W-IQ-TREE: a fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2016 Jul 8;44(W1):W232-5.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw256. Epub 2016 Apr 15.
Affiliations
- PMID: 27084950
- PMCID: PMC4987875
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw256
W-IQ-TREE: a fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis
Jana Trifinopoulos et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016.
Abstract
This article presents W-IQ-TREE, an intuitive and user-friendly web interface and server for IQ-TREE, an efficient phylogenetic software for maximum likelihood analysis. W-IQ-TREE supports multiple sequence types (DNA, protein, codon, binary and morphology) in common alignment formats and a wide range of evolutionary models including mixture and partition models. W-IQ-TREE performs fast model selection, partition scheme finding, efficient tree reconstruction, ultrafast bootstrapping, branch tests, and tree topology tests. All computations are conducted on a dedicated computer cluster and the users receive the results via URL or email. W-IQ-TREE is available at http://iqtree.cibiv.univie.ac.at It is free and open to all users and there is no login requirement.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
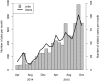
Figure 1.
Number of all W-IQ-TREE jobs per month irrespective of the IP-addresses submitted by external users and number of distinct users per month.
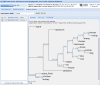
Figure 2.
Screenshot of an example result with W-IQ-TREE for a chordate data set.
Similar articles
- IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies.
Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ. Nguyen LT, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2015 Jan;32(1):268-74. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu300. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Mol Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25371430 Free PMC article. - PhyloDraw: a phylogenetic tree drawing system.
Choi JH, Jung HY, Kim HS, Cho HG. Choi JH, et al. Bioinformatics. 2000 Nov;16(11):1056-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/16.11.1056. Bioinformatics. 2000. PMID: 11159323 - SeaView version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building.
Gouy M, Guindon S, Gascuel O. Gouy M, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2010 Feb;27(2):221-4. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp259. Epub 2009 Oct 23. Mol Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 19854763 - ConSurf 2016: an improved methodology to estimate and visualize evolutionary conservation in macromolecules.
Ashkenazy H, Abadi S, Martz E, Chay O, Mayrose I, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N. Ashkenazy H, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 8;44(W1):W344-50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw408. Epub 2016 May 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27166375 Free PMC article. - [A bird's eye view of the algorithms and software packages for reconstructing phylogenetic trees].
Zhang LN, Rong CH, He Y, Guan Q, He B, Zhu XW, Liu JN, Chen HJ. Zhang LN, et al. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2013 Dec;34(6):640-50. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2013. PMID: 24415699 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
- Genetic and functional diversity of allorecognition receptors in the urochordate, Botryllus schlosseri.
Rodriguez-Valbuena H, Salcedo J, De Their O, Flot JF, Tiozzo S, De Tomaso AW. Rodriguez-Valbuena H, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 18:2024.10.16.618699. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.16.618699. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39463968 Free PMC article. Preprint. - Massive citizen science sampling and integrated taxonomic approach unravel Danish cryptogam-dwelling tardigrade fauna.
Gąsiorek P, Sørensen MV, Lillemark MR, Leerhøi F, Tøttrup AP. Gąsiorek P, et al. Front Zool. 2024 Oct 21;21(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12983-024-00547-x. Front Zool. 2024. PMID: 39434133 Free PMC article. - Prevalence, Infection Intensity and Molecular Diagnosis of Mixed Infections with Metastrongylus spp. (Metastrongylidae) in Wild Boars in Uzbekistan.
Kuchboev AE, Krücken J. Kuchboev AE, et al. Pathogens. 2022 Nov 9;11(11):1316. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11111316. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36365067 Free PMC article. - New arrangement of three genera of fish tapeworms (Cestoda: Proteocephalidae) in catfishes (Siluriformes) from the Neotropical Region: taxonomic implications of molecular phylogenetic analyses.
Alves PV, de Chambrier A, Luque JL, Takemoto RM, Tavares LER, Scholz T. Alves PV, et al. Parasitol Res. 2021 May;120(5):1593-1603. doi: 10.1007/s00436-021-07138-3. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Parasitol Res. 2021. PMID: 33835243 - Bovine Polyomavirus-1 (Epsilonpolyomavirus bovis): An Emerging Fetal Pathogen of Cattle That Causes Renal Lesions Resembling Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy of Humans.
Giannitti F, da Silva Silveira C, Bullock H, Berón M, Fernández-Ciganda S, Benítez-Galeano MJ, Rodríguez-Osorio N, Silva-Flannery L, Perdomo Y, Cabrera A, Puentes R, Colina R, Ritter JM, Castells M. Giannitti F, et al. Viruses. 2022 Sep 14;14(9):2042. doi: 10.3390/v14092042. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146848 Free PMC article.
References
- Schmidt H.A., Strimmer K., Vingron M., von Haeseler A. TREE-PUZZLE: maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics. 2002;18:502–504. - PubMed
- Guindon S., Dufayard J.F., Lefort V., Anisimova M., Hordijk W., Gascuel O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010;59:307–321. - PubMed
- Lanfear R., Calcott B., Ho S.Y., Guindon S. Partitionfinder: combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012;29:1695–1701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources