Patient-initiated appointments compared with standard outpatient care for rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised controlled trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Patient-initiated appointments compared with standard outpatient care for rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised controlled trial
Cecilia Fredriksson et al. RMD Open. 2016.
Abstract
Objectives: To test the hypothesis that implementing a patient-initiated system of care could improve clinical outcome in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using disease activity guided management.
Methods: An 18-month controlled blinded end point two-centre study with 131 patients with RA randomised to intervention (n=64) or control (n=67). The intervention group participants were guaranteed appointments to a rheumatologist within 10 working days if they subjectively experienced a flare in disease activity. The control group participants were booked in advance according to guidelines. Independent assessments were performed in the two groups at 0, 3, 6, 12 and 18 months. Outcome measures included: Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28), a Visual Analogue Scale (satisfaction with care, confidence in care), number of appointments with a rheumatologist.
Results: DAS28 decreased. Median satisfaction and confidence in care were >90 mm on Visual Analog Scale. Median number of appointments was 3. There were no significant differences between the groups among these outcomes. Visits in the intervention group more often resulted in change of treatment than in the control group (p<0.001).
Conclusions: Patient-initiated care was neither better nor inferior to traditional care in terms of outcomes analysed. Patient-initiated appointments can safely be used in everyday outpatient care of RA to empower the patient, if disease activity guided management is applied. Further research should investigate if this intervention can target a subgroup of patients and hence also result in released resources.
Keywords: Early Rheumatoid Arthritis; Health services research; Outcomes research; Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Figures
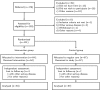
Figure 1
Flowchart of participants’ progress through the trial.
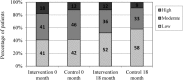
Figure 2
Percentage of patients in the disease activity index categories at 0 and 18 months.
Similar articles
- Patient initiated outpatient follow up in rheumatoid arthritis: six year randomised controlled trial.
Hewlett S, Kirwan J, Pollock J, Mitchell K, Hehir M, Blair PS, Memel D, Perry MG. Hewlett S, et al. BMJ. 2005 Jan 22;330(7484):171. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38265.493773.8F. Epub 2004 Nov 16. BMJ. 2005. PMID: 15546895 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Shared care or nursing consultations as an alternative to rheumatologist follow-up for rheumatoid arthritis outpatients with low disease activity--patient outcomes from a 2-year, randomised controlled trial.
Primdahl J, Sørensen J, Horn HC, Petersen R, Hørslev-Petersen K. Primdahl J, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Feb;73(2):357-64. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202695. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 23385306 Clinical Trial. - Disease activity guided dose reduction and withdrawal of adalimumab or etanercept compared with usual care in rheumatoid arthritis: open label, randomised controlled, non-inferiority trial.
van Herwaarden N, van der Maas A, Minten MJ, van den Hoogen FH, Kievit W, van Vollenhoven RF, Bijlsma JW, van den Bemt BJ, den Broeder AA. van Herwaarden N, et al. BMJ. 2015 Apr 9;350:h1389. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h1389. BMJ. 2015. PMID: 25858265 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Patient-controlled outpatient follow-up on demand for patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a 2-year randomized controlled trial.
Poggenborg RP, Madsen OR, Sweeney AT, Dreyer L, Bukh G, Hansen A. Poggenborg RP, et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Sep;40(9):3599-3604. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05674-y. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33677724 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Functional and work outcomes improve in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who receive targeted, comprehensive occupational therapy.
Macedo AM, Oakley SP, Panayi GS, Kirkham BW. Macedo AM, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Nov 15;61(11):1522-30. doi: 10.1002/art.24563. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19877106 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
- [Digital nephrology].
Boss K, Woywodt A, Kribben A, Mülling N, Becker S. Boss K, et al. Nephrologe. 2021;16(1):57-61. doi: 10.1007/s11560-020-00478-8. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Nephrologe. 2021. PMID: 33425034 Free PMC article. German. No abstract available. - Patient focused registries can improve health, care, and science.
Nelson EC, Dixon-Woods M, Batalden PB, Homa K, Van Citters AD, Morgan TS, Eftimovska E, Fisher ES, Ovretveit J, Harrison W, Lind C, Lindblad S. Nelson EC, et al. BMJ. 2016 Jul 1;354:i3319. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i3319. BMJ. 2016. PMID: 27370543 Free PMC article. - Patient-Initiated Follow-Up (PIFU) as reorganized support for increased patient involvement - focus group discussions among patients' with inflammatory arthritis.
Bech B, Lykkegaard JJ, Lundbak T, Schrøder HM, Birkeland LM, Schlyter ML, Hansen LH, Dalsgaard L, Esbensen BA. Bech B, et al. BMC Rheumatol. 2020 Jun 30;4:44. doi: 10.1186/s41927-020-00143-6. eCollection 2020. BMC Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32613158 Free PMC article. - Smartphone-Assisted Patient-Initiated Care Versus Usual Care in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Low Disease Activity: A Randomized Controlled Trial.
Seppen B, Wiegel J, Ter Wee MM, van Schaardenburg D, Roorda LD, Nurmohamed MT, Boers M, Bos WH. Seppen B, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022 Nov;74(11):1737-1745. doi: 10.1002/art.42292. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35818342 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Self-monitoring combined with patient-initiated care in RA patients with low disease activity: cost-effectiveness analysis of an RCT.
Seppen BF, Greuter MJE, Wiegel J, Ter Wee MM, Boers M, Nurmohamed MT, Bos WH. Seppen BF, et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 Oct 3;62(10):3366-3372. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead084. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023. PMID: 36799560 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Pollard L, Choy EH, Scott DL. The consequences of rheumatoid arthritis: quality of life measures in the individual patient. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2005;23(Suppl 39):S43–52. - PubMed
- Emery P, Breedveld FC, Hall S et al. . Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomised, double-blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet 2008;372:375–82. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61000-4 - DOI - PubMed
- Verstappen SM, Jacobs JW, van der Veen MJ et al. . Intensive treatment with methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis: aiming for remission. Computer Assisted Management in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (CAMERA, an open-label strategy trial). Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66:1443–9. 10.1136/ard.2007.071092 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources