003). Give the null hypothesis a chance: Reasons to remain doubtful about the existence of psi. J. Conscious. Stud. 10, 29–50.
- Alexander C. N., Rainforth M. V., Gelderloos P. (1991). Transcendental meditation, self actualization, and psychological health: a conceptual overview and meta-analysis. J. Soc. Behav. Pers. 6, 189–247.
- Alexander C. N., Robinson P., Orme-Johnson D. W., Schneider R. H., Walton K. G. (1994a). The effects of transcendental meditation compared to other methods of relaxation and meditation in reducing risk factors, morbidity, and mortality. Homeostasis 35, 243–264.
- Alexander C. N., Robinson P., Rainforth M. (1994b). Treating and preventing alcohol, nicotine, and drug abuse through transcendental meditation: a review and statistical meta-analysis. Alcohol. Treat. Q. 11, 13–87. 10.1300/J020v11n01_02 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources